BMB 400 PART THREE - ANSWERS ANSWERS to Questions from
... in vitro, and this was a key technique in deciphering the genetic code. However, it differs from DNA and RNA polymerases in points 1 and 4. Polynucleotide phosphorylase does not use a template, but rather adds ribonucleotides to an RNA in a highly reversible reaction. The substrates (in the directio ...
... in vitro, and this was a key technique in deciphering the genetic code. However, it differs from DNA and RNA polymerases in points 1 and 4. Polynucleotide phosphorylase does not use a template, but rather adds ribonucleotides to an RNA in a highly reversible reaction. The substrates (in the directio ...
UNIT 4 NOTES
... c. amino acids have a carbon atom bonded to 1) a hydrogen atom, 2) an amino group, NH2, 3) a carboxyl group and 4) a side group that makes them unique d. polypeptide bonds bind amino acids together 4. Nucleic acids – polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides a. a nucleotide is made up of a sug ...
... c. amino acids have a carbon atom bonded to 1) a hydrogen atom, 2) an amino group, NH2, 3) a carboxyl group and 4) a side group that makes them unique d. polypeptide bonds bind amino acids together 4. Nucleic acids – polymers made up of monomers called nucleotides a. a nucleotide is made up of a sug ...
Level 2 Biology (91159) 2013
... in such research, because they are born as quadruplets derived from a single fertilised egg. This means that all four armadillo pups share the same genetic sequence. In a number of experiments carried out by scientists in the 1960s, genetically identical armadillos were found to show significant phe ...
... in such research, because they are born as quadruplets derived from a single fertilised egg. This means that all four armadillo pups share the same genetic sequence. In a number of experiments carried out by scientists in the 1960s, genetically identical armadillos were found to show significant phe ...
Protein Synthesis Notes - Hamilton Local Schools
... • Know where each stage of protein synthesis occurs in the cell. • Given a sequence of DNA construct the protein using transcription and translation. • Understand and demonstrate how start and stop codons effect the synthesis of a protein. ...
... • Know where each stage of protein synthesis occurs in the cell. • Given a sequence of DNA construct the protein using transcription and translation. • Understand and demonstrate how start and stop codons effect the synthesis of a protein. ...
2- All essential amino acids are glucogenic. False
... True or False with explanation: 1- An increase in gluconeogenesis from amino acids results in a decrease in urea formation. ...
... True or False with explanation: 1- An increase in gluconeogenesis from amino acids results in a decrease in urea formation. ...
File
... Carries amino acids to ribosome Contains an “anticodon” of nitrogen bases Anticodons use complementary bond with codons Less tRNA’s than codons, so one tRNA may bind with more than one codon. • Supports the degenerate code • “Wobble” hypothesis: anticodon with U in third position can bind to A or G ...
... Carries amino acids to ribosome Contains an “anticodon” of nitrogen bases Anticodons use complementary bond with codons Less tRNA’s than codons, so one tRNA may bind with more than one codon. • Supports the degenerate code • “Wobble” hypothesis: anticodon with U in third position can bind to A or G ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
Name: Chapter 8 DNA Study Guide There are two main nucleic
... 20. ___________________________ (rRNA) binds to the mRNA and uses the instructions to assemble amino acids in the correct order 21. ___________________________ (tRNA) is the supplier. Transfer RNA delivers amino acids to the ribosome to be assembled into a protein 22. In the nucleus, enzymes make a ...
... 20. ___________________________ (rRNA) binds to the mRNA and uses the instructions to assemble amino acids in the correct order 21. ___________________________ (tRNA) is the supplier. Transfer RNA delivers amino acids to the ribosome to be assembled into a protein 22. In the nucleus, enzymes make a ...
Genes and Inheritance
... • Long strands of DNA with many genes (20-30 thousand) • Diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosomes ...
... • Long strands of DNA with many genes (20-30 thousand) • Diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosomes ...
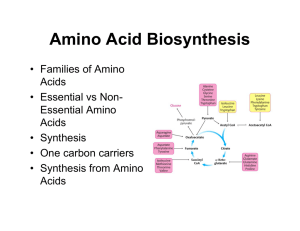
Amino Acid Biosynthesis
... Nitrogen • Atmospheric N2 is the ultimate source of biological nitrogen • Nitrogen fixation: a few bacteria possess nitrogenase which can reduce N2 to ammonia • Nitrogen is recycled in nature through the nitrogen cycle ...
... Nitrogen • Atmospheric N2 is the ultimate source of biological nitrogen • Nitrogen fixation: a few bacteria possess nitrogenase which can reduce N2 to ammonia • Nitrogen is recycled in nature through the nitrogen cycle ...
From Gene to Protein
... tRNA= carries a specific amino acid to ribosome based on its anticodon to mRNA codon rRNA= makes up 60% of the ribosome; site of protein synthesis snRNA=small nuclear RNA; part of a spliceosome. Has structural and catalytic roles srpRNA=a signal recognition particle that binds to signal peptides RNA ...
... tRNA= carries a specific amino acid to ribosome based on its anticodon to mRNA codon rRNA= makes up 60% of the ribosome; site of protein synthesis snRNA=small nuclear RNA; part of a spliceosome. Has structural and catalytic roles srpRNA=a signal recognition particle that binds to signal peptides RNA ...
DNA Structure and Function
... C. translation D. transcription 2. What is DNA? P148 A. a type of molecule composed mostly of ...
