CHEMISTRY LIST OF TOPICS 1. Nature of chemistry (matter, mass
... heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and complex lipids, fatty acids, waxes, phospholipids, isoprenoids, terpenes and st ...
... heterocycles, five and six- membered ring containing heterocycles with one and more heteroatom(s), heterocycle derivatives);. 12. Carbohydrates (monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides); 13. Lipids (simple and complex lipids, fatty acids, waxes, phospholipids, isoprenoids, terpenes and st ...
Final spring 2016
... Figure 12–3 50. In Figure 12–3, A, B, and C are three types of ____________________. 51. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 52. The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of ____________________ in proteins. 53. There is no ____________ ...
... Figure 12–3 50. In Figure 12–3, A, B, and C are three types of ____________________. 51. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 52. The order of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the order of ____________________ in proteins. 53. There is no ____________ ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis - Emerald Meadow Stables
... • Translation is taking mRNA and making proteins • Proteins code for traits! • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides • There are 20 different amino acids – the order of amino acids determine what proteins will be made • “Language” of mRNA instructions is the g ...
... • Translation is taking mRNA and making proteins • Proteins code for traits! • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides • There are 20 different amino acids – the order of amino acids determine what proteins will be made • “Language” of mRNA instructions is the g ...
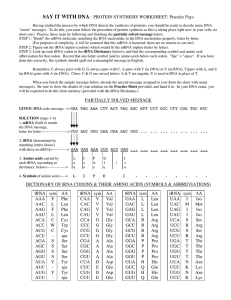
SAY IT WITH DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS WORKSHEET: Practice
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
... Having studied the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of proteins, you should be ready to decode some DNA "secret" messages. To do this, you must follow the procedure of protein synthesis as this is taking place right now in your cells; no short cuts! Practice these steps by following and fi ...
DNA RNA PSyn notes
... 4. Given the following nitrogen base sequence in a molecule of DNA: AATCGTTCGTTAGCGCCA (this is obviously only one side of the DNA molecule) answer the following: a. what would the other side of the DNA strand look like? b. what would a transcribed mRNA strand look like? c. how many amino acids woul ...
... 4. Given the following nitrogen base sequence in a molecule of DNA: AATCGTTCGTTAGCGCCA (this is obviously only one side of the DNA molecule) answer the following: a. what would the other side of the DNA strand look like? b. what would a transcribed mRNA strand look like? c. how many amino acids woul ...
Bio 139 Exam Review Outline: Exam #3
... RNA polymerase: synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. What is a codon? How many nucleotides does it take to encode one amino acid?(3) What is the “genetic code” and how is it “degenerate”? Know that some codons mean “stop” (don’t need to memorize which ones). tRNAs have two functional ends: one binds ...
... RNA polymerase: synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. What is a codon? How many nucleotides does it take to encode one amino acid?(3) What is the “genetic code” and how is it “degenerate”? Know that some codons mean “stop” (don’t need to memorize which ones). tRNAs have two functional ends: one binds ...
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... for a specific reaction Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
... for a specific reaction Double sugar needs to be broken apart Only one enzyme can function for this reaction Shape of an Enzyme can determine its functions ...
Notes - Humble ISD
... all genes on that chromosome! 2. These errors generally occur during meiosis or mitosis. 3. May result in a number disorder (extra chromosome or deleted chromosome) insertion, deletion, or translocation of a piece of chromosome and the corresponding genetic information. B. Gene Mutation Gene mutatio ...
... all genes on that chromosome! 2. These errors generally occur during meiosis or mitosis. 3. May result in a number disorder (extra chromosome or deleted chromosome) insertion, deletion, or translocation of a piece of chromosome and the corresponding genetic information. B. Gene Mutation Gene mutatio ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... 1 activators; 2 anticodon; 3 bacteriophage;4 base-pairing rules; 5 base sequence; 6 cloning; 7 chromosome condensation; 8 complementary base pair; 9 codon;10 degenerative diseases; 11 deoxyribose; 12 DNA polymerase; 13 DNA replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 ge ...
... 1 activators; 2 anticodon; 3 bacteriophage;4 base-pairing rules; 5 base sequence; 6 cloning; 7 chromosome condensation; 8 complementary base pair; 9 codon;10 degenerative diseases; 11 deoxyribose; 12 DNA polymerase; 13 DNA replication; 14 frameshift mutation;15 galls;16 germ-line gene therapy; 17 ge ...
protein - 4J Blog Server
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
... • How the sequence and subcomponents of proteins determine their properties. • The cellular functions of proteins. (Brief – we will come back to this in other chapters.) • The four structural levels of proteins and how changes at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach ...
DNA - Doctor Jade Main
... • additions make RNA more stable • ends protect molecule from attack by ...
... • additions make RNA more stable • ends protect molecule from attack by ...
THE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS ESSAY MUST: be in the FHS Essay
... Typed Double Spaced 12 point font size Standard font (i.e. New Roman Times (windows) Helvitica (Macintosh)) WRITTEN IN YOUR OWN WORDS! ...
