* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5: Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
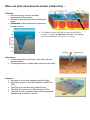
Test Support Ocean Floor Structure and Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Features: Earth's rocky surface is divided into two types: 1. oceanic crust thin dense crust 6 km-10 km thick. It is made of basaltic type rock 2. continental crust thick light (lower density than the oceanic crust) crust about 50 km thick. floats higher on the mantle than the oceanic crust. This forms the basins that hold our oceans It is made mostly of granitic rock. The diagram below illustrates the basic set up of the ocean floor. Continental Shelves – the area beside a continent goes from the low-water line to the edge of the continent under water, Maximum depth is about 200 m, They are often areas of rich in sea life They are important economic zone of the nearby countries. Continental Slope – the drop off at the edge of the continental slope Both the continental shelf and slope are considered structurally part of the continents, even though they are below the sea surface. Continental Rise – The gentler slope at the bottom of the slope It is made of sand and sediments that comes from the land and the continental self. Kind of like a rubble pile. Abyssal Plain – The relatively flat bottom of the ocean They are the deepest parts of the ocean, except for the trenches. The average depth is about 4000m (4 km) from the surface to the abyssal plain. Mid-ocean ridges – continuous mountain chains on the sea floor. They occur where two oceanic plates are moving apart (diverging) Magma bubbles up between the 2 plates forming new land. Abyssal Hills – Small, cone shaped formations on the ocean floor Shorter than 1000 m Seamounts – underwater mountains that are at least 1000 m (1 km) tall. They are usually cone-shaped. They are volcanoes mountains that rise from the ocean floor (abyssal plain). Volcanic Island – A seamount that extends above the surface of the water. Guyots – a seamount with a flat top created by wave action when the seamount was at sea level When one plate dives beneath another (subduction) … Trenches – trenches are long, narrow, and deep depressions of the sea-floor they have steep sides that form at subduction zones. Subduction is when one tectonic plate dives beneath another. The deepest trench on Earth is found in the Pacific Ocean. It is called the Marianas Trench. The deepest part of the Marianas Trench is 11 km deep. Island arcs – volcanic island chains that form on the other side of a subducted plate. This happens when to ocean plates crash into each other. Canyons – are deep cuts into the continental shelf and slope, the largest canyon in The North Atlantic is called The Gully The Gully is just off the coast of Nova Scotia. The Gully is home to lots of different forms of life. The Gully is now a protected area so that endangered animals have a chance to recover.