2. If 20% of the DNA in a guinea pig cell is adenine, what
... U, or poly C. Then make all possible combinations of the nucleotides taken two at a time—for example, GCGC, CGCG, AGAG, and so on. Next, make other combinations of nucleotides taken three at a time— for example, AAAGGGAAAGGG and so on. Continue with combinations of nucleotides taken four at a time—f ...
... U, or poly C. Then make all possible combinations of the nucleotides taken two at a time—for example, GCGC, CGCG, AGAG, and so on. Next, make other combinations of nucleotides taken three at a time— for example, AAAGGGAAAGGG and so on. Continue with combinations of nucleotides taken four at a time—f ...
Mistakes Happen
... New Amino Acids 4. Silent Mutations – time for a silent mutation. You’ll need to think about this one a little. Remember, what ever change you make, it must still code for the same amino acid. Start by looking at the codon charts to see which amino acids have multiple codons. Original DNA RNA Transc ...
... New Amino Acids 4. Silent Mutations – time for a silent mutation. You’ll need to think about this one a little. Remember, what ever change you make, it must still code for the same amino acid. Start by looking at the codon charts to see which amino acids have multiple codons. Original DNA RNA Transc ...
1.5 Page 4 - csfcbiology
... genetic engineering where genes have been transferred from one organism to another. The genetic code is also described as being a non-overlapping code, each set of three bases codes for a separate amino acid in the polypeptide chain. There is no overlap in the coding sequence in all-living organisms ...
... genetic engineering where genes have been transferred from one organism to another. The genetic code is also described as being a non-overlapping code, each set of three bases codes for a separate amino acid in the polypeptide chain. There is no overlap in the coding sequence in all-living organisms ...
End of chapter 14 questions and answers from the text book
... of the coding DNA strand. (b) Describe the role of tRNA in the process of translation The anticodon complementary to the codon reads the message on mRNA and brings the specific acid which is transferred to the ribosome and the correct sequence of amino acids is formed to make the polypeptide ...
... of the coding DNA strand. (b) Describe the role of tRNA in the process of translation The anticodon complementary to the codon reads the message on mRNA and brings the specific acid which is transferred to the ribosome and the correct sequence of amino acids is formed to make the polypeptide ...
Hemoglobin, or haemoglobin, is an iron
... with Hb. It is not clear how Hp and Hb bind to each other. The aim of this work was to identify amino acids in Hp that are involved in its binding to Hb. The approach used was to first select amino acid residues that are likely to be involved in binding by comparing the sequence of human Hp with tho ...
... with Hb. It is not clear how Hp and Hb bind to each other. The aim of this work was to identify amino acids in Hp that are involved in its binding to Hb. The approach used was to first select amino acid residues that are likely to be involved in binding by comparing the sequence of human Hp with tho ...
Protein Synthesis
... What is the sequence of the complementary strand? B. What is the mRNA sequence made? ...
... What is the sequence of the complementary strand? B. What is the mRNA sequence made? ...
From Gene to Protein Genes code for... Proteins RNAs Remember
... This forms a mRNA transcript with a continuous coding sequence ...
... This forms a mRNA transcript with a continuous coding sequence ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Answer: The AUG triplet would have shown radioactivity in the methionine test tube. Even though AUG acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found ...
... Answer: The AUG triplet would have shown radioactivity in the methionine test tube. Even though AUG acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found ...
biology name
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
... 14. Codons are found on _________ while anticodons are found on _________. In each case, the code is really a sequence of ____ bases (use a number) that code for a particular _____________________. 15. What would the transfer RNA and corresponding amino acids be according to the mRNA below? mRNA ...
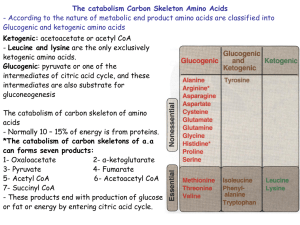
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Protein Synthesis - No Brain Too Small
... Protein synthesis involves two stages: transcription and translation. Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
... Protein synthesis involves two stages: transcription and translation. Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
Level 2 Biology - No Brain Too Small
... Protein synthesis involves two stages: transcription and translation. Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
... Protein synthesis involves two stages: transcription and translation. Compare and contrast these two cell processes and their role in protein synthesis. In your answer: ...
