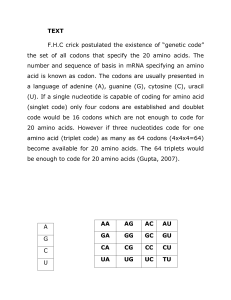
TEXT F.H.C crick postulated the existence of “genetic code” the set
... relationship of some 61 codons has been established to certain specific amino acids. The remaining three codons, UAA (also called ochre), UAG (also called amber) and UGA (also called opal) do not code for specific amino acids and before the functions of these codons was discoved they were called non ...
... relationship of some 61 codons has been established to certain specific amino acids. The remaining three codons, UAA (also called ochre), UAG (also called amber) and UGA (also called opal) do not code for specific amino acids and before the functions of these codons was discoved they were called non ...
Worksheet – Proteins Proteins are polymers of amino acids, joined
... The unreacted amine is called the N-terminus and phenylalanine is amino acid1 in this sequence. The unreacted carboxylic acid on valine is called the Cterminus, which marks the end of this dipeptide. ...
... The unreacted amine is called the N-terminus and phenylalanine is amino acid1 in this sequence. The unreacted carboxylic acid on valine is called the Cterminus, which marks the end of this dipeptide. ...
Section 1.3 Name:
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
... second difference is that RNA has the nitrogen base _______________ (U) instead of _______________ (T). Uracil always pairs with _______________ (A), while cytosine (C) will still always pair with ______________ (g). • There are three types of RNA that work together to produce proteins: o RNA that i ...
Choosing Healthful Foods
... • You need 20 amino acids for your body to function properly. The body makes 11 of those amino acids. The 9 you need from food are known as essential amino acids. • Example of complete protein: meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, and eggs • Example of incomplete protein: grains, legumes, nuts, seeds ...
... • You need 20 amino acids for your body to function properly. The body makes 11 of those amino acids. The 9 you need from food are known as essential amino acids. • Example of complete protein: meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, and eggs • Example of incomplete protein: grains, legumes, nuts, seeds ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Power Point
... 4. If the sequence of one strand is known, the other strand is known ...
... 4. If the sequence of one strand is known, the other strand is known ...
T T PowerPoint
... cause B cells and T cells to grow and divide? Each cell has a receptor on its cell surface that recognizes a specific part of a microbe. That receptor triggers a ...
... cause B cells and T cells to grow and divide? Each cell has a receptor on its cell surface that recognizes a specific part of a microbe. That receptor triggers a ...
Amino acids & proteins part 2
... – Explain why some backbone conformations are “forbidden”, i.e. not found in natural proteins. – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Name more amino acids than you could before One and three letter codes ...
... – Explain why some backbone conformations are “forbidden”, i.e. not found in natural proteins. – Name properties on which the amino acids can be grouped. – Name more amino acids than you could before One and three letter codes ...
Mutations - Lakeland Regional High School / Overview
... Types of Mutations • A. Chromosomal Mutations –Occurs during cell division ...
... Types of Mutations • A. Chromosomal Mutations –Occurs during cell division ...
from_Bi_150_molbiol
... Genes can be localized crudely by hybridizing a fluorescent nucleotide probe to chromosomes ...
... Genes can be localized crudely by hybridizing a fluorescent nucleotide probe to chromosomes ...
Study guide
... the protein that it codes for) can be controlled in each cell; Second we briefly talked about the genetic basis of cancer (see figure 11.17). Ch. 12: DNA technology (Study for this chapter along with the lab exercise from this week and last) In class we used a template strand of DNA and made the com ...
... the protein that it codes for) can be controlled in each cell; Second we briefly talked about the genetic basis of cancer (see figure 11.17). Ch. 12: DNA technology (Study for this chapter along with the lab exercise from this week and last) In class we used a template strand of DNA and made the com ...
Amino Acid and Nucleobase Synthesis in Meteoritic Parent Bodies
... 3. As more amino acids added, proteins ever more useful - finally DNA/protein code takes over (eg. Wong 2005) 4. Thermodynamics + Darwinian selection may produce early ...
... 3. As more amino acids added, proteins ever more useful - finally DNA/protein code takes over (eg. Wong 2005) 4. Thermodynamics + Darwinian selection may produce early ...
