Chapter 11.2 Notes RNA and Protein RNA Contains the sugar and
... ______________ segments of RNA nucleotides that transport ______________ _____________ to the _______________________ ...
... ______________ segments of RNA nucleotides that transport ______________ _____________ to the _______________________ ...
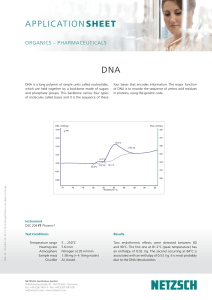
Application Sheet: DNA - NETZSCH Thermal Analysis
... APPLICATION SHEET ORGANICS – PHARMACEUTICALS ...
... APPLICATION SHEET ORGANICS – PHARMACEUTICALS ...
Chemistry of Cooking, Chemisty in the Kitchen
... 5. force applied over a specific surface area 11. one of 3 main nutrients: contain elements C,H,O (commonly 2 Hydrogen for each Oxygen atom) 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this ...
... 5. force applied over a specific surface area 11. one of 3 main nutrients: contain elements C,H,O (commonly 2 Hydrogen for each Oxygen atom) 12. Fe(II) wheel 13. a 'carboxylic acid' that fuels living cells 16. uncommon in nature - ie: elaidic acid 17. element Fe: blood, Flatirons are red b/c of this ...
From http://www
... When the RNA copy is complete, it snakes out into the outer part of the cell. Then in a dazzling display of choreography, all the components of a molecular machine lock together around the RNA to form a miniature factory called a ribosome. It translates the genetic information in the RNA into a stri ...
... When the RNA copy is complete, it snakes out into the outer part of the cell. Then in a dazzling display of choreography, all the components of a molecular machine lock together around the RNA to form a miniature factory called a ribosome. It translates the genetic information in the RNA into a stri ...
Chapter 13 – RNA and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... 1. What is the genetic code? The relationship between specific sequences of nitrogen bases to amino acids. 2. How is one protein different from another protein? Proteins are different by the sequence and type of amino acids that form the polypeptide. 3. What is translation? Translation is the proces ...
... 1. What is the genetic code? The relationship between specific sequences of nitrogen bases to amino acids. 2. How is one protein different from another protein? Proteins are different by the sequence and type of amino acids that form the polypeptide. 3. What is translation? Translation is the proces ...
Protein Synthesis - TangHua2012-2013
... ______________________________________________. Many amino acids make up a protein. Each 3 base set is called a _____________________. _________________________________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________. Many amino acids make up a protein. Each 3 base set is called a _____________________. _________________________________________________________________ ...
Miller/Urey Experiment
... was now in the form of organic compounds. Two percent of the carbon had formed some of the amino acids which are used to make proteins. Perhaps most importantly, Miller's experiment showed that organic compounds such as amino acids, which are essential to cellular life, could be made easily under th ...
... was now in the form of organic compounds. Two percent of the carbon had formed some of the amino acids which are used to make proteins. Perhaps most importantly, Miller's experiment showed that organic compounds such as amino acids, which are essential to cellular life, could be made easily under th ...
Help Wanted
... to GCG. By looking at the codon chart, you can see that both of these codons code for the amino acid alanine. So even though the DNA and mRNA have changed, there is no change in the protein! ...
... to GCG. By looking at the codon chart, you can see that both of these codons code for the amino acid alanine. So even though the DNA and mRNA have changed, there is no change in the protein! ...
energy, chemical reactions and organic compounds list the four
... Fatty Acids – a chain of 4 – 24 carbon atoms with a carboxyl group on one end and a methyl group on the other and hydrogen bonded along the sides. Can be saturated (as much hydrogen as it can carry) or unsaturated (have carbon atoms joined by double bonded covalent bonds with no hydrogen). Trigly ...
... Fatty Acids – a chain of 4 – 24 carbon atoms with a carboxyl group on one end and a methyl group on the other and hydrogen bonded along the sides. Can be saturated (as much hydrogen as it can carry) or unsaturated (have carbon atoms joined by double bonded covalent bonds with no hydrogen). Trigly ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Asparagine is now added to the growing amino acid chain. ...
... Asparagine is now added to the growing amino acid chain. ...
transcription - moleculesoflife1
... End product 2. Proteins are made up of _______________________________, which our bodies either make or come from our food. 3. What is the mRNA strand that would be copied from this DNA strand? G G C ...
