Protein Synthesis (Transcription and Translation)
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
... • A point mutation is a change in a single base pair in DNA. • A change in a single nitrogenous base can change the entire structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid can affect the shape of the protein. ...
Practicing Protein Synthesis
... both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. Using the DNA sequence, make a co ...
... both humans and cows, the sequence contains the gene to make the protein insulin. Insulin is necessary for the uptake of sugar from the blood. Without insulin, a person (or a cow) cannot digest sugars the same way others can, and they have a disease called diabetes. Using the DNA sequence, make a co ...
I. Biology (35 points total) The following questions cover some of the
... three nucleotides at a time (codon) from the 5' end to the 3' end. Each amino acid is specified by the mRNA's codon, and then pairs with a sequence of three complementary nucleotides carried by a particular tRNA (anticodon). Since RNA is constructed from four types of nucleotides, there are 64 possi ...
... three nucleotides at a time (codon) from the 5' end to the 3' end. Each amino acid is specified by the mRNA's codon, and then pairs with a sequence of three complementary nucleotides carried by a particular tRNA (anticodon). Since RNA is constructed from four types of nucleotides, there are 64 possi ...
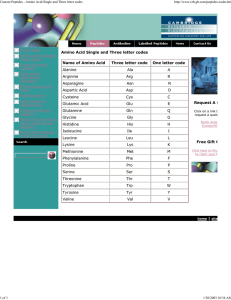
Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...
... Amino Acid Single and Three letter codes Name of Amino Acid ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Notes Guide Part 2
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
... Primary structure- Form a __________________ of amino acids. Secondary structure- ______________________________ the chain of amino acids. Tertiary Structure- Fold the chain ________________________________. Quaternary Structure- Bring _____ to ________ amino acid subunits together. ...
From DNA to Protein synthesis lab
... transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA. In eukaryotic cells, the mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome, where IRNA anticodons translate the mRNA into amino acids. The completed amino acid chain, or polypeptide, then fo ...
... transcribed into a complementary strand of mRNA. In eukaryotic cells, the mRNA then leaves the nucleus and enters the cl.toplasm. In all cells, the mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome, where IRNA anticodons translate the mRNA into amino acids. The completed amino acid chain, or polypeptide, then fo ...
Name
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
... 33-37. Label where you would find each of the following. If it’s both inside and outside the nucleus, show an arrow coming out of the nucleus. □ DNA □ ribosomes □ mRNA □ tRNA □ amino acids ...
Biology EOC One Page Quick Review Prokaryote – a unicellular
... Cell differentiation - a process that occurs in which cells and tissues become specialized Nucleotide – phosphate , sugar, base subunit of DNA, RNA Nitrogen bases – A, T, C, G, sequence of these determine amino acids that make proteins that give organisms traits Transcription – process of making mRN ...
... Cell differentiation - a process that occurs in which cells and tissues become specialized Nucleotide – phosphate , sugar, base subunit of DNA, RNA Nitrogen bases – A, T, C, G, sequence of these determine amino acids that make proteins that give organisms traits Transcription – process of making mRN ...
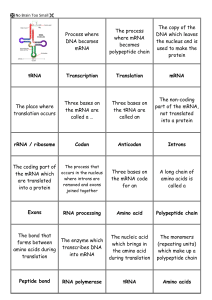
Gene expression flash cards
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
The Master Molecule
... of the DNA molecule. Noncoding sequences are called introns, and do not lead to the production of products. Exons encode specific peptides and proteins: structural molecules, neurotransmitters, and enzymes regulating chemical processes. The evolution of different species is the result of genetic muta ...
... of the DNA molecule. Noncoding sequences are called introns, and do not lead to the production of products. Exons encode specific peptides and proteins: structural molecules, neurotransmitters, and enzymes regulating chemical processes. The evolution of different species is the result of genetic muta ...
Slide 1
... • Each codon produces the same amino acid in transcription and translation, regardless of the species. • So the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide remains unchanged. • Therefore, we can take genes from one species and insert them into the genome of another species. ...
... • Each codon produces the same amino acid in transcription and translation, regardless of the species. • So the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide remains unchanged. • Therefore, we can take genes from one species and insert them into the genome of another species. ...
dna ppt ques – ANSWERS2
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
... 2. The mRNA then leaves the ___NUCLEUS_________ and attaches itself to a __RIBOSOME_______________ and passes on the ___MESSAGE__________. 3. The tRNA then attaches to ___MRNA_______ and hooks up the ____AMINO ACIDS___ in the right order. Then it goes back to pick up some __MORE________(like a _TAX ...
Chapter Twelve Protein Synthesis: Translation of the
... 61 code for amino acids 3 (UAA, UAG, and UGA) serve as termination signals only Trp and Met have one codon each the third base is irrelevant for Leu, Val, Ser, Pro, Thr, Ala, Gly, and Arg • the second base is important for the type of amino acid; for example, if the second base is U, the amino acids ...
... 61 code for amino acids 3 (UAA, UAG, and UGA) serve as termination signals only Trp and Met have one codon each the third base is irrelevant for Leu, Val, Ser, Pro, Thr, Ala, Gly, and Arg • the second base is important for the type of amino acid; for example, if the second base is U, the amino acids ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
Gene expression flash cards
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
... The codon found at the end of the mRNA which tells the ribosome to stop translation ...
1. I can tell the difference between mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
... Transcription: The DNA sequence is replaced with the complementary RNA sequence. G bonds with C. RNA does not have T, so A bonds with U. DNA (gene): GGC– TAC – CCA – GTA– GAG – TAG – CTG – ATT – ACG mRNA: CCG –AUG –GGU –CAU– CUC – AUC – GAC – UAA – UGC 8. I can use a codon chart to translate a seque ...
... Transcription: The DNA sequence is replaced with the complementary RNA sequence. G bonds with C. RNA does not have T, so A bonds with U. DNA (gene): GGC– TAC – CCA – GTA– GAG – TAG – CTG – ATT – ACG mRNA: CCG –AUG –GGU –CAU– CUC – AUC – GAC – UAA – UGC 8. I can use a codon chart to translate a seque ...
The DNA Connection - Conackamack Middle School
... born with such an uncommon phenotype? • To answer this question, you need to know how the genes on the chromosome control an organism’s traits. ...
... born with such an uncommon phenotype? • To answer this question, you need to know how the genes on the chromosome control an organism’s traits. ...
Cow DNA: How DNA Controls the Workings of the Cell
... The normal gene reads T A G. What amino acid does the mutant DNA and the normal DNA code for and will the person with this mutation be diabetic? ...
... The normal gene reads T A G. What amino acid does the mutant DNA and the normal DNA code for and will the person with this mutation be diabetic? ...
OCR Biology B - Centre of the Cell
... (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecule, including a review of the evidence for complementary base pairing (Chargaff’s rules) (e) the nature of the genetic code. To include reference to the triplet, non-overlapping, ...
... (a) the structure of a nucleotide as the monomer from which nucleic acids are made (c) (i) the structure of the DNA molecule, including a review of the evidence for complementary base pairing (Chargaff’s rules) (e) the nature of the genetic code. To include reference to the triplet, non-overlapping, ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.