Amino Acids - WordPress.com
... Enzymes help with this process: Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complimentary strands DNA Polymerases build the new strands and then proofread the nucleotide sequence ...
... Enzymes help with this process: Helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the complimentary strands DNA Polymerases build the new strands and then proofread the nucleotide sequence ...
Chapter 12 Test Review
... 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polymer of nucleotide ____________________________________________________ 5. A DNA nucleo ...
... 2. Chargaff’s rules state that in DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals the amount of ______________ 3. Because of base pairing in DNA, the percentage of _______ = _______ & ________ = _________ 4. What is the polymer of nucleotide ____________________________________________________ 5. A DNA nucleo ...
Unit 6: Genetics
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
... Describe the role of ribosomes, ER, Golgi apparatus, and the nucleus in the production of specific types of proteins. ◦ Ribosomes: A cellular structure composed of RNA and proteins that is the site of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. ◦ Endoplasmic reticulum: An organelle, conta ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... introns) are removed from the message and the remaining sequences (exons) are linked together to produce a sequence of codons that will translate into a polypeptide. This process occurs before the message leaves the nucleus. ...
... introns) are removed from the message and the remaining sequences (exons) are linked together to produce a sequence of codons that will translate into a polypeptide. This process occurs before the message leaves the nucleus. ...
Semiconservative
... The regulation of amino acids such as arginine involves repression when arginine accumulates, and no repression when arginine is being used. ...
... The regulation of amino acids such as arginine involves repression when arginine accumulates, and no repression when arginine is being used. ...
Chapter 11 and 12 Genetics is the scientific study of heredity
... 2. RNA polymerase builds a strand of RNA using on strand of DNA as a template. 3. The DNA is transcribed into RNA using base pair rules, except that uracil binds to adenine. The directions for making proteins are in the order of the four nitrogenous bases. This code is read 3 letters at a time. Each ...
... 2. RNA polymerase builds a strand of RNA using on strand of DNA as a template. 3. The DNA is transcribed into RNA using base pair rules, except that uracil binds to adenine. The directions for making proteins are in the order of the four nitrogenous bases. This code is read 3 letters at a time. Each ...
Science summary I Exam-1 - Relufeas
... The kind, position and number of amino acids determine the protein´s function. - If bonds or links break, that causes the denaturing of the protein and lost of its biological functions. D. What are nucleic acids? Nucleotides are the monomers (main units) of the nucleic acid chains. The basic p ...
... The kind, position and number of amino acids determine the protein´s function. - If bonds or links break, that causes the denaturing of the protein and lost of its biological functions. D. What are nucleic acids? Nucleotides are the monomers (main units) of the nucleic acid chains. The basic p ...
Show DNA to Protein HC
... therefore protein • Two types of Point Mutations – Base pair substitutions replacement of nucleotide – Insertions and Deletions -additions or losses of ...
... therefore protein • Two types of Point Mutations – Base pair substitutions replacement of nucleotide – Insertions and Deletions -additions or losses of ...
Protein Synthesis I
... iii. Only about ½ of the proteins we make get folded- one reason is that there is a 10-20% failure of synthetases to put the right amino acid on the right tRNA 1. So not all proteins are synthesized properly 2. That is one reason why it is more economical to make quaternary structures out of small n ...
... iii. Only about ½ of the proteins we make get folded- one reason is that there is a 10-20% failure of synthetases to put the right amino acid on the right tRNA 1. So not all proteins are synthesized properly 2. That is one reason why it is more economical to make quaternary structures out of small n ...
Name - PSUSDscienceresources
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
... and put in their place the genes for hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan assembled his fleet of ...
Protein Synthesis – Part 3
... 1. The codons MUST be read 5’ 3’on the mRNA! (Because this is how the mRNA was made. You do not write a sentence and then read it backwards do you. It would make no sense.) B. RNA Codon Chart for Amino Acids (Contains the 20 known amino acids for living organisms.) 1. There are three essential thin ...
... 1. The codons MUST be read 5’ 3’on the mRNA! (Because this is how the mRNA was made. You do not write a sentence and then read it backwards do you. It would make no sense.) B. RNA Codon Chart for Amino Acids (Contains the 20 known amino acids for living organisms.) 1. There are three essential thin ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... 4. Protein (chain of amino acids) and detaches from ribosome and goes off to work in the cell. rRNA- Combines with proteins to make ...