A1983QY47000001
... genetic variation in the major milk protein, a -casein. Despite the use of crude 51 electrophoretic methods, Aschaffenburg noted polymorphisms in both a -and ~3-caseins, which my more ...
... genetic variation in the major milk protein, a -casein. Despite the use of crude 51 electrophoretic methods, Aschaffenburg noted polymorphisms in both a -and ~3-caseins, which my more ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... • Made in the Nucleus • Copies DNA • leaves through nuclear pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U • ( no T ) ...
... • Made in the Nucleus • Copies DNA • leaves through nuclear pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U • ( no T ) ...
Acid/Base, AAs, Collagen, Hb
... Proline is Imino Acid L-Amino & D-Amino Does NOT tell the direction of polarized light, just opposite Designate absolute configuration around alpha carbon Same properties, but react differently Naturally occurring as L-Amino Acids Zwitterion Double ionic charge with overall 0 charge pKa (ask them if ...
... Proline is Imino Acid L-Amino & D-Amino Does NOT tell the direction of polarized light, just opposite Designate absolute configuration around alpha carbon Same properties, but react differently Naturally occurring as L-Amino Acids Zwitterion Double ionic charge with overall 0 charge pKa (ask them if ...
Transcription - Effingham County Schools
... RNA doesn’t have thymine though, it’s replaced by another nucleotide URACIL. ...
... RNA doesn’t have thymine though, it’s replaced by another nucleotide URACIL. ...
BIO 10 Lecture 2
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
... Could destroy the function of a protein or subtly alter its function • Will get passed on and increase in frequency if it increases the reproductive fitness of its host ...
Transcription and Translation
... Prior to leaving the nucleus, the mRNA must be modified DNA sequence has ...
... Prior to leaving the nucleus, the mRNA must be modified DNA sequence has ...
Mutations Worksheet
... There are several types of genetic point mutations (a change in only one letter of the genetic code): FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) ...
... There are several types of genetic point mutations (a change in only one letter of the genetic code): FRAMESHIFT, meaning the reading “frame” changes, changing the amino acid sequence. DELETION (a base is lost) INSERTION (an extra base is inserted) SUBSTITUTION (one base is substituted for another) ...
U - Helena High School
... • RNA molecules are produced by copying part of DNA into a complementary sequence of mRNA • This process is started and controlled by an enzyme called Helicase – “unzips” the double stranded DNA. ...
... • RNA molecules are produced by copying part of DNA into a complementary sequence of mRNA • This process is started and controlled by an enzyme called Helicase – “unzips” the double stranded DNA. ...
File - Biology withMrs. Ellsworth
... DNA code is redundant but not ambiguous no punctuation between codons – depends on starting point ATC GCC TAG CAA CTG CTT ...
... DNA code is redundant but not ambiguous no punctuation between codons – depends on starting point ATC GCC TAG CAA CTG CTT ...
Biology Standards (For the Year) *DO NOT LOSE THIS!* CST
... create a specific protein needed in an organism. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and translated using a ribosome. Each 3 nucleotides make a codon, to which tRNA brings the anticodon which is attached to a certain amino acids. The # and order of AA creates that specific protein coded for in the DNA. 4b) ...
... create a specific protein needed in an organism. DNA is transcribed into mRNA and translated using a ribosome. Each 3 nucleotides make a codon, to which tRNA brings the anticodon which is attached to a certain amino acids. The # and order of AA creates that specific protein coded for in the DNA. 4b) ...
The process represented in the diagram below occurs in many cells
... physical features, but not the aggressive nature of the old bulldogs, were mated. The result was a bulldog that was similar in appearance to the extinct bulldog, but without its fierce nature. Which ...
... physical features, but not the aggressive nature of the old bulldogs, were mated. The result was a bulldog that was similar in appearance to the extinct bulldog, but without its fierce nature. Which ...
Prebiotics – the Origins of Life
... Chemists and biologists have for long time explored the possibility that life evolved from previously existing but non-living chemical systems (or prebiotic systems). The Atmosphere of the Primordial Earth When the Earth was newly formed it was very hot and molten and shrouded by a primary atmospher ...
... Chemists and biologists have for long time explored the possibility that life evolved from previously existing but non-living chemical systems (or prebiotic systems). The Atmosphere of the Primordial Earth When the Earth was newly formed it was very hot and molten and shrouded by a primary atmospher ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.