... Typed Double Spaced 12 point font size Standard font (i.e. New Roman Times (windows) Helvitica (Macintosh)) WRITTEN IN YOUR OWN WORDS! ...
Powerpoint prezentácia
... • DNA = string of nucleotides (A, C, G, T). • Codon = group of 3 nucleotides, specifies amino acids. • Amino acids = basic building blocks of proteins. • In order to generate a protein from the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA, the nucleotide sequence is first transcribed into an RNA. ...
... • DNA = string of nucleotides (A, C, G, T). • Codon = group of 3 nucleotides, specifies amino acids. • Amino acids = basic building blocks of proteins. • In order to generate a protein from the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA, the nucleotide sequence is first transcribed into an RNA. ...
Chapter 10 (Sample questions)
... e. Both choices b and d are correct A random change in a DNA nucleotide base sequence: a. Has no influence on genetic variation b. Is never expressed phenotypically c. Constitutes a mutation d. Is never beneficial to the organism e. Will kill the cell when it occurs A gene mutation is defined as cha ...
... e. Both choices b and d are correct A random change in a DNA nucleotide base sequence: a. Has no influence on genetic variation b. Is never expressed phenotypically c. Constitutes a mutation d. Is never beneficial to the organism e. Will kill the cell when it occurs A gene mutation is defined as cha ...
Gene expression powerpoint
... mRNA is in triplet code – 3 bases = codon tRNA molecule with complimentary anticodon binds to exposed codon on mRNA. The codon determines which amino acid the tRNA carries AUG is always the start codon – it codes for the amino acid Methionine (Met) ...
... mRNA is in triplet code – 3 bases = codon tRNA molecule with complimentary anticodon binds to exposed codon on mRNA. The codon determines which amino acid the tRNA carries AUG is always the start codon – it codes for the amino acid Methionine (Met) ...
Nitrogen Anabolism
... Haber-Bosch Cycle N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated ...
... Haber-Bosch Cycle N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 500oC, 300 ATM •Ammonia was first made on an industrial scale in 1913. •Critical for the German munitions effort. •Later, principally used to make fertilizer, allowing more efficient food production. •Nearly 80% of the nitrogen found in human tissues originated ...
Unit Study Guide
... Why does transcription have to take place; in other words, why is mRNA made? What is the role of the enzyme RNA polymerase in the process of transcription? Where does the mRNA strand go after it is made? What is a codon? In your explanation include the following: Where is it located? How many bases ...
... Why does transcription have to take place; in other words, why is mRNA made? What is the role of the enzyme RNA polymerase in the process of transcription? Where does the mRNA strand go after it is made? What is a codon? In your explanation include the following: Where is it located? How many bases ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation. State the purpose of each. Why must the genetic code be written in triplets of nucleotides? From where do ribosomes orginate? Describe the relationship between a DNA triplet, a codon, and an anticodon. What is the evolutionary si ...
Proteins and DNA
... acids. They form a kind of alphabet, making it possible to build innumerable different proteins. These strings of pearls fold in manners that are determined by the order of the amino acids in them. Thus proteins get different shapes, and those shapes determine their properties. Therefore, one protei ...
... acids. They form a kind of alphabet, making it possible to build innumerable different proteins. These strings of pearls fold in manners that are determined by the order of the amino acids in them. Thus proteins get different shapes, and those shapes determine their properties. Therefore, one protei ...
facts about maple syrup urine disease (msud)
... in one of three genes, BCKDHA, BCKDHB, or DBT. At least 80% of MSUD is caused by mutations in BCKDHA or BCKDHB. The remaining 20% of MSUD is caused by mutations in the DBT gene. Individuals have two copies of each of the genes causing MSUD. Carriers of MSUD have a single mutation in one of the MSUD ...
... in one of three genes, BCKDHA, BCKDHB, or DBT. At least 80% of MSUD is caused by mutations in BCKDHA or BCKDHB. The remaining 20% of MSUD is caused by mutations in the DBT gene. Individuals have two copies of each of the genes causing MSUD. Carriers of MSUD have a single mutation in one of the MSUD ...
C H E M I S T R Y
... Mutagens are agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations. Examples are chemicals and radiation. ...
... Mutagens are agents that interact with DNA to cause mutations. Examples are chemicals and radiation. ...
Amino Acids - WordPress.com
... • rRNA = Ribosomes are made of rRNA which Bond amino acids together to build the Polypeptide (protein) ...
... • rRNA = Ribosomes are made of rRNA which Bond amino acids together to build the Polypeptide (protein) ...
Slide 1
... b. Ribonucleic acid (RNA-single strand) • Nucleic acids are composed of long chains of nucleotides linked by dehydration synthesis. • nitrogenous bases: adenine (A) thymine (T)DNAonly uracil (U) RNA only cytosine (C) ...
... b. Ribonucleic acid (RNA-single strand) • Nucleic acids are composed of long chains of nucleotides linked by dehydration synthesis. • nitrogenous bases: adenine (A) thymine (T)DNAonly uracil (U) RNA only cytosine (C) ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.