THE NUCLEIC ACIDS
... protein is synthesized, the ribosome reaches the the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the protein can take on it’s 3-D structure (some protei ...
... protein is synthesized, the ribosome reaches the the “stop” codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG • There is no tRNA with an anticodon for the “stop” codons • Therefore, protein synthesis ends (termination) • The polypeptide is released from the ribosome and the protein can take on it’s 3-D structure (some protei ...
DNA Replication Transcription translation [Read
... Gene Expression • Prokaryotic cells regulate gene expression with a set of genes called an operon (also located in some eukaryotes). • An operon is a group of closely linked genes that produces a single mRNA molecule in transcription and that consists of structural genes and regulating elements ...
... Gene Expression • Prokaryotic cells regulate gene expression with a set of genes called an operon (also located in some eukaryotes). • An operon is a group of closely linked genes that produces a single mRNA molecule in transcription and that consists of structural genes and regulating elements ...
Protein Folding and The Impact of Mutations
... TYPES OF MUTATIONS Different types of mutations exist Deletion mutations occur when a base is completely lost from DNA ...
... TYPES OF MUTATIONS Different types of mutations exist Deletion mutations occur when a base is completely lost from DNA ...
Protein synthesis and mut ppt
... Message coming from the mRNA is now translated in the cytoplasm into a polypeptide tRNA is the interpreter that reads the codon from the mRNA through its anti-codon and carries the correct amino acid that matches. Structure of tRNA About 80 nucleotides long forming and 3 dimensional shape that ...
... Message coming from the mRNA is now translated in the cytoplasm into a polypeptide tRNA is the interpreter that reads the codon from the mRNA through its anti-codon and carries the correct amino acid that matches. Structure of tRNA About 80 nucleotides long forming and 3 dimensional shape that ...
Goal 2.01 Biochem
... Water-fearing amino acids Hydrophobic (phobia – fear) “water fearing” amino acids try to get away from water in cell – but HOW? ...
... Water-fearing amino acids Hydrophobic (phobia – fear) “water fearing” amino acids try to get away from water in cell – but HOW? ...
gida bi̇yoteknoloji̇si̇-2
... amino acid of synthesized polypeptide chain. • Formyl group is removed after the tRNA attaches to the initiation codon. Thus, the first a.a becomes methionine. • After the protein synthesis is completed, methionine is usualy removed from the protein by methionine aminopeptidase. ...
... amino acid of synthesized polypeptide chain. • Formyl group is removed after the tRNA attaches to the initiation codon. Thus, the first a.a becomes methionine. • After the protein synthesis is completed, methionine is usualy removed from the protein by methionine aminopeptidase. ...
Bioknowlodgy worksheet 2.4
... Understandings, Applications and Skills (This is what you maybe assessed on) Statement ...
... Understandings, Applications and Skills (This is what you maybe assessed on) Statement ...
RNA
... Each “Nucleotide” is made up of 3 components: 1. A phosphate group 2. A sugar – the sugar in RNA is Ribose. ...
... Each “Nucleotide” is made up of 3 components: 1. A phosphate group 2. A sugar – the sugar in RNA is Ribose. ...
CRACKING THE GENETIC CODE
... amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and the end of the growing chain. Although this general process was understood, the question remained: How do ...
... amino acids, beginning protein synthesis. The nascent protein chain is elongated by the subsequent binding of additional tRNAs and formation of a peptide bond between the incoming amino acid and the end of the growing chain. Although this general process was understood, the question remained: How do ...
Slide 1
... Most amino acids are encoded by several different codons. For example, if the third base in the TCT codon for serine is changed to any one of the other three bases, serine will still be encoded. Such mutations are said to be silent because they cause no change in their product and cannot be detected ...
... Most amino acids are encoded by several different codons. For example, if the third base in the TCT codon for serine is changed to any one of the other three bases, serine will still be encoded. Such mutations are said to be silent because they cause no change in their product and cannot be detected ...
Organic Macromolecules Cloze Worksheet
... Proteins are macromolecules that consist of long, unbranched chains of amino acids. These chains may contain about 20 up to hundreds of acids. An example of the size of proteins is the red pigment in red blood cells called haemoglobin with the chemical formula – C3032 H4816 O872 N780 S8 Fe4 Each cel ...
... Proteins are macromolecules that consist of long, unbranched chains of amino acids. These chains may contain about 20 up to hundreds of acids. An example of the size of proteins is the red pigment in red blood cells called haemoglobin with the chemical formula – C3032 H4816 O872 N780 S8 Fe4 Each cel ...
CAÑIHUA (Chenopodium pallidicaule) Origin Highlands
... (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, phosphorus and manganese. Properties It works as a regulator of intestinal act ...
