Topic 3.5 Transcription (9-13)
... acids Triplet-any set of three bases that determine the identity of one amino acids When a triplet is found on the mRNA molecule, it is called a codon or codon triplet ...
... acids Triplet-any set of three bases that determine the identity of one amino acids When a triplet is found on the mRNA molecule, it is called a codon or codon triplet ...
From Genes to Proteins - Yale Center for Teaching and Learning
... – have difficulty visualizing the role of the key components in translation. – become mired in the details of transcription/translation & miss larger concept about how genotype determines phenotype. – see molecular processes of gene expression as separate from classical genetics/inheritance. ...
... – have difficulty visualizing the role of the key components in translation. – become mired in the details of transcription/translation & miss larger concept about how genotype determines phenotype. – see molecular processes of gene expression as separate from classical genetics/inheritance. ...
Mutations in Splice Sites
... Codon Translation by Aminoacyl tRNAs • Each tRNA has an anticodon sequence that allows it to pair with the codon for its cognate amino acid in the mRNA. • Because base pairing is involved, the orientation of this interaction will be complementary and antiparallel. • The arg-tRNAarg has an anticodon ...
... Codon Translation by Aminoacyl tRNAs • Each tRNA has an anticodon sequence that allows it to pair with the codon for its cognate amino acid in the mRNA. • Because base pairing is involved, the orientation of this interaction will be complementary and antiparallel. • The arg-tRNAarg has an anticodon ...
Review Questions Chapter 12 Review Sheet
... n. How are proteins important to living organisms? Protein and protein interactions are responsible for expressing our phenotype ( or the traits that we can see - eye color, hair color, skin color, shape of our noses, mouths, eyes, etc.) In addition, proteins are enzymes and therefore regulate many ...
... n. How are proteins important to living organisms? Protein and protein interactions are responsible for expressing our phenotype ( or the traits that we can see - eye color, hair color, skin color, shape of our noses, mouths, eyes, etc.) In addition, proteins are enzymes and therefore regulate many ...
Chapter 13 powerpoint
... ribosomal binding site in the order specified by the mRNA • Peptide bonds form between the amino acids and the polypeptide chain grows ...
... ribosomal binding site in the order specified by the mRNA • Peptide bonds form between the amino acids and the polypeptide chain grows ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... The genetic information contained within the DNA can be thought of as a list of genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the a ...
... The genetic information contained within the DNA can be thought of as a list of genetic instructions that the cells uses to make proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids joined together into chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids and the differences between proteins are due to the a ...
Dr. D. Y. Patil Biotechnology And Bioinformatics Institute, Pune
... Amino acids have characteristic titration curves: Titration curve of glycine. Applications of titration curve of glycine. ...
... Amino acids have characteristic titration curves: Titration curve of glycine. Applications of titration curve of glycine. ...
transcriptiontranslation lecture
... Ribosomes, consist of two subunits, each of which contains rRNA and ribosomal proteins…rRNA serves as the catalyst (called a ribozyme)of peptide bond formation! ...
... Ribosomes, consist of two subunits, each of which contains rRNA and ribosomal proteins…rRNA serves as the catalyst (called a ribozyme)of peptide bond formation! ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... o translate the code into the amino acid sequence 3 codons code for “stop” AUG codes for methionine which means “start” RNA is single stranded, has a ribose sugar, and Uracil instead of thymine. 64 possible codons for the 20 amino acids. Some amino acids have several codons. Codons and anticodons ar ...
... o translate the code into the amino acid sequence 3 codons code for “stop” AUG codes for methionine which means “start” RNA is single stranded, has a ribose sugar, and Uracil instead of thymine. 64 possible codons for the 20 amino acids. Some amino acids have several codons. Codons and anticodons ar ...
Computational Prediction of Beta Structure from Amino Acid
... Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, these efforts have proven ineffective for beta-rich proteins such as amyloids and au ...
... Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, these efforts have proven ineffective for beta-rich proteins such as amyloids and au ...
Basics of DNA
... So then A bonds with a U (Uracil) Proceeds in the 5’-3’ position mRNA – leaves nucleus as a copy and codes for an amino acid (translation) ...
... So then A bonds with a U (Uracil) Proceeds in the 5’-3’ position mRNA – leaves nucleus as a copy and codes for an amino acid (translation) ...
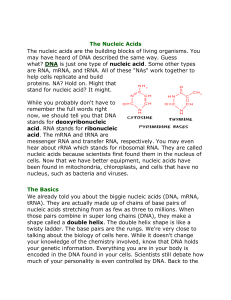
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. The mRNA and tRNA are messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we h ...
... stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. The mRNA and tRNA are messenger RNA and transfer RNA, respectively. You may even hear about rRNA which stands for ribosomal RNA. They are called nucleic acids because scientists first found them in the nucleus of cells. Now that we h ...
