The Central Dogma – Protein Synthesis
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
The Central Dogma – Protein Synthesis
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
... • The alphabet of RNA is A, U, G and C • Within a molecule of mRNA, groups of 3 sequential nucleotides form meaningful “words” called codons – complementary to triplets in the template strand of the gene that was transcribed by RNA polymerase • each codon is a code for an amino acid of the protein c ...
snews
... plastics that are better for the environment. Some are made from natural materials, like parts of corn or sugar plants. These are called bioplastics. NatureWorks, a company in Minnesota, USA, uses corn to make plastic that they claim is biodegradable. They buy corn from farmers and break down the ke ...
... plastics that are better for the environment. Some are made from natural materials, like parts of corn or sugar plants. These are called bioplastics. NatureWorks, a company in Minnesota, USA, uses corn to make plastic that they claim is biodegradable. They buy corn from farmers and break down the ke ...
G - haynayan
... methionine and phenylalanine—and breaks the bond between methionine and its tRNA. The tRNA floats away, allowing the ribosome to bind to another tRNA. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, binding new tRNA molecules and amino acids. ...
... methionine and phenylalanine—and breaks the bond between methionine and its tRNA. The tRNA floats away, allowing the ribosome to bind to another tRNA. The ribosome moves along the mRNA, binding new tRNA molecules and amino acids. ...
Biochemistry of Cells - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Their folded conformation creates an area known as the active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
... Their folded conformation creates an area known as the active site. The nature and arrangement of amino acids in the active site make it specific for only one type of substrate. ...
Enzymes - preabenagh
... How are proteins able to do so many things? 20 different kinds amino acids - different R-groups Non-polar ...
... How are proteins able to do so many things? 20 different kinds amino acids - different R-groups Non-polar ...
Dried blood spot analysis on the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser
... A number of tests are then carried out on these blood spots for the purposes of newborn screening. Typically the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser is used for the amino acid analysis of plasma and urine. However it can also be used for analysis of other types of samples such as dried blood spots follo ...
... A number of tests are then carried out on these blood spots for the purposes of newborn screening. Typically the Biochrom 30 Amino Acid Analyser is used for the amino acid analysis of plasma and urine. However it can also be used for analysis of other types of samples such as dried blood spots follo ...
RNA nucleotides
... 4. However, tRNA can’t start matching its anticodon and dropping off amino acids until it comes to the start codon (AUG). Now once it sees the start codon, it’s on!!!! 5. tRNA will keep matching it’s anticodon with mRNA’s codon and leaving behind amino acids until it comes to one of the stop codons. ...
... 4. However, tRNA can’t start matching its anticodon and dropping off amino acids until it comes to the start codon (AUG). Now once it sees the start codon, it’s on!!!! 5. tRNA will keep matching it’s anticodon with mRNA’s codon and leaving behind amino acids until it comes to one of the stop codons. ...
Lesson Overview Ribosomes and Protein Synthesis
... Start and Stop Codons The genetic code has punctuation marks. The methionine codon AUG serves as the initiation, or “start,” codon for protein synthesis. Following the start codon, mRNA is read, three bases at a time, until it reaches one of three different “stop” codons, which end translation. ...
... Start and Stop Codons The genetic code has punctuation marks. The methionine codon AUG serves as the initiation, or “start,” codon for protein synthesis. Following the start codon, mRNA is read, three bases at a time, until it reaches one of three different “stop” codons, which end translation. ...
Activity: Can You Crack the Code
... Chromosomes are composed mostly of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of four different nitrogen bases – adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These bases form the rungs of the DNA “ladder.” A single gene on a chromosome may contain anywhere from several hundred to a million or more o ...
... Chromosomes are composed mostly of DNA. A DNA molecule is made up of four different nitrogen bases – adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). These bases form the rungs of the DNA “ladder.” A single gene on a chromosome may contain anywhere from several hundred to a million or more o ...
Chapter 17: Gene Expression Gene Expression DNA houses all
... Complimentary regions allow it to H-bond & fold over on itself o Anti-codon – one end has 3 nucleotide segment to match mRNA codon (61) o 3’ end extends off other end & will bind an amino acid o 45-50 human tRNA (vs. 61 AA codons) due to ‘wobble’ o Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Enzyme that catalyzes ...
... Complimentary regions allow it to H-bond & fold over on itself o Anti-codon – one end has 3 nucleotide segment to match mRNA codon (61) o 3’ end extends off other end & will bind an amino acid o 45-50 human tRNA (vs. 61 AA codons) due to ‘wobble’ o Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Enzyme that catalyzes ...
Chap 3
... 9. DNA polymerase I has both 3’-5’and 5’-3’exonuclease activity (remove or excise nucleotides just added). This “proofreading” function ensures fidelity of replication. 10. Replication may be divided into three stages: (1) Initiation (2) Elongation: the complex of proteins associated with this stage ...
