CH 17_ From Gene to Protein
... • There are 2 ribosomal subunits, each composed of ribosomal RNA or rRNA – Genes on chromosomal DNA are transcribed, and the RNA is processed and assembled with proteins imported from the cytoplasm – This occurs in the nucleolus – The completed ribosomal subunits are then exported through a nuclear ...
... • There are 2 ribosomal subunits, each composed of ribosomal RNA or rRNA – Genes on chromosomal DNA are transcribed, and the RNA is processed and assembled with proteins imported from the cytoplasm – This occurs in the nucleolus – The completed ribosomal subunits are then exported through a nuclear ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Modified genetic code is “translated” into proteins Codon code is specific, but redundant! 20 amino acids 64 triplet (codon) combinations ...
... Modified genetic code is “translated” into proteins Codon code is specific, but redundant! 20 amino acids 64 triplet (codon) combinations ...
CHEM 260 | ELEMENTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY L/L
... - Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells - Describe the chemical and physical properties of water, acids, bases, buffers - Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation - Illustrate Coupled Reactions - Classify amino acids, identify amino acid functions and isoelectric points - Compare prot ...
... - Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells - Describe the chemical and physical properties of water, acids, bases, buffers - Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation - Illustrate Coupled Reactions - Classify amino acids, identify amino acid functions and isoelectric points - Compare prot ...
Mini lab 11.1 and 11.2
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
gene expression - cloudfront.net
... sequences of nucleotides that carry useful information fro protein synthesis, and INTRONS, sequences that do not. 8. Before leaving the nucleus, the initial RNA transcript is processed to remove introns and splice (join) exons together. This processed RNA, now properly called mRNA, is transported fr ...
... sequences of nucleotides that carry useful information fro protein synthesis, and INTRONS, sequences that do not. 8. Before leaving the nucleus, the initial RNA transcript is processed to remove introns and splice (join) exons together. This processed RNA, now properly called mRNA, is transported fr ...
49 fv protein synth.p65
... This Factsheet summarises the key aspects of the mechanisms of protein synthesis. 1. The nature of the genetic code. 2. The relationships of transfer RNA (tRNA) to amino acids and their role in polypeptide synthesis. 3. The roles of messenger RNA (mRNA), rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) and ribosome ...
... This Factsheet summarises the key aspects of the mechanisms of protein synthesis. 1. The nature of the genetic code. 2. The relationships of transfer RNA (tRNA) to amino acids and their role in polypeptide synthesis. 3. The roles of messenger RNA (mRNA), rough endoplasmic reticulum(RER) and ribosome ...
Unit #3 Retake Ticket Unit 3 Retake Ticket
... because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, ___________. Thirdly, Structure D, also known as _________, is responsible for carrying both the ( ...
... because it carries the DNA message from the (A)_____________ to the _______________. There, the (G) _________ attaches to the surface of (C) ___________, which is made partly of the second type of RNA, ___________. Thirdly, Structure D, also known as _________, is responsible for carrying both the ( ...
Session 2 – Origin of Life
... this event, it will almost certainly happen at least once…. The time… is of the order of two billion years.… Given so much time, the “impossible” becomes possible, the possible probable, and the probable virtually certain. One only has to wait: time itself performs the miracles.” — George Wald - In ...
... this event, it will almost certainly happen at least once…. The time… is of the order of two billion years.… Given so much time, the “impossible” becomes possible, the possible probable, and the probable virtually certain. One only has to wait: time itself performs the miracles.” — George Wald - In ...
3.PROTEIN SYNTHESIS overview
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
... The same genetic code is used for translation in every organism from bacteria to mammals It’s universality is powerful evidence that evolution of the code happened ________________________________________________ _______ amino acids found in proteins are coded for by _____ different bases of RNA 3 n ...
Slide 1
... The ribosome reads the nucleotides on the RNA in sets of three – each set of three nucleotides is called a codon. DNA Coding DNA Template ...
... The ribosome reads the nucleotides on the RNA in sets of three – each set of three nucleotides is called a codon. DNA Coding DNA Template ...
Nucleic Acids
... • After a polypeptide with all the amino acids for a protein is synthesized, the ribosome reaches the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the pr ...
... • After a polypeptide with all the amino acids for a protein is synthesized, the ribosome reaches the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the pr ...
Structure-function study of the C-terminal tail of Thioredoxin Reductase
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
Enterokinase (E4906)
... The FLAG protein expression system is based on the fusion of the 8 amino acid FLAG tag to the recombinant protein of choice. The rare 5 amino acid recognition sequence of the enterokinase cleavage site is incorporated into the FLAG tag. The FLAG sequence is: N-Asp-Tyr-Lys-Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys-C Clea ...
