Part I: To Transcribe! In previous lessons, you`ve learned the
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
Problem Set 1 Questions
... 7. For each of the terms in the left column, choose the best matching phrase in the right column. (a). codon ...
... 7. For each of the terms in the left column, choose the best matching phrase in the right column. (a). codon ...
Biomolecules
... result of functional groups • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects their function • Hydroxyl group (-OH) is one of the most ...
... result of functional groups • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects their function • Hydroxyl group (-OH) is one of the most ...
CHNOPS Simulating Protein Synthesis
... the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is "read" on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The proces ...
... the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is "read" on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The proces ...
Slide 1
... Summary of my argument Selection acts at the time of addition of new amino acids to the code. The new amino acid is assigned to codons that formerly coded for an amino acid with similar properties. This minimizes disruption to existing genes. ...
... Summary of my argument Selection acts at the time of addition of new amino acids to the code. The new amino acid is assigned to codons that formerly coded for an amino acid with similar properties. This minimizes disruption to existing genes. ...
Recombinant Human Glutathione S Transferase theta 1
... MRGSHHHHHH KDRWGSHMGL NDIPFELRIV VPALKDGDFT WYPQDLQARA LWHKVMFPVF LQLLEDKFLQ LMHPVGAGCQ EDLFQEAHEV ...
... MRGSHHHHHH KDRWGSHMGL NDIPFELRIV VPALKDGDFT WYPQDLQARA LWHKVMFPVF LQLLEDKFLQ LMHPVGAGCQ EDLFQEAHEV ...
NUTRIENT Handout
... because some of the carbohydrates are very digestible and some are very indigestible. For purposes of ANALYSIS, we often use a very old scheme called: _______________________ in which we analyze for: __________, ______________, ___________________, ____________________, ____________________ and ____ ...
... because some of the carbohydrates are very digestible and some are very indigestible. For purposes of ANALYSIS, we often use a very old scheme called: _______________________ in which we analyze for: __________, ______________, ___________________, ____________________, ____________________ and ____ ...
GHW Questions
... nucleotides. There are two Types of Nucleic Acids: DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Found within cell nucleus for storing and transfering of genetic information that are passed from one cell to other during cell division RNA: Ribonucleic Acid: Occurs in all parts of cell serving the primary function is t ...
... nucleotides. There are two Types of Nucleic Acids: DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Found within cell nucleus for storing and transfering of genetic information that are passed from one cell to other during cell division RNA: Ribonucleic Acid: Occurs in all parts of cell serving the primary function is t ...
Appendix Genomic
... A group of propagating organisms, either single cell or multicellular, derived from a single progenitor cell. Such organisms should be genetically identical, although this can be invalidated due to mutation events. CODOMINANCE Two dominant alleles within a single gene that equally affect the phenoty ...
... A group of propagating organisms, either single cell or multicellular, derived from a single progenitor cell. Such organisms should be genetically identical, although this can be invalidated due to mutation events. CODOMINANCE Two dominant alleles within a single gene that equally affect the phenoty ...
Genetics RNA and Protein Synthesis
... nucleotide triplet (codon) of mRNA, a specific tRNA molecule matches up with the sequence and carries with it a specific amino acid. • The amino acid then binds to the growing amino acid (polypeptide) chain until the mRNA message comes to a stop and a protein is created. ...
... nucleotide triplet (codon) of mRNA, a specific tRNA molecule matches up with the sequence and carries with it a specific amino acid. • The amino acid then binds to the growing amino acid (polypeptide) chain until the mRNA message comes to a stop and a protein is created. ...
SECTION D What Does DNA Do?
... that are used for building complex organisms out of cells. Those important jobs are fulfilled by a very different class of molecules called proteins. DNA’s “claim to fame” is that it is the class of molecules within which all of the instructions are stored that are necessary for making all of the pr ...
