DNA Test Review What are the four nucleotides in DNA? Which
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
... 12. Why is tRNA important in translation? 13. What is the difference between DNA and RNA? 14. How many amino acids does this DNA sequence represent: TAAAGGCCC? 15. How can only 20 amino acids make thousands of proteins? 16. What is the ratio of A:T and C:G? 17. Why is DNA replication called semicons ...
UNIT 4 PART1 MODERN GENETICS
... • One gene makes one polypeptide. • The order of bases of three adjacent nucleotides codes for a particular amino acid. These 3 bases are called a codon. – e.g. CAG is the DNA codon for glutamine ...
... • One gene makes one polypeptide. • The order of bases of three adjacent nucleotides codes for a particular amino acid. These 3 bases are called a codon. – e.g. CAG is the DNA codon for glutamine ...
Chapter Five
... Two or more food proteins whose amino acid assortments complement each other in such a way that the essential amino acids limited in or missing from each are supplied by the others. ...
... Two or more food proteins whose amino acid assortments complement each other in such a way that the essential amino acids limited in or missing from each are supplied by the others. ...
Answers for possible questions about the new material HbS·(O2)4 (aq)
... Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). Secondary structure is maintained by hydrogen bonds formed between a hydrogen (donor) attached to the nitrogen in the b ...
... Secondary (2o) structure is a regular repeating structure due to folding of the polypeptide chain. The main types are alpha-helix and beta sheet (either parallel or anti-parallel). Secondary structure is maintained by hydrogen bonds formed between a hydrogen (donor) attached to the nitrogen in the b ...
PS Webquest
... 2. What protein copies the luc gene into messenger RNA? ___________________________________ 3. What is the process of making RNA copies of DNA (genes) called? ______________________________ 4. After the mRNA copy of luc gene moves into the cytoplasm; what organelle is going to read it to make it int ...
... 2. What protein copies the luc gene into messenger RNA? ___________________________________ 3. What is the process of making RNA copies of DNA (genes) called? ______________________________ 4. After the mRNA copy of luc gene moves into the cytoplasm; what organelle is going to read it to make it int ...
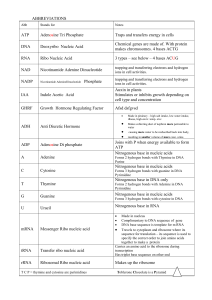
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
... Nitrogenous base in DNA only Forms 2 hydrogen bonds with Adenine in DNA Pyrimidine Forms 3 hydrogen bonds with cytosine in DNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... building of a polypeptide (protein) from mRNA Uses transfer RNA (tRNA) to help Occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome ...
... building of a polypeptide (protein) from mRNA Uses transfer RNA (tRNA) to help Occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome ...
2421 _Ch8.ppt
... codon (usually AUG, which codes methionine) first tRNA, carrying an amino, binds in the ribosome to the mRNA by the anticodon The next codon position if filled by the appropriate charged tRNA ...
... codon (usually AUG, which codes methionine) first tRNA, carrying an amino, binds in the ribosome to the mRNA by the anticodon The next codon position if filled by the appropriate charged tRNA ...
DNA - Valhalla High School
... nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
... nucleotides long. (The entire human genome consists of 3 BILLION nucleotides). Each gene is a series of nucleotides which contains the information to make a protein. 1 gene = 1 protein. ...
Protein Synthesis
... UUU and UUC both code for Phenylalanine If there is a mutation/mistake it might not cause a problem ...
... UUU and UUC both code for Phenylalanine If there is a mutation/mistake it might not cause a problem ...
with L-Amino Acids - Foliar-Pak
... a longer time period which increases the window of foliar uptake. Amino polymer technology maximizes plant nutrition, allowing better use of low dose applications. L-18 Amino Technology is an exclusive L-Amino acid package derived through enzyme hydrolysis of soybean plants, resulting in 100% L-Ami ...
... a longer time period which increases the window of foliar uptake. Amino polymer technology maximizes plant nutrition, allowing better use of low dose applications. L-18 Amino Technology is an exclusive L-Amino acid package derived through enzyme hydrolysis of soybean plants, resulting in 100% L-Ami ...
amino acid
... There are four classes of biological macromolecules: Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids ...
... There are four classes of biological macromolecules: Proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids ...
Study Questions for the Second Exam in Bio 0200
... recombination rate significantly greater than 50% (such as 80 or 90%)? Why are recombination frequencies not additive? Is it possible for a cross of two green parakeets to produce a white parakeet? How would this work? What’s the principal difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What is the c ...
