From Genes to Proteins - Yale Center for Teaching and Learning
... transcription/translation & miss larger concept about how genotype determines phenotype. – see molecular processes of gene expression as separate from classical genetics/inheritance. ...
... transcription/translation & miss larger concept about how genotype determines phenotype. – see molecular processes of gene expression as separate from classical genetics/inheritance. ...
DNA to Proteins to Natural Selection - Cal State LA
... alters small segments of DNA, usually within a single gene b. Beneficial = increases the survival or ability of an individual to reproduce; rare; alters small segments of DNA, usually within a single gene c. Lethal = eventually leads to an individual’s death or inability to reproduce; common; alters ...
... alters small segments of DNA, usually within a single gene b. Beneficial = increases the survival or ability of an individual to reproduce; rare; alters small segments of DNA, usually within a single gene c. Lethal = eventually leads to an individual’s death or inability to reproduce; common; alters ...
Lecture 6 S
... • Spontaneous Mutations: – occur in the natural environment without the addition of mutagens (agents that cause mutations) – Occur randomly and spontaneously ...
... • Spontaneous Mutations: – occur in the natural environment without the addition of mutagens (agents that cause mutations) – Occur randomly and spontaneously ...
in non sex cells
... 1.The gene-chromosome theory states that genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes and are found in homologous pairs. Which figure below would represent the theory? ...
... 1.The gene-chromosome theory states that genes are segments of DNA located on chromosomes and are found in homologous pairs. Which figure below would represent the theory? ...
3D modelling activity
... Amino acid coding region * RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and transcribes the DNA into RNA until reaches a transcription stop sequence. ...
... Amino acid coding region * RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence and transcribes the DNA into RNA until reaches a transcription stop sequence. ...
Pathology Chapter 5 pg 137-140 [10-22
... chain of hemoglobin. Here the nucleotide triplet CTC (or GAG in mRNA), which encodes glutamic acid, is changed to CAC (or GUG in mRNA), which encodes valine. This single amino acid substitution alters the physicochemical properties of hemoglobin, giving rise to sickle cell anemia. A nonsense mutatio ...
... chain of hemoglobin. Here the nucleotide triplet CTC (or GAG in mRNA), which encodes glutamic acid, is changed to CAC (or GUG in mRNA), which encodes valine. This single amino acid substitution alters the physicochemical properties of hemoglobin, giving rise to sickle cell anemia. A nonsense mutatio ...
Goal 3
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
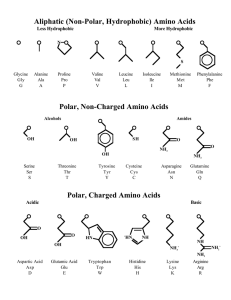
Amino Acids - Sehr Gut Web
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
... In these structures, the top circle represents the amino acid backbone (H2N—CH—COOH), with the R group depicted. In the case of proline, which is and alpha imino acid, rather than an amino acid, the circle represents the —CH—COOH group, the imino nitrogen being depicted as an element in the proline ...
Chapter Three The Biological Basis of Life
... specific amino acids. The base triplets on the tRNA match up with the codons on the mRNA. As each tRNA line up in the sequence of mRNA codons their amino acids link to form a protein. ...
... specific amino acids. The base triplets on the tRNA match up with the codons on the mRNA. As each tRNA line up in the sequence of mRNA codons their amino acids link to form a protein. ...
Lecture2-2010
... atom in the protein - but which one? Our 36 amino acid protein is a mess! The record to date is 723 amino acids With full assignment of the spectrum - how did they do this? 3.) Interpret the data. ...
... atom in the protein - but which one? Our 36 amino acid protein is a mess! The record to date is 723 amino acids With full assignment of the spectrum - how did they do this? 3.) Interpret the data. ...
Investigating the effects of different types of mutations
... How does information go from a sequence made of the four different bases of DNA (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine) to a protein sequence made up of one of 20 different amino acids? The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes ne ...
... How does information go from a sequence made of the four different bases of DNA (adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine) to a protein sequence made up of one of 20 different amino acids? The sequence of DNA that encodes for a protein is called a gene. Genes encode for all proteinsfrom the enzymes ne ...
Slide 1
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
Protein degradation in mouse brain slices
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
... a role for neurotoxic and unusual neuroexitatory amino acids in the aetiology of certain neurodegenerative disordcrs (Spencer er ul., 1987). This has led us to speculate whether those amino acids that are implicated as possible causativc o r contributory agents in these diseases, might also be invol ...