... C. translation D. transcription 2. What is DNA? P148 A. a type of molecule composed mostly of ...
1. There are three main classes of biological polymers
... Use any resource at your disposal to answer these questions. Submit via course website prior to class Feb. 2nd. ...
... Use any resource at your disposal to answer these questions. Submit via course website prior to class Feb. 2nd. ...
Biochem 4 protein notes - The Bronx High School of Science
... - FIBROUS. - long fiber shape EX: actin or collagen - GLOBULAR - overall spherical structure EX: hemoglobin, MUTATIONS CAN CHANGE PROTEIN SHAPE Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence ...
... - FIBROUS. - long fiber shape EX: actin or collagen - GLOBULAR - overall spherical structure EX: hemoglobin, MUTATIONS CAN CHANGE PROTEIN SHAPE Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence ...
proteins aminacids notesKelly
... - FIBROUS. - long fiber shape EX: actin or collagen - GLOBULAR - overall spherical structure EX: hemoglobin, MUTATIONS CAN CHANGE PROTEIN SHAPE Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence ...
... - FIBROUS. - long fiber shape EX: actin or collagen - GLOBULAR - overall spherical structure EX: hemoglobin, MUTATIONS CAN CHANGE PROTEIN SHAPE Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence ...
Week 2
... sequence of pre-RNA, the exons are sticthed together to form the mature RNA The mature RNA then travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to carry out the protein synthesis message Alternative splicing refers to alternative ways in which a pre-mRNA molecule can be spliced into a different mRNA molec ...
... sequence of pre-RNA, the exons are sticthed together to form the mature RNA The mature RNA then travels from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to carry out the protein synthesis message Alternative splicing refers to alternative ways in which a pre-mRNA molecule can be spliced into a different mRNA molec ...
Lipids,proteins, and nucleic acids
... • There are two types of nucleic acid: 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) *Contains coded info that programs all cell activity. *Contains directions for its own replication. *Copied and passed on from one generation to another. *In eukaryotic cells, it is found primarily in the nucleus. ...
... • There are two types of nucleic acid: 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) *Contains coded info that programs all cell activity. *Contains directions for its own replication. *Copied and passed on from one generation to another. *In eukaryotic cells, it is found primarily in the nucleus. ...
Lipids,proteins, and nucleic acids
... • There are two types of nucleic acid: 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) *Contains coded info that programs all cell activity. *Contains directions for its own replication. *Copied and passed on from one generation to another. *In eukaryotic cells, it is found primarily in the nucleus. ...
... • There are two types of nucleic acid: 1. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) *Contains coded info that programs all cell activity. *Contains directions for its own replication. *Copied and passed on from one generation to another. *In eukaryotic cells, it is found primarily in the nucleus. ...
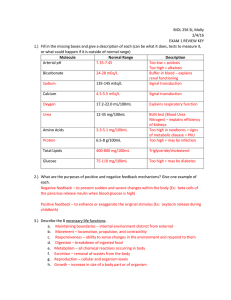
Exam 1 Review KEY
... __transcription________. After that, the strand of RNA creates a protein strand. This process is called ____translation___________. 16.) Name the five nitrogenous bases and correctly pair them. A-T (DNA) A-U (RNA) C-G 17.) Name the three types of RNA and describe their main functions. mRNA – carries ...
... __transcription________. After that, the strand of RNA creates a protein strand. This process is called ____translation___________. 16.) Name the five nitrogenous bases and correctly pair them. A-T (DNA) A-U (RNA) C-G 17.) Name the three types of RNA and describe their main functions. mRNA – carries ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 9) Leucine is derived from the same pathway that generates valine. What additional carbon source is used in this synthesis? The later stages of leucines biosynthetic pathway are similar to what other pathway? 10) Threonine is derived from what non-proteinacious amino acid? Which common amino acid is ...
... 9) Leucine is derived from the same pathway that generates valine. What additional carbon source is used in this synthesis? The later stages of leucines biosynthetic pathway are similar to what other pathway? 10) Threonine is derived from what non-proteinacious amino acid? Which common amino acid is ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
... Define isoenzymes. Discuss the role of isoenzymes in clinical diagnosis with suitable examples. ...
PostScript - Theoretical Biochemistry Group
... i.e. pairing of strong amino acid determining positions with most degenerate ones. However, from the viewpoint of evolutionary compatibility pairing of fixed codon positions with flexible ones (2-3 pairing) is highly disadvantageous. Given the inflexibility of the second codon position silent mutati ...
... i.e. pairing of strong amino acid determining positions with most degenerate ones. However, from the viewpoint of evolutionary compatibility pairing of fixed codon positions with flexible ones (2-3 pairing) is highly disadvantageous. Given the inflexibility of the second codon position silent mutati ...
U - Lakewood City Schools
... genetic information to the ribosomes Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
... genetic information to the ribosomes Ribosomal RNA (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are synthesized ...
answers to study guide
... solid at room temp / liquid at room temp b/c double bonds make kinks in structure polypeptide polymer of amino acids parts of an amino acid amino group, carboxyl groups, H, central carbon, and R group what makes amino acids different from one another The R group, or side chain types of R groups ( po ...
... solid at room temp / liquid at room temp b/c double bonds make kinks in structure polypeptide polymer of amino acids parts of an amino acid amino group, carboxyl groups, H, central carbon, and R group what makes amino acids different from one another The R group, or side chain types of R groups ( po ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.