... (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, phosphorus and manganese. Properties It works as a regulator of intestinal act ...
DNA, genes and chromosomes
... coding regions, called exons, which specify a sequence of amino acids non-coding regions, called introns, which do not specify amino acids regulatory sequences, which play a role in determining when and where the protein is made (and how much is made) A human being has 20,000 to 25,000 genes located ...
... coding regions, called exons, which specify a sequence of amino acids non-coding regions, called introns, which do not specify amino acids regulatory sequences, which play a role in determining when and where the protein is made (and how much is made) A human being has 20,000 to 25,000 genes located ...
biochemistry - SchoolNotes.com
... • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the middle, and a amino group on the other end. • Attached to the methyl group is a R group. ...
... • composed of MANY amino acid subunits • The basic amino acid form has a carboxyl group on one end, a methyl group that only has one hydrogen in the middle, and a amino group on the other end. • Attached to the methyl group is a R group. ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
... 8. Phospholipids contain 2 fatty acid chains and a phosphate group; they are critical components of membranes. 9. PROTEINS are made from 21 amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end and the carboxyl (acid) group in the other. They are different because of the 21 different side groups ...
Ch. 13 Section Assessment Answers
... 7. If the intron were not removed, its codons would be translated and become part of a protein. As a result, the protein might not function properly. 8. C 9. D 10. C 11. C 12. A three-base code “word” in the genetic code that specifies a particular amino acid, start, or stop. 13. At the ribosome, an ...
... 7. If the intron were not removed, its codons would be translated and become part of a protein. As a result, the protein might not function properly. 8. C 9. D 10. C 11. C 12. A three-base code “word” in the genetic code that specifies a particular amino acid, start, or stop. 13. At the ribosome, an ...
Nedmolecularbio1of32013 40 KB
... changes are called frameshifts (abbreviated fs below). In multiples of three, these changes cause a gain or loss of single amino acids when translated. -Frameshift mutation: a base pair insertion or deletion that alters interpretation of the genetic code downstream of the error. This often causes th ...
... changes are called frameshifts (abbreviated fs below). In multiples of three, these changes cause a gain or loss of single amino acids when translated. -Frameshift mutation: a base pair insertion or deletion that alters interpretation of the genetic code downstream of the error. This often causes th ...
BEBERAPA MUTASI GEN katG
... Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Resistance to RIF is caused by mutations in the rpoB gene encoding the β subunit of RNA polymerase, with the highest frequency at codon 526 and 531. While Isoniazid is a prodrug, must be activated by the enzym ...
... Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Resistance to RIF is caused by mutations in the rpoB gene encoding the β subunit of RNA polymerase, with the highest frequency at codon 526 and 531. While Isoniazid is a prodrug, must be activated by the enzym ...
Biology 1 Notes Chapter 12 - DNA and RNA Prentice Hall pages
... Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a promoter site. Promoters are signals in the DNA strand (a certain sequence of bases) that indicate to the enzyme where to bind to make RNA. ...
... Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a promoter site. Promoters are signals in the DNA strand (a certain sequence of bases) that indicate to the enzyme where to bind to make RNA. ...
Document
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
... c.) in the promoter? Ask yourself—What acts at the promoter?! RNA Polymerase…Okay, there are some critical regions in the promoter (namely –10 and –35) that serve as binding sites for RNA Polymerase. If those were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mut ...
Chemical Level of Organization
... and non-polar attractions • Quaternary structure: attractions between separate protein molecules Proteins - Activity • Activity affected by 3-D shape of protein • Shape altered by temperature, pH, and electrolyte concentration • Inactive protein called denatured Proteins - Enzymes • Control chemical ...
... and non-polar attractions • Quaternary structure: attractions between separate protein molecules Proteins - Activity • Activity affected by 3-D shape of protein • Shape altered by temperature, pH, and electrolyte concentration • Inactive protein called denatured Proteins - Enzymes • Control chemical ...
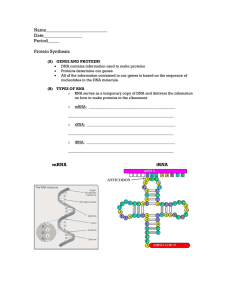
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. ...
Life
... • A key step is the discovery of RNA molecules with a cataly8c func8on, Ribozymes, capable of catalyzing specific biochemical reac8ons, similar to the ac8on of protein enzymes • The 1982 discovery (Altman and Cech, Nobel, 1989) of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both gene&c material (li ...
... • A key step is the discovery of RNA molecules with a cataly8c func8on, Ribozymes, capable of catalyzing specific biochemical reac8ons, similar to the ac8on of protein enzymes • The 1982 discovery (Altman and Cech, Nobel, 1989) of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both gene&c material (li ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.