... 9. DNA polymerase I has both 3’-5’and 5’-3’exonuclease activity (remove or excise nucleotides just added). This “proofreading” function ensures fidelity of replication. 10. Replication may be divided into three stages: (1) Initiation (2) Elongation: the complex of proteins associated with this stage ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Some codons do not recognize any kind of amino acids. They are called nonsense codons. They act as "starting points" or "full stops" in the process of polypeptide synthesis. ...
... Some codons do not recognize any kind of amino acids. They are called nonsense codons. They act as "starting points" or "full stops" in the process of polypeptide synthesis. ...
File chemical comp. in cells notes 8a
... You are surrounded by particles that you can’t see! Air is made up of millions of tiny particle. They bump into your skin, hide in the folds of your clothes, and whoosh into your nose every time you take a breath! You and the world around you, including the cells in your body, are composed of tiny p ...
... You are surrounded by particles that you can’t see! Air is made up of millions of tiny particle. They bump into your skin, hide in the folds of your clothes, and whoosh into your nose every time you take a breath! You and the world around you, including the cells in your body, are composed of tiny p ...
Amino Acids
... Ionization of Amino Acids • At acidic pH, the carboxyl group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form. • At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions ...
... Ionization of Amino Acids • At acidic pH, the carboxyl group is protonated and the amino acid is in the cationic form. • At neutral pH, the carboxyl group is deprotonated but the amino group is protonated. The net charge is zero; such ions ...
Proteins 1 - Dr Rob's A
... – The number, type and sequence of amino acids – Specific to each protein – Coded for by DNA ...
... – The number, type and sequence of amino acids – Specific to each protein – Coded for by DNA ...
Answers questions chapter 15
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? Suggested Answer: tRNAs all share a secondary structure that resembles a cloverleaf, including a stem, three ...
... c. Describe the structural and sequence elements that are common to all tRNA molecules, addressing the function of each of the elements. What forces stabilize the tRNAs' structural features? Suggested Answer: tRNAs all share a secondary structure that resembles a cloverleaf, including a stem, three ...
Proteins
... • Steroids are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings (Fig 5:14, pg 68). They include cholesterol, which help make the plasma membrane of the cell. Recall that there are two forms of cholesterol. HDL and LDL. Which ones are better for you? ...
... • Steroids are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four rings (Fig 5:14, pg 68). They include cholesterol, which help make the plasma membrane of the cell. Recall that there are two forms of cholesterol. HDL and LDL. Which ones are better for you? ...
Proteins
... Proteins • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
... Proteins • . essential life substance of all living matter . • act as structural unit to build our bodies . • specific structural chemical units amino acids • amino [alkaline substance carbon, hydrogen ,o2& NH2. ...
Genetics 3 - MaxSkyFan
... translated. The mRNA is transcribed from DNA and then travels outside the nucleus to the ribosome. rRNA: ribosomal RNA is the main machinery that accomplishes translation by reading the mRNA and getting the appropriate amino acid (the building block of proteins) from tRNA. tRNA: transfer RNA is set ...
... translated. The mRNA is transcribed from DNA and then travels outside the nucleus to the ribosome. rRNA: ribosomal RNA is the main machinery that accomplishes translation by reading the mRNA and getting the appropriate amino acid (the building block of proteins) from tRNA. tRNA: transfer RNA is set ...
Transcription &
... Complementary DNA Strand: ________________________________________________ mRNA Strand: ____________________________________________________________ tRNA Strand: _____________________________________________________________ ...
... Complementary DNA Strand: ________________________________________________ mRNA Strand: ____________________________________________________________ tRNA Strand: _____________________________________________________________ ...
NAME CH. 8 HONORS STUDY GUIDE SCIENTISTS: Hershey
... 13. What is the job of rRNA? 14. What is the job of tRNA? 15. What RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis? 16. Which RNA molecule functions as the blueprint of the genetic code? 17. Where is mRNA edited? Explain what is removed & what is put back together. 18. What nucleotide bases are foun ...
... 13. What is the job of rRNA? 14. What is the job of tRNA? 15. What RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis? 16. Which RNA molecule functions as the blueprint of the genetic code? 17. Where is mRNA edited? Explain what is removed & what is put back together. 18. What nucleotide bases are foun ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
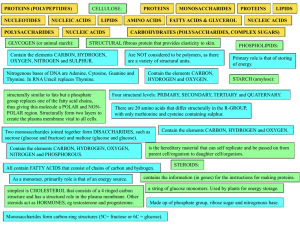
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
Expanded genetic code
An expanded genetic code is an artificially modified genetic code in which one or more specific codons have been re-allocated to encode an amino acid that is not among the 22 encoded proteinogenic amino acids.The key prerequisites to expand the genetic code are: the non-standard amino acid to encode, an unused codon to adopt, a tRNA that recognises this codon, and a tRNA synthase that recognises only that tRNA and only the non-standard amino acid.Expanding the genetic code is an area of research of synthetic biology, an applied biological discipline whose goal is to engineer living systems for useful purposes. The genetic code expansion enriches the repertoire of useful tools available to science.