Study Guide Test 3
... 3. Be able to describe the basics of protein metabolism from digestion of protein to protein anabolism. 4. Know the difference between a complete protein and an incomplete protein. 5. Know the basic difference between plant and animal protein relative to amino acid content. 6. Be able to fundamental ...
... 3. Be able to describe the basics of protein metabolism from digestion of protein to protein anabolism. 4. Know the difference between a complete protein and an incomplete protein. 5. Know the basic difference between plant and animal protein relative to amino acid content. 6. Be able to fundamental ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Innovation
... 1. The DNA helix unzips itself and RNA polymerase makes an exact copy of the DNA strand in the form of mRNA. This process is called transcription. 2. The mRNA moves out of the nucleus via a nuclear pore and goes to a ribosome. A codon is made up from three organic bases and these are what code for s ...
... 1. The DNA helix unzips itself and RNA polymerase makes an exact copy of the DNA strand in the form of mRNA. This process is called transcription. 2. The mRNA moves out of the nucleus via a nuclear pore and goes to a ribosome. A codon is made up from three organic bases and these are what code for s ...
Ch. 5 Notes
... A. Polypeptides - polymers of amino acids - A protein consists of one or more polypeptides. 1. Amino Acid Monomers - the building blocks of proteins - organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups - differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups - 20 different ...
... A. Polypeptides - polymers of amino acids - A protein consists of one or more polypeptides. 1. Amino Acid Monomers - the building blocks of proteins - organic molecules possessing both carboxyl and amino groups - differ in their properties due to differing side chains, called R groups - 20 different ...
outline File - selu moodle
... one gene / one polypeptide hypothesis. The central dogma of molecular biology DNA RNA proteins Transcription translation Modified with discovery of reverse transcriptase (found in retroviruses) DNA ↔ RNA proteins Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the ...
... one gene / one polypeptide hypothesis. The central dogma of molecular biology DNA RNA proteins Transcription translation Modified with discovery of reverse transcriptase (found in retroviruses) DNA ↔ RNA proteins Transcription uses the template strand of DNA to make a mRNA strand that has the ...
Final
... Which of the following is characteristic of a plasmid? Circle all that apply a. b. c. d. ...
... Which of the following is characteristic of a plasmid? Circle all that apply a. b. c. d. ...
PPT 4
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
... H –C–C–H + Cl2 H–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H If more chlorine is provided, the reaction will produce... H H H H H –C–C–Cl + Cl2 Cl–C–C–Cl + HCl H H H H AND SO ON. ...
Protein Synthesis
... • The instructions (mRNA) are read by tRNA, and tRNA joins amino acids in the right order in the ribosome • Main Goal: make a polypeptide! ...
... • The instructions (mRNA) are read by tRNA, and tRNA joins amino acids in the right order in the ribosome • Main Goal: make a polypeptide! ...
Chemistry notes 2013
... move molecules from one place to another around the body. Examples include hemoglobin and cytochromes. Hemoglobin transports oxygen through the blood. Cytochromes operate in the electron transport chain as electron carrier proteins ...
... move molecules from one place to another around the body. Examples include hemoglobin and cytochromes. Hemoglobin transports oxygen through the blood. Cytochromes operate in the electron transport chain as electron carrier proteins ...
Quiz 3 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... 15. When an organism loses control of its ability to maintain overall homeostasis it will soon be ____________. a. diseased or dead b. dormant c. hibernating d. shivering 16. What are the major organ systems of the body that control homeostasis? a. respiratory and digestive b. skeletal and muscular ...
... 15. When an organism loses control of its ability to maintain overall homeostasis it will soon be ____________. a. diseased or dead b. dormant c. hibernating d. shivering 16. What are the major organ systems of the body that control homeostasis? a. respiratory and digestive b. skeletal and muscular ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Occur at a single point in the DNA sequence • Include substitutions, insertions and deletions Substitution: one base is changed to another Insertions: base is inserted into the DNA sequence Deletion: Base is deleted from the DNA sequence ...
... • Occur at a single point in the DNA sequence • Include substitutions, insertions and deletions Substitution: one base is changed to another Insertions: base is inserted into the DNA sequence Deletion: Base is deleted from the DNA sequence ...
Note 7.1 - Gene to Protein
... RNA polymerase – is an enzyme that reads a DNA strand and creates a complementary strand of RNA. Template strand – is the DNA strand that is copied into an mRNA molecule during gene transcription. Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) – is the initial RNA transcription product. Transcription is the first step i ...
... RNA polymerase – is an enzyme that reads a DNA strand and creates a complementary strand of RNA. Template strand – is the DNA strand that is copied into an mRNA molecule during gene transcription. Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) – is the initial RNA transcription product. Transcription is the first step i ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.