Protein Synthesis
... http://207.207.4.198/pub/flash/26/transmenu_s.s wf (very good but need to skip some parts) ...
... http://207.207.4.198/pub/flash/26/transmenu_s.s wf (very good but need to skip some parts) ...
DNA Transcription Translation The Central Dogma Trait RNA
... Many antibiotics block steps in translation within bacterial cells. ...
... Many antibiotics block steps in translation within bacterial cells. ...
Reporting Category 2
... •Uses complementary nucleotides just like replication •Except that A pairs with U instead of T ...
... •Uses complementary nucleotides just like replication •Except that A pairs with U instead of T ...
The amino acids, peptide bonds, and the primary structure of proteins
... • If you know the pH and pKa, you can determine whether an amino acid is charged or uncharged ...
... • If you know the pH and pKa, you can determine whether an amino acid is charged or uncharged ...
genetic code and translation
... i- Silent mutation: i.e. the codon containg the changed base may code for the same amino acid. For example, in serine codon UCA, if A is changed to U giving the codon UCU, it still code for serine. See table. ii- Missense mutation: the codon containing the changed base may code for a different amino ...
... i- Silent mutation: i.e. the codon containg the changed base may code for the same amino acid. For example, in serine codon UCA, if A is changed to U giving the codon UCU, it still code for serine. See table. ii- Missense mutation: the codon containing the changed base may code for a different amino ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... • 20 different amino acids used to produce proteins. • The code for a specific amino acid is controlled by the 4 different nucleotides (T,C,A,G) in the DNA. • This code goes in sequences of three (Triplets) • A triplet codes for a single amino acid • WHY? ...
... • 20 different amino acids used to produce proteins. • The code for a specific amino acid is controlled by the 4 different nucleotides (T,C,A,G) in the DNA. • This code goes in sequences of three (Triplets) • A triplet codes for a single amino acid • WHY? ...
Document
... Translocation requires GTP and EF-G. EF-G enters A site, shifting tRNAs. When EF-G leaves, A site is open for a new ternary complex. A new ternary complex associates with A site, and deacylated tRNA leaves from E site. ...
... Translocation requires GTP and EF-G. EF-G enters A site, shifting tRNAs. When EF-G leaves, A site is open for a new ternary complex. A new ternary complex associates with A site, and deacylated tRNA leaves from E site. ...
outline File - selu moodle
... one gene / one polypeptide hypothesis. The central dogma of molecular biology DNA RNA proteins Transcription translation Modified with discovery of reverse transcriptase (found in retroviruses) DNA ↔ RNA proteins Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the ...
... one gene / one polypeptide hypothesis. The central dogma of molecular biology DNA RNA proteins Transcription translation Modified with discovery of reverse transcriptase (found in retroviruses) DNA ↔ RNA proteins Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the ...
Answer Key Lab DNA Structure
... phenotype of the person the DNA came from. (If arginine is the 3rd amino acid, the person will have dimples.) DNA ...
... phenotype of the person the DNA came from. (If arginine is the 3rd amino acid, the person will have dimples.) DNA ...
Information Flow 2
... The mRNA that is first transcribed is much longer than the mRNA that will eventually be translated. Eukaryotic genes commonly have intervening sequences that must be removed before an mRNA that codes for the proper sequence of amino acids can be created. The intervening sequences that must be remove ...
... The mRNA that is first transcribed is much longer than the mRNA that will eventually be translated. Eukaryotic genes commonly have intervening sequences that must be removed before an mRNA that codes for the proper sequence of amino acids can be created. The intervening sequences that must be remove ...
Genes
... "Parenthood is about raising and celebrating the child you have, not the child you thought you would have. It's about understanding that he is exactly the person he is supposed to be. And that, if you're lucky, he just might be the teacher who turns you into the person you are supposed to be.” -Jo ...
... "Parenthood is about raising and celebrating the child you have, not the child you thought you would have. It's about understanding that he is exactly the person he is supposed to be. And that, if you're lucky, he just might be the teacher who turns you into the person you are supposed to be.” -Jo ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.