... that are used for building complex organisms out of cells. Those important jobs are fulfilled by a very different class of molecules called proteins. DNA’s “claim to fame” is that it is the class of molecules within which all of the instructions are stored that are necessary for making all of the pr ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... amino (NH2) group of one amino acid and the carboxylic group (COOH) of another >Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together >Polypeptide – 3+ amino acids bonded together ...
... amino (NH2) group of one amino acid and the carboxylic group (COOH) of another >Dipeptide – two amino acids bonded together >Polypeptide – 3+ amino acids bonded together ...
Ch. 11 - Holden R-III School District
... embryo to die, or help the offspring Body cells- changes in the DNA of a nonreproductive cell that are not passed on to offspring These can show no effect, damage individual cells, or lead to the formation of cancer ...
... embryo to die, or help the offspring Body cells- changes in the DNA of a nonreproductive cell that are not passed on to offspring These can show no effect, damage individual cells, or lead to the formation of cancer ...
FARM ANIMAL NUTRITION
... Unsaturated & polyunsaturated – plant origin Precursors of cholesterol, prostaglandin and structural components of cells • Some vitamins are fat soluble ...
... Unsaturated & polyunsaturated – plant origin Precursors of cholesterol, prostaglandin and structural components of cells • Some vitamins are fat soluble ...
Nucleic Acids Placemat
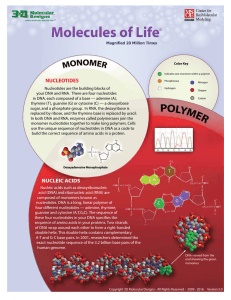
... NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA ...
... NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are composed of monomers known as nucleotides. DNA is a long, linear polymer of four different nucleotides — adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine (A,T,G,C). The sequence of these four nucleotides in your DNA ...
Unit 3 Biochemistry - The Naked Science Society
... Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
... Biochemists study the structures and physical properties of biological molecules. ...
Macromolecules: Proteins
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
DNA Replication
... DNA, separating the two strands. 2. The enzyme moves down the DNA, building a strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA. __________________ STOP code 3. The enzyme reads a ________ and the new strand of RNA is completed and moves into the cytoplasm _______________. ...
... DNA, separating the two strands. 2. The enzyme moves down the DNA, building a strand of RNA that is complementary to the DNA. __________________ STOP code 3. The enzyme reads a ________ and the new strand of RNA is completed and moves into the cytoplasm _______________. ...
LB145-lecture16
... Which of the following is NOT true of a codon? A. It consists of three nucleotides. B. It may code for the same amino acid as another codon. C. It never codes for more than one amino acid. D. It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule. E. It is the basic unit of the genetic code. ...
... Which of the following is NOT true of a codon? A. It consists of three nucleotides. B. It may code for the same amino acid as another codon. C. It never codes for more than one amino acid. D. It extends from one end of a tRNA molecule. E. It is the basic unit of the genetic code. ...
Organic Biomolecules Fill in Notes 2016
... • Only contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio of 1:2:1 Example: formula for glucose is C6H12O6 ...
... • Only contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio of 1:2:1 Example: formula for glucose is C6H12O6 ...
Lecture 5: Powerpoint
... Hydrophobic interactions among hydrophobic R groups. Disulphide bridges that form strong, stable bonds between parts of the molecule ...
... Hydrophobic interactions among hydrophobic R groups. Disulphide bridges that form strong, stable bonds between parts of the molecule ...
File - singhscience
... including any two from the following points • change in a base from C to T (1) • (causes) change in one codon/triplet of bases (1) • results in a different amino acid (1) ...
... including any two from the following points • change in a base from C to T (1) • (causes) change in one codon/triplet of bases (1) • results in a different amino acid (1) ...
Document
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
... 5. Which scientific term describes the shape of the DNA molecule? 6. What process forms messenger RNA? 7. Describe the role of the following RNA molecules in the production of proteins: (Ch. 11.2) mRNA: ___________________________________________________ tRNA: _______________________________________ ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.