From RNA to protein
... The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: • Transcription = DNA → RNA • Translation = RNA → protein Taken together, they make up the "central dogma" of biology: DNA → RNA → protein. ...
... The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: • Transcription = DNA → RNA • Translation = RNA → protein Taken together, they make up the "central dogma" of biology: DNA → RNA → protein. ...
Genetics
... codon does not change the encoded amino acid; a more broad definition = a change that does not change the function of the encoded protein • by this definition a silent mutation could be any of these types of base substitions, as long as the function of the protein (phenotype) was not affected) ...
... codon does not change the encoded amino acid; a more broad definition = a change that does not change the function of the encoded protein • by this definition a silent mutation could be any of these types of base substitions, as long as the function of the protein (phenotype) was not affected) ...
Cause and effect of mutation
... chromosome abnormalities as males produce new gametes throughout their lifetime ...
... chromosome abnormalities as males produce new gametes throughout their lifetime ...
Group presentations guide 10-4
... the production of proteins. If a cell's DNA is mutated, an abnormal protein may be produced, which can disrupt the body's usual processes and lead to a disease, such as cancer. The Human Genome Project The Human Genome Project, which was led at the National Institutes of Health, produced a very high ...
... the production of proteins. If a cell's DNA is mutated, an abnormal protein may be produced, which can disrupt the body's usual processes and lead to a disease, such as cancer. The Human Genome Project The Human Genome Project, which was led at the National Institutes of Health, produced a very high ...
Transcription and Translation
... move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
... move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
... If one base was equal to one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 4. If two bases was equal one amino acid, the maximum would be 16 codes. If three bases equal one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 64. ...
... If one base was equal to one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 4. If two bases was equal one amino acid, the maximum would be 16 codes. If three bases equal one amino acid, the maximum codes would be 64. ...
Translation Tjian lec 26
... amino acid to its tRNA molecule in a high-energy linkage. The amino acid is first activated through the linkage of its carboxyl group directly to an AMP moiety, forming and adenylated amino acid; the linkage of the AMP, normally an unfavorable reaction, is driven by the hydrolysis of the ATP molecul ...
... amino acid to its tRNA molecule in a high-energy linkage. The amino acid is first activated through the linkage of its carboxyl group directly to an AMP moiety, forming and adenylated amino acid; the linkage of the AMP, normally an unfavorable reaction, is driven by the hydrolysis of the ATP molecul ...
BSCS Ch 1 review cdmodified - JBHA-Sci-US-tri1
... they are ideal emulsifiers can keep oil and water mixed This property makes phospholipids a perfect structural element for cell membranes able to communicate with the watery environments of the blood and cell fluids, yet with a lipid portion that allows other lipids to enter and exit cells ...
... they are ideal emulsifiers can keep oil and water mixed This property makes phospholipids a perfect structural element for cell membranes able to communicate with the watery environments of the blood and cell fluids, yet with a lipid portion that allows other lipids to enter and exit cells ...
CHAPTER 12 - powerpoint
... codons. • The number of different codons possible is 64 (43), because each position in the codon can be occupied by one of four different bases. • The 64 possible codons code for only 20 amino acids and the start and stop signals. ...
... codons. • The number of different codons possible is 64 (43), because each position in the codon can be occupied by one of four different bases. • The 64 possible codons code for only 20 amino acids and the start and stop signals. ...
Transcription and Translation Candy Activity
... red Twizzlers, black Twizzlers, marshmallows toothpicks, paperclips, Smarties, pasta, packing puffs, cotton balls, sticky Notes labels Other? RNA: RNA has some key differences from DNA. List them below and make a key for the 4 RNA nucleotides. Paste a picture of the 4 RNA nucleotides clearly labelin ...
... red Twizzlers, black Twizzlers, marshmallows toothpicks, paperclips, Smarties, pasta, packing puffs, cotton balls, sticky Notes labels Other? RNA: RNA has some key differences from DNA. List them below and make a key for the 4 RNA nucleotides. Paste a picture of the 4 RNA nucleotides clearly labelin ...
Pipe-Cleaner Proteins
... the order of colours is up to you (don’t use the order listed in step 1!), but only use each colour once. Be sure that the order you choose is NOT the same as your partners. Write out/colour the order below: Strand 1 Strand 2 3. Once coloured from end to end, what you have represents a chain of amin ...
... the order of colours is up to you (don’t use the order listed in step 1!), but only use each colour once. Be sure that the order you choose is NOT the same as your partners. Write out/colour the order below: Strand 1 Strand 2 3. Once coloured from end to end, what you have represents a chain of amin ...
AP Macromolecule Notes 09
... Characteristics: 4 levels o Primary: Amino acid chain o Secondary: H bonds cause coils (alpha helix) & folding (pleated sheet) o Tertiary: 3D shape results from interactions with the ‘R’ group o Quaternary: binding of 2 or polypeptide chains ...