... 4. Protein (chain of amino acids) and detaches from ribosome and goes off to work in the cell. rRNA- Combines with proteins to make ...
Ch 40-42 wrap
... • Do you know the importance of these vitamins? B1, folic acid, C, A, D Ch 41 • Do you know the importance of these minerals? Ca, P, S, K, Fe, I Ch 41 • Are you familiar with the insulin/glucagon feedback system? Ch 41 • What is in blood? Ch 42 • What is the Bohr shift? Ch 42 • How does the nervous ...
... • Do you know the importance of these vitamins? B1, folic acid, C, A, D Ch 41 • Do you know the importance of these minerals? Ca, P, S, K, Fe, I Ch 41 • Are you familiar with the insulin/glucagon feedback system? Ch 41 • What is in blood? Ch 42 • What is the Bohr shift? Ch 42 • How does the nervous ...
DNA.Protein.Synthesis Notes
... attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
... attachment site • Does the order of amino acids matter? Yes, they must be in order for the protein to fold correctly. ...
CHNOPS- Simulating Protein Synthesis
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
... place. The code, in DNA or mRNA, specifies the order in which the amino acids are joined together to form a polypeptide. The code words in mRNA, however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino ...
[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the
... • 1) transcription – DNA transcribed to produce RNA • 2) translation – RNA then translated to produce proteins • Protein Synthesis DNA--------- mRNA---------- Protein Transcription Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics ...
... • 1) transcription – DNA transcribed to produce RNA • 2) translation – RNA then translated to produce proteins • Protein Synthesis DNA--------- mRNA---------- Protein Transcription Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics ...
12-4 Mutations - Lincoln Park High School
... b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
... b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
Explain the steps in protein synthesis.
... • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
... • 3. Complementary nucleotides are added using the base pairing rules EXCEPT: • A=U • The rest are the same C=G, T=A, G=C ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... stop codon is reached. There are three different stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG. The release factor recognizes the stop codon and releases the polypeptide strand. All the factors break apart and are reused. ...
... stop codon is reached. There are three different stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG. The release factor recognizes the stop codon and releases the polypeptide strand. All the factors break apart and are reused. ...
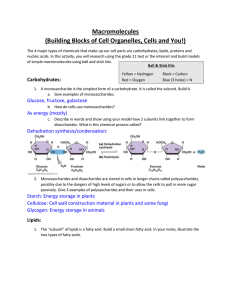
Macromolecules
... 3. Show your partner how two amino acids form a peptide bond. What type of chemical reaction is this? ...
... 3. Show your partner how two amino acids form a peptide bond. What type of chemical reaction is this? ...
Unit 2 - Subcortical systems, neurochemistry and brain function
... - the “blueprint” of life. - as with amino acids, nucleotides combine in any order. - only four different types of nucleotides (slightly different for DNA and RNA). - single nucleotides made of three components: a. __________ b. ____________________________________________ c. _______________________ ...
... - the “blueprint” of life. - as with amino acids, nucleotides combine in any order. - only four different types of nucleotides (slightly different for DNA and RNA). - single nucleotides made of three components: a. __________ b. ____________________________________________ c. _______________________ ...
Transcription and Translation
... • The first tRNA detaches and leaves it’s amino acid. • Two new tRNA with their amino acids move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
... • The first tRNA detaches and leaves it’s amino acid. • Two new tRNA with their amino acids move into position (positions are called A and P) • The new tRNAs have the correct amino acid for that specific codon. Each copyright cmassengale ...
DNA repair mechanism File
... • Induced mutations are defined as those that arise after purposeful treatment with mutagens, environmental agents that are known to increase the rate of mutations • Spontaneous mutations are those that arise in the absence of known mutagen treatment. They account for the "background rate" of mutati ...
... • Induced mutations are defined as those that arise after purposeful treatment with mutagens, environmental agents that are known to increase the rate of mutations • Spontaneous mutations are those that arise in the absence of known mutagen treatment. They account for the "background rate" of mutati ...
Central Dogma - We Heart Science
... incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. • Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. ...
... incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. • Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.














![[Type the document title] Microbial Genetics Molecular biology is the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010247892_1-83bf00ba7ef17902054c2b83fe295408-300x300.png)