Lesson 2: DNA Transcription and Translation Introduction This
... complimentary strand to the section of DNA coding for the protein. In mRNA, adenine compliments with uracil instead of thymine, the compliment in DNA. The messenger RNA carries the complimentary strand out of the nucleus to the ribosome, the organelle where proteins are manufactured. This is where t ...
... complimentary strand to the section of DNA coding for the protein. In mRNA, adenine compliments with uracil instead of thymine, the compliment in DNA. The messenger RNA carries the complimentary strand out of the nucleus to the ribosome, the organelle where proteins are manufactured. This is where t ...
Nucleotide Sequence of Rainbow Trout a
... constructed by cloning cDNA into pUC118. The library was screened with carp a-globin cDNA (Takeshita et al., 1984). Two positive clones (clone 1 and 5 ) were identified and sequenced with the dideoxy method. Comparison with Related Sequence. The deduced amino acid sequence of clone 1 showed 97.9% id ...
... constructed by cloning cDNA into pUC118. The library was screened with carp a-globin cDNA (Takeshita et al., 1984). Two positive clones (clone 1 and 5 ) were identified and sequenced with the dideoxy method. Comparison with Related Sequence. The deduced amino acid sequence of clone 1 showed 97.9% id ...
Exam 1
... ______________________, with ______________ proteins coming off of the column first. 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/ ...
... ______________________, with ______________ proteins coming off of the column first. 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/ ...
Slide 1
... How to Read Codons Most amino acids can be specified by more than one codon. For example, six different codons—UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG—specify leucine. But only one codon—UGG— specifies the amino acid tryptophan. ...
... How to Read Codons Most amino acids can be specified by more than one codon. For example, six different codons—UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG—specify leucine. But only one codon—UGG— specifies the amino acid tryptophan. ...
B1: You and Your Genes
... the phenotype is the feature or features that result from this combination and interaction with the environment Part 2: how genetic information is inherited I know that....... that the two versions of each gene in a pair of chromosomes are called alleles alleles can be the same (homozygous) alleles ...
... the phenotype is the feature or features that result from this combination and interaction with the environment Part 2: how genetic information is inherited I know that....... that the two versions of each gene in a pair of chromosomes are called alleles alleles can be the same (homozygous) alleles ...
Welcome! 3/21/14
... 2) What does tRNA carry to the ribosome? 3) If the mRNA strand AAA-UUU-CCC codes for Lys-Phe-Pro, which amino acid does AAA code for? ...
... 2) What does tRNA carry to the ribosome? 3) If the mRNA strand AAA-UUU-CCC codes for Lys-Phe-Pro, which amino acid does AAA code for? ...
investigating dna
... four base pairs: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). In DNA, A always bonds with T, and G always bonds with C. codon- a sequence of three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid transcription – the synthesis of an mRNA molecule from DNA protein translation - mRNA molecule ...
... four base pairs: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). In DNA, A always bonds with T, and G always bonds with C. codon- a sequence of three nucleotides that code for a specific amino acid transcription – the synthesis of an mRNA molecule from DNA protein translation - mRNA molecule ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany Principles of Life
... A poly A tail is added to the 3′ end at the end of transcription and assists in export from the nucleus and aids stability. Concept 10.3 The Genetic Code in RNA Is Translated into the Amino Acid Sequences of Proteins The genetic code—specifies which amino acids will be used to build a protein Codon— ...
... A poly A tail is added to the 3′ end at the end of transcription and assists in export from the nucleus and aids stability. Concept 10.3 The Genetic Code in RNA Is Translated into the Amino Acid Sequences of Proteins The genetic code—specifies which amino acids will be used to build a protein Codon— ...
Biochemistry Notes
... Most enzymes have an optimal pH of 7. Some enzymes function more effectively in acidic or basic conditions. ...
... Most enzymes have an optimal pH of 7. Some enzymes function more effectively in acidic or basic conditions. ...
Carbohydrate PPT Notes
... – 2nd electron level not full – Only has 4 electrons in 2nd level – Will bond up to four times • Monomer: Small carbon molecules – Ex: Amino acid • Polymer: chain of linked monomers – Ex: Protein ...
... – 2nd electron level not full – Only has 4 electrons in 2nd level – Will bond up to four times • Monomer: Small carbon molecules – Ex: Amino acid • Polymer: chain of linked monomers – Ex: Protein ...
Chapter 7.1 - Fredericksburg City Schools
... The sides of a DNA molecule are made up of sugar molecules alternating with ______ molecules. Chromosomes are made up mostly of ...
... The sides of a DNA molecule are made up of sugar molecules alternating with ______ molecules. Chromosomes are made up mostly of ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.