... Characteristics: 4 levels o Primary: Amino acid chain o Secondary: H bonds cause coils (alpha helix) & folding (pleated sheet) o Tertiary: 3D shape results from interactions with the ‘R’ group o Quaternary: binding of 2 or polypeptide chains ...
Application of Algorithm Research to Molecular Biology
... and it is the protein which determines the function of the cell. • For instance, in red blood cells, there must be oxygen carrying protein haemoglobin and the production of this protein is controlled by a certain gene. ...
... and it is the protein which determines the function of the cell. • For instance, in red blood cells, there must be oxygen carrying protein haemoglobin and the production of this protein is controlled by a certain gene. ...
No Slide Title
... mRNA IS READ AND CONVERTED TO A SPECIFIC AMINO ACID SEQUENCE mRNA CODES FOR AMINO ACID tRNA BRINGS AMINO ACID TO ...
... mRNA IS READ AND CONVERTED TO A SPECIFIC AMINO ACID SEQUENCE mRNA CODES FOR AMINO ACID tRNA BRINGS AMINO ACID TO ...
Protein Synthesis
... 2. Transfer RNA previously made by DNA and sent to the cytoplasm goes to be sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA occurs in groups of threes because three bases code one amino acid ...
... 2. Transfer RNA previously made by DNA and sent to the cytoplasm goes to be sure it matches the RNA pattern on the ribosome. 3. If it matches correctly then Transfer RNA goes and picks up its amino acid in the cytoplasm. Transfer RNA occurs in groups of threes because three bases code one amino acid ...
(1) Give brief definitions or unique descriptions of the following terms:
... (5) – Transcription errors are not necessarily a problem as (1) multiple transcripts are produced from a single gene, (2) redundancy in the genetic code means the resulting codon may encode the same amino acid residue and (3) many mutations in protein sequence do affect function. In the case of euca ...
... (5) – Transcription errors are not necessarily a problem as (1) multiple transcripts are produced from a single gene, (2) redundancy in the genetic code means the resulting codon may encode the same amino acid residue and (3) many mutations in protein sequence do affect function. In the case of euca ...
problem set #4 - U of L Class Index
... (5) – Transcription errors are not necessarily a problem as (1) multiple transcripts are produced from a single gene, (2) redundancy in the genetic code means the resulting codon may encode the same amino acid residue and (3) many mutations in protein sequence do affect function. In the case of euca ...
... (5) – Transcription errors are not necessarily a problem as (1) multiple transcripts are produced from a single gene, (2) redundancy in the genetic code means the resulting codon may encode the same amino acid residue and (3) many mutations in protein sequence do affect function. In the case of euca ...
Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism
... where protein synthesis will occur. They lie across the __ribosome_ and wait for the ___transfer RNA to bring in the appropriate amino acids. The correct amino acids will be lined up because the tRNA bases are arranged in _anti-codons_ that are complementary to the __cocons_ of the bases of the mRNA ...
... where protein synthesis will occur. They lie across the __ribosome_ and wait for the ___transfer RNA to bring in the appropriate amino acids. The correct amino acids will be lined up because the tRNA bases are arranged in _anti-codons_ that are complementary to the __cocons_ of the bases of the mRNA ...
The Four major Groups of
... dehydrated to form polypeptides or proteins. • Humans have about 20 different amino acids from which proteins are synthesized. The difference between one protein and another has to do with the number of amino acids that a protein contains and the unique sequences in which the amino acids are arrange ...
... dehydrated to form polypeptides or proteins. • Humans have about 20 different amino acids from which proteins are synthesized. The difference between one protein and another has to do with the number of amino acids that a protein contains and the unique sequences in which the amino acids are arrange ...
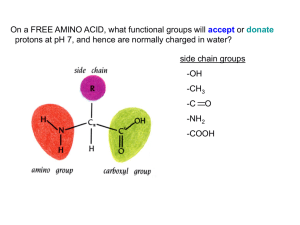
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
... nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
... nature of the resonance hybrid form • Peptide groups (blue planes) are therefore planar; restrict conformations possible in protein chains ...
12.4 Mutations ppt
... Sickle Cell: http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/17-sickle-cell.html Mutating virus: http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/nationalgeographic-channel/shows/naked-science/ngc-deadly-mutation/ Radiation leading to mutations and cancer: ...
... Sickle Cell: http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/17-sickle-cell.html Mutating virus: http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/nationalgeographic-channel/shows/naked-science/ngc-deadly-mutation/ Radiation leading to mutations and cancer: ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct the synthesis of organic molecules, and are responsible for cell structure and movement. DNA carries the infor ...
... or synthesizes. Protein molecules, formed by sequencing twenty different amino acids in various combinations, are important to living things because they control biological pathways, direct the synthesis of organic molecules, and are responsible for cell structure and movement. DNA carries the infor ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.