Genetic Code
... • One strand of DNA is copied • Complementary bases build mRNA DNA(1 strand) mRNA • In mRNA uracil (U) complements A (DNA) • New mRNA moves out of nucleus to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
... • One strand of DNA is copied • Complementary bases build mRNA DNA(1 strand) mRNA • In mRNA uracil (U) complements A (DNA) • New mRNA moves out of nucleus to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
purpose - cloudfront.net
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis
... reading frame of the genetic code. Which of these 3 mutations is a frameshift mutation? ...
... reading frame of the genetic code. Which of these 3 mutations is a frameshift mutation? ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – make up part of the structure of a ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transfers amino acids to the ribosomes ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – make up part of the structure of a ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transfers amino acids to the ribosomes ...
Protein Synthesis Notes Review
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
... 2. To make proteins, what does the DNA have to be decoded into? 3. What are the three parts that make up a RNA nucleotide? 4. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA? 5. If a DNA chain had the following sequence, CCGTAATAGCAT, what RNA nucleotides would attach to this sequence? 6. What is ...
Project Proposal: Genetic Code Reassignments
... genomes of specific organisms argues that the genetic code is evolving and not frozen. From Escherichia coli to humans use the universal genetic code which has been frozen for billions of years and it has been argued that the codon reassignment causes mistranslation of the genetic information and mu ...
... genomes of specific organisms argues that the genetic code is evolving and not frozen. From Escherichia coli to humans use the universal genetic code which has been frozen for billions of years and it has been argued that the codon reassignment causes mistranslation of the genetic information and mu ...
Protein Synthesis A gene is a segment of DNA that is located on a
... a. mRNA enters the ribosome. b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one en ...
... a. mRNA enters the ribosome. b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one en ...
Assignment 1
... Q9: Which one of the following options correctly lists the second, third and fourth amino acids of the polypeptide that would result from the translation of the mRNA? You may consult the genetic code from the text book or in the video file. a. Cys-Glu-Trp b. Asp-Asn-Asn c. Val-Trp-Thr d. Met-Asp-As ...
... Q9: Which one of the following options correctly lists the second, third and fourth amino acids of the polypeptide that would result from the translation of the mRNA? You may consult the genetic code from the text book or in the video file. a. Cys-Glu-Trp b. Asp-Asn-Asn c. Val-Trp-Thr d. Met-Asp-As ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy for cellular activities 2. Su ...
... 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy for cellular activities 2. Su ...
1.The general formula for amino acids, explain it term by
... 6.Give a list from the smallest to biggest common terms in molecular biology. Nucleotide
... 6.Give a list from the smallest to biggest common terms in molecular biology. Nucleotide
Transcription/Translation Notes
... i. Step 1: DNA molecule unwinds and separates just like in replication. ii. Step 2: RNA nucleotides match up with their complimentary bases on the template strand. 1. Practice: Write the complimentary mRNA strand from this DNA… ATCGATGGCAAGCTA iii. Step 3: mRNA detaches once entire gene is done and ...
... i. Step 1: DNA molecule unwinds and separates just like in replication. ii. Step 2: RNA nucleotides match up with their complimentary bases on the template strand. 1. Practice: Write the complimentary mRNA strand from this DNA… ATCGATGGCAAGCTA iii. Step 3: mRNA detaches once entire gene is done and ...
CHAPTER 10 - Protein Synthesis The DNA genotype is expressed
... The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life • Virtually all organisms share the same genetic code ...
... The genetic code is the Rosetta stone of life • Virtually all organisms share the same genetic code ...
4.13 notes
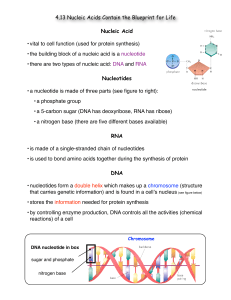
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
... • there are two types of nucleic acid: DNA and RNA Nucleotides • a nucleotide is made of three parts (see figure to right): • a phosphate group • a 5-carbon sugar (DNA has deoxyribose, RNA has ribose) • a nitrogen base (there are five different bases available) RNA • is made of a single-stranded cha ...
13 Transcription and translation
... – binds to it Ribosome moves along mRNA in 5’ to 3’ direction - adds amino acids to polypeptide chain once it reads a codon Must start reading in correct spot on mRNA - START codon (AUG) - ensures ribosome translates code using reading frame of mRNA molecule - results in correct sequence of amin ...
... – binds to it Ribosome moves along mRNA in 5’ to 3’ direction - adds amino acids to polypeptide chain once it reads a codon Must start reading in correct spot on mRNA - START codon (AUG) - ensures ribosome translates code using reading frame of mRNA molecule - results in correct sequence of amin ...
Study Guide
... structure. Deoxyribose is the sugar that makes up this molecule. DNA is contained in the nucleus of the cell. 4. The genetic code is the order of the nitrogen bases that form along a gene and directs what type of protein the cell will make. 5. RNA is a single stranded molecule. It is made up of the ...
... structure. Deoxyribose is the sugar that makes up this molecule. DNA is contained in the nucleus of the cell. 4. The genetic code is the order of the nitrogen bases that form along a gene and directs what type of protein the cell will make. 5. RNA is a single stranded molecule. It is made up of the ...
Ch9outline
... Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Structures and Properties 9.1: The basic units of DNA and RNA are nucleotides 9.2: Nucleotides form biological polymers 9.3: DNA is a double helix DNA: The Genetic Message 9.4: The nucleotide structure of DNA carries information 9.5: Specific sequences of nucleotides are g ...
... Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA Structures and Properties 9.1: The basic units of DNA and RNA are nucleotides 9.2: Nucleotides form biological polymers 9.3: DNA is a double helix DNA: The Genetic Message 9.4: The nucleotide structure of DNA carries information 9.5: Specific sequences of nucleotides are g ...
Brooker Chapter 13
... Recognition Between tRNA and mRNA • During mRNA-tRNA recognition, the anticodon in tRNA binds to a complementary codon in mRNA ...
... Recognition Between tRNA and mRNA • During mRNA-tRNA recognition, the anticodon in tRNA binds to a complementary codon in mRNA ...
Translation
... (GTP and elongation factor) • Uncharged tRNA released from the E site • Repeat Process until stop codon ...
... (GTP and elongation factor) • Uncharged tRNA released from the E site • Repeat Process until stop codon ...
The sequence of amino acids
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
... multiple translation on the same mRNA strand may be required to enable a protein to perform its specific function ...
The Code of Life: Topic 3
... •Point of attachment for a small •Appears to control the subunit of the ribosome during movement of mRNA across the translation. nuclear membrane. ...
... •Point of attachment for a small •Appears to control the subunit of the ribosome during movement of mRNA across the translation. nuclear membrane. ...
Chapter 6: Biochemistry
... Copy the 4 molecules into your notes (lipid, carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid) ...
... Copy the 4 molecules into your notes (lipid, carbohydrate, protein, nucleic acid) ...
Notes Protein Synthesis
... amino acid • At one end tRNA loosely binds the amino acid and at the other end it has a nucleotide triplet called the anticodon • The anticodon allows it to pair specifically with a complementary codon on mRNA ...
... amino acid • At one end tRNA loosely binds the amino acid and at the other end it has a nucleotide triplet called the anticodon • The anticodon allows it to pair specifically with a complementary codon on mRNA ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.