... End product 2. Proteins are made up of _______________________________, which our bodies either make or come from our food. 3. What is the mRNA strand that would be copied from this DNA strand? G G C ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
... Complete the chart on the three chemical differences between DNA and RNA. Structure ...
a. Define chromosome? Describe the structure, functions and their
... moderately assembles them and ships them off to be completed 2.Transfer RNA (tRNA) A class of RNA that has triplet nucleotide sequence complementary to the triplet nucleotide coding sequences of messenger RNA (mRNA). The role of tRNAs is to bond near amino acids and transfer them to the ribosomes, w ...
... moderately assembles them and ships them off to be completed 2.Transfer RNA (tRNA) A class of RNA that has triplet nucleotide sequence complementary to the triplet nucleotide coding sequences of messenger RNA (mRNA). The role of tRNAs is to bond near amino acids and transfer them to the ribosomes, w ...
DNA RNA
... • special initiator tRNA binds to the start codon bringing in the amino acid MET • large ribosomal subunit binds to the small one creating a functional ribosome ...
... • special initiator tRNA binds to the start codon bringing in the amino acid MET • large ribosomal subunit binds to the small one creating a functional ribosome ...
translational - Bioinformatics Institute
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) associates with a set of proteins to form ribosomes, structures that function as protein-synthesizing machines ...
... Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) associates with a set of proteins to form ribosomes, structures that function as protein-synthesizing machines ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... mRNA adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
... mRNA adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. ...
El Diamante Biology
... a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on page 410 (figure 13.11) and answer the following questions: a. Which type of organism co ...
... a. Which organism is a producer? Where does it get its energy? What is that process called? b. Of the 3 organisms illustrated by this food chain, which type has the smallest population? 14. Study the food web on page 410 (figure 13.11) and answer the following questions: a. Which type of organism co ...
ppt - cse.sc.edu
... Stereo Chemistry of Amino Acids • Amino acids are three dimensional entities • Carbon forms 4 bonds • In SP3 hybridization, these four bonds form a tetrahedron • Stereoisomer: two identical molecules that can not be superimposed • D and L are two different enantiomers • A mixture of equal amounts o ...
... Stereo Chemistry of Amino Acids • Amino acids are three dimensional entities • Carbon forms 4 bonds • In SP3 hybridization, these four bonds form a tetrahedron • Stereoisomer: two identical molecules that can not be superimposed • D and L are two different enantiomers • A mixture of equal amounts o ...
Structure of Proteins, Carbohydrates and Fats
... thousands of different proteins that exist in nature, they are all made up of different combinations of amino acids. Proteins are large molecules that may consist of hundreds, or even thousands of amino acids. Amino acids all have the general structure: The R in the diagram represents a functional g ...
... thousands of different proteins that exist in nature, they are all made up of different combinations of amino acids. Proteins are large molecules that may consist of hundreds, or even thousands of amino acids. Amino acids all have the general structure: The R in the diagram represents a functional g ...
Cell Building Blocks
... The term is more-specifically used to refer to fatty-acids and their derivatives (including tn-, di-, and mono-glyccrides and phospholipids) as well as other fatsoluble sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Lipids serve many functions in living organisms including energy storage, serve ...
... The term is more-specifically used to refer to fatty-acids and their derivatives (including tn-, di-, and mono-glyccrides and phospholipids) as well as other fatsoluble sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. Lipids serve many functions in living organisms including energy storage, serve ...
3rd quarter Assessment
... DNA Transcription • Takes place in the NUCLEUS • Process of making mRNA from DNA • RNA POLYMERASE is the enzyme that unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds… • New RNA bases pair with the exposed DNA ...
... DNA Transcription • Takes place in the NUCLEUS • Process of making mRNA from DNA • RNA POLYMERASE is the enzyme that unzips DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds… • New RNA bases pair with the exposed DNA ...
Unit 3 Practice Exam
... Unit 3 Practice Exam 1. A chain of _____ results in a polypeptide chain that folds up into a _____. a. RNA bases ... transcript b. amino acids ... gene c. proteins ... ribosome d. DNA bases ... gene e. amino acids ... protein 2. What mRNA sequence signals the start of a sequence to be translated? a. ...
... Unit 3 Practice Exam 1. A chain of _____ results in a polypeptide chain that folds up into a _____. a. RNA bases ... transcript b. amino acids ... gene c. proteins ... ribosome d. DNA bases ... gene e. amino acids ... protein 2. What mRNA sequence signals the start of a sequence to be translated? a. ...
Translation
... Translation - a process - whereby the genetic information in mRNA strand - is translated into sequence of amino acids to form polypeptide/protein ...
... Translation - a process - whereby the genetic information in mRNA strand - is translated into sequence of amino acids to form polypeptide/protein ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.