Stg Chp 11 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mamre organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromoso ...
... 5. Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because a. the zygote usually dies. b. the mamre organism is sterile. c. the mature organism is often incapable of producing offspring. d. all of the above. 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromoso ...
Gene!
... Detect potential coding regions by looking at ORFs A genome of length n is comprised of (n/3) codons Stop codons break genome into segments between consecutive Stop codons The subsegments of these that start from the Start codon (ATG) are ORFs ORFs in different frames may overlap ATG ...
... Detect potential coding regions by looking at ORFs A genome of length n is comprised of (n/3) codons Stop codons break genome into segments between consecutive Stop codons The subsegments of these that start from the Start codon (ATG) are ORFs ORFs in different frames may overlap ATG ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Nature uses a triplet nucleic acid sequence to code for a single amino acid. This genetic code has common characteristics for all organisms. o Each triplet sequence of mRNA is called a codon. o Every gene starts with the same codon, AUG, though this codon can also occur elsewhere in the protein sequ ...
... Nature uses a triplet nucleic acid sequence to code for a single amino acid. This genetic code has common characteristics for all organisms. o Each triplet sequence of mRNA is called a codon. o Every gene starts with the same codon, AUG, though this codon can also occur elsewhere in the protein sequ ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Nature uses a triplet nucleic acid sequence to code for a single amino acid. This genetic code has common characteristics for all organisms. o Each triplet sequence of mRNA is called a codon. o Every gene starts with the same codon, AUG, though this codon can also occur elsewhere in the protein sequ ...
... Nature uses a triplet nucleic acid sequence to code for a single amino acid. This genetic code has common characteristics for all organisms. o Each triplet sequence of mRNA is called a codon. o Every gene starts with the same codon, AUG, though this codon can also occur elsewhere in the protein sequ ...
Match each macromolecule (Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids
... These molecules are primarily used for structural and mediator components of the cell, are grouped by chemical properties of their R side chains. __________________________________ Identify which chemical group each of the following R side chains belongs to: ...
... These molecules are primarily used for structural and mediator components of the cell, are grouped by chemical properties of their R side chains. __________________________________ Identify which chemical group each of the following R side chains belongs to: ...
12-1 DNA
... •An anticodon is a set of three nucleotides that is complementary to an mRNA codon. •An anticodon is carried by a tRNA. A. mRNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released into the cytoplasm. B. Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. a. As each ...
... •An anticodon is a set of three nucleotides that is complementary to an mRNA codon. •An anticodon is carried by a tRNA. A. mRNA must be transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and released into the cytoplasm. B. Translation begins when an mRNA molecule in the cytoplasm attaches to a ribosome. a. As each ...
survey of biochemistry - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... What is the molar concentration of a solution of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) that exhibits an A280 of 0.75 with a path length of 1 cm? Conc. = ...
... What is the molar concentration of a solution of Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) that exhibits an A280 of 0.75 with a path length of 1 cm? Conc. = ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
Presentation
... medium medium medium medium plus plus plus plus plus other amino arginine tryptophan lysine leucine acids ...
... medium medium medium medium plus plus plus plus plus other amino arginine tryptophan lysine leucine acids ...
Chapter 03 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... enzyme be defective, then the enzyme would likely also be defective ...
... enzyme be defective, then the enzyme would likely also be defective ...
2421 _Ch8.ppt
... codon (usually AUG, which codes methionine) first tRNA, carrying an amino, binds in the ribosome to the mRNA by the anticodon The next codon position if filled by the appropriate charged tRNA ...
... codon (usually AUG, which codes methionine) first tRNA, carrying an amino, binds in the ribosome to the mRNA by the anticodon The next codon position if filled by the appropriate charged tRNA ...
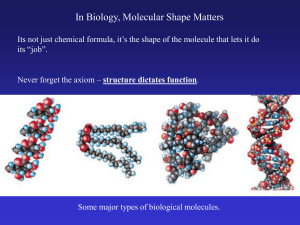
In Biology, Molecular Shape Matters
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
... Its not just chemical formula, it’s the shape of the molecule that lets it do its “job”. ...
Which diagram most correctly represents the process of mitosis
... molecules called amino acids (of which 20 kinds exist) into proteins. Each amino acid is specified by a code of three bases. The helpers in this effort are molecules of transfer RNA (tRNA). Each tRNA molecule contains its own triplet code (to match the mRNA code), and each tRNA ferries a particular ...
... molecules called amino acids (of which 20 kinds exist) into proteins. Each amino acid is specified by a code of three bases. The helpers in this effort are molecules of transfer RNA (tRNA). Each tRNA molecule contains its own triplet code (to match the mRNA code), and each tRNA ferries a particular ...
What happens to proteins key
... Name the 5 parts of an amino acid, can you draw them? Central carbon, its “off-side” hydrogen, carboxylic acid group, amine group & side chain (R-group) ...
... Name the 5 parts of an amino acid, can you draw them? Central carbon, its “off-side” hydrogen, carboxylic acid group, amine group & side chain (R-group) ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... polydeoxyribonucleotide chain determines the specificity of amino acids sequence along the polypeptide chain to be synthesized. What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain synthesized by the portion of the DNA with nucleotides TTTCGACCC? Lys-Ala-Gly ...
... polydeoxyribonucleotide chain determines the specificity of amino acids sequence along the polypeptide chain to be synthesized. What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain synthesized by the portion of the DNA with nucleotides TTTCGACCC? Lys-Ala-Gly ...
MUTATIONS CAN OCCUR IN SOMATIC OR IN REPRODUCTIVE
... A change in the genetic composition of an organism ...
... A change in the genetic composition of an organism ...
Translation: DNA to mRNA to Protein
... second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is cleaved to form guanosine d ...
... second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is cleaved to form guanosine d ...
1. lysine
... F. anitcodon G.ribosome 8. Which cellular function does this model represent? A. Transcription ...
... F. anitcodon G.ribosome 8. Which cellular function does this model represent? A. Transcription ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... RNA is different from DNA because instead of the nitrogenous base ________ found on DNA, RNA has the nitrogenous base__________: ...
... RNA is different from DNA because instead of the nitrogenous base ________ found on DNA, RNA has the nitrogenous base__________: ...
Lecture #7 Date ______ - Phillips Scientific Methods
... • Mutants-are unable to make certain organic molecules: amino acids, lipids, etc. • These substances are added to the media which will allow mutants to grow successfully • Exposed the haploid spores to x rays & UV to induce ...
... • Mutants-are unable to make certain organic molecules: amino acids, lipids, etc. • These substances are added to the media which will allow mutants to grow successfully • Exposed the haploid spores to x rays & UV to induce ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.