... The FLAG protein expression system is based on the fusion of the 8 amino acid FLAG tag to the recombinant protein of choice. The rare 5 amino acid recognition sequence of the enterokinase cleavage site is incorporated into the FLAG tag. The FLAG sequence is: N-Asp-Tyr-Lys-Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys-C Clea ...
Protein Synthesis Overview
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
... The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an anticodon whose bases are complementary to a codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon, which is part of the tRNA that b ...
Biochem Quiz
... a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrates, d) lipids, e) nucleic acids. ____ 2. Fats and oils are: a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrates, d) lipids, e) nucleic acids ____ 3. Molecules used to store energy and provide lubrication and insulation: a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrat ...
... a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrates, d) lipids, e) nucleic acids. ____ 2. Fats and oils are: a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrates, d) lipids, e) nucleic acids ____ 3. Molecules used to store energy and provide lubrication and insulation: a) amino acids, b) proteins, c) carbohydrat ...
pgat biotechnology-2016
... the same gene can code for several different proteins several different genes can code for the same protein gene expression can be regulated at the level of transcription places of DNA can be moved around within the genome ...
... the same gene can code for several different proteins several different genes can code for the same protein gene expression can be regulated at the level of transcription places of DNA can be moved around within the genome ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
... Changes in pH, salt, temp, or other environmental factors can cause proteins to unravel o Denaturation – loss of protein’s native structure; becomes biologically inactive Protein Folding o Most go thru several states on way to a stable structure o Chaperonin – protein that assists in proper fold ...
Protein synthesis - Aurora City Schools
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
Chapter 8.qxp
... natural selection. Perhaps there were once many codes, all with different degrees of error susceptibility. Organisms whose codes coped best with error were more likely to survive, and the standard genetic code simply won in the struggle for existence. We know that variant codes are possible, so this ...
... natural selection. Perhaps there were once many codes, all with different degrees of error susceptibility. Organisms whose codes coped best with error were more likely to survive, and the standard genetic code simply won in the struggle for existence. We know that variant codes are possible, so this ...
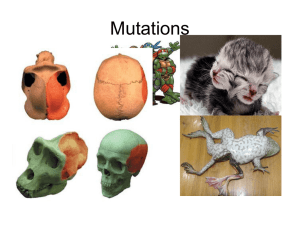
MUTATIONS
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
Table of nitrogen base
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, like hair color and blood type. Genes are composed of DNA. The DNA code is based on a triplet of nitrogen bases. The triplet code codes for a specific amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription ( ...
... Genes are the units that determine inherited characteristics, like hair color and blood type. Genes are composed of DNA. The DNA code is based on a triplet of nitrogen bases. The triplet code codes for a specific amino acid. Amino acids combine to form proteins. In a process known as transcription ( ...
Co-metabolism of amino acids and polyfructans by
... Introduction. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is considered to be human symbiont that stabilizes the colon ecosystem by multiple functions including catabolism of wide variety of polysaccharides (1). Levan (β2-6 fructan) and levan-type oligosaccharides are produced mostly by extracellular enzymes of se ...
... Introduction. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is considered to be human symbiont that stabilizes the colon ecosystem by multiple functions including catabolism of wide variety of polysaccharides (1). Levan (β2-6 fructan) and levan-type oligosaccharides are produced mostly by extracellular enzymes of se ...
A Glance on Genetics
... • Polymers of amino acids are also called peptides or polypeptides • Polymers fold themselves to generate a shape characteristic of each different protein • The shape of the protein along with different chemical properties of the 20 amino acids determine the function of the protein • In theory, by ...
... • Polymers of amino acids are also called peptides or polypeptides • Polymers fold themselves to generate a shape characteristic of each different protein • The shape of the protein along with different chemical properties of the 20 amino acids determine the function of the protein • In theory, by ...
3.4: Transcription and Translation - ISM-Online
... IB Question: Explain the process of translation. [8] messenger / mRNA attaches to ribosome (small unit); many ribosome/polyribosomes bind to same mRNA; carries codons / triplet of bases each coding for one amino acid; transfer / tRNA each have specific anticodon; triplet of bases for specific amino ...
... IB Question: Explain the process of translation. [8] messenger / mRNA attaches to ribosome (small unit); many ribosome/polyribosomes bind to same mRNA; carries codons / triplet of bases each coding for one amino acid; transfer / tRNA each have specific anticodon; triplet of bases for specific amino ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.