... recombination rate significantly greater than 50% (such as 80 or 90%)? Why are recombination frequencies not additive? Is it possible for a cross of two green parakeets to produce a white parakeet? How would this work? What’s the principal difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What is the c ...
DNA Workshop_Protein_Synthesis
... Translation: Match tRNA anticodon to mRNA codon Drag and drop from well: UAC (methionine; compl. of AUG) CCG (glycine; compl. of GGC) AGG (serine; compl. of UCC) Help Window: Like DNA, mRNA consists of four bases. The bases in mRNA are grouped into sets of three called codons. Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
... Translation: Match tRNA anticodon to mRNA codon Drag and drop from well: UAC (methionine; compl. of AUG) CCG (glycine; compl. of GGC) AGG (serine; compl. of UCC) Help Window: Like DNA, mRNA consists of four bases. The bases in mRNA are grouped into sets of three called codons. Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
Topic 12 (Ch9/7) – Microbial Genetics Genetics Chromosome
... • Copy of a structural gene or genes of DNA – Can encode for multiple proteins on one message ...
... • Copy of a structural gene or genes of DNA – Can encode for multiple proteins on one message ...
Assessment Schedule – 2007 Biology: Describe the role of DNA in
... 2(f) (i) 50% are likely to have sickle cell anaemia. (ii) 0% will be homozygous normal. Correct odds for both (i) and (ii). 2(g) Pleiotropy: a single gene can have multiple / many phenotypic effects. ...
... 2(f) (i) 50% are likely to have sickle cell anaemia. (ii) 0% will be homozygous normal. Correct odds for both (i) and (ii). 2(g) Pleiotropy: a single gene can have multiple / many phenotypic effects. ...
chapter20
... of 1679 pulses were emitted, which can be arranged in only two ways: 23 rows of 73 or 73 rows of 23. Resulting 23x73 grid contained basic information about our human society. ...
... of 1679 pulses were emitted, which can be arranged in only two ways: 23 rows of 73 or 73 rows of 23. Resulting 23x73 grid contained basic information about our human society. ...
DNA vs. RNA - WordPress.com
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) separates the DNA strands RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
... RNA molecules are produced by copying part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA into a complementary sequence in RNA required enzyme = RNA polymerase RNA polymerase binds to DNA (in nucleus) separates the DNA strands RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a ...
introduction
... appropriate nitrogen sources and cofactors. Recently, amino acids are isolated from farm wastes ( Tsuruoka, 1987). Production of Lamino acids by fermentation is now being used in industrial scale and this potentiality of microbes have been exploited commercially in countries like Japan and USA (Dula ...
... appropriate nitrogen sources and cofactors. Recently, amino acids are isolated from farm wastes ( Tsuruoka, 1987). Production of Lamino acids by fermentation is now being used in industrial scale and this potentiality of microbes have been exploited commercially in countries like Japan and USA (Dula ...
The nucleotide sequence of a gene is colinear with the amino acid
... Single base insertion (trp-) and a deletion causes reversion (trp+) ...
... Single base insertion (trp-) and a deletion causes reversion (trp+) ...
Human and fly protein-coding genes contain more stop resistant
... Human and fly protein-coding genes contain more stop resistant codons than random nucleotide sequences Francisco Prosdocimi1, J. Miguel Ortega1 ¹ Lab. Biodados, ICB-UFMG. It is well known that genetic code minimizes the effect of mutations and similar codons usually codify for the same amino acid, a ...
... Human and fly protein-coding genes contain more stop resistant codons than random nucleotide sequences Francisco Prosdocimi1, J. Miguel Ortega1 ¹ Lab. Biodados, ICB-UFMG. It is well known that genetic code minimizes the effect of mutations and similar codons usually codify for the same amino acid, a ...
Unit 4 - University of Colorado Boulder
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
... The central dogma is a cellular “chain of command.” 7. Define the “central dogma” in one sentence 8. List the major steps in the process of transcription in the order in which they happen; describe the roles played by the main molecules or DNA regions that are involved (RNA polymerase, transcription ...
Protein Synthesis Math Relays!
... mathematical value, the teacher can immediately see if there was a mistake. If the student gives an incorrect value, the teacher should encourage the students to problem solve: look back at their steps to identifying where the error lies. If students are still having difficulty working backwards, th ...
... mathematical value, the teacher can immediately see if there was a mistake. If the student gives an incorrect value, the teacher should encourage the students to problem solve: look back at their steps to identifying where the error lies. If students are still having difficulty working backwards, th ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.