Mod three revision
... • mercury has been known since least the time of the Sumerians (3rd million bc) • the greeks gave mercury two • names,hermes as an evening star,Apollo for its morning star ...
... • mercury has been known since least the time of the Sumerians (3rd million bc) • the greeks gave mercury two • names,hermes as an evening star,Apollo for its morning star ...
Kepler`s Laws wkst
... 6. Use data from Table 1 in your textbook to calculate the length of Neptune’s “year” (the period of its orbit around the Sun). Express your answer in Earth years. ...
... 6. Use data from Table 1 in your textbook to calculate the length of Neptune’s “year” (the period of its orbit around the Sun). Express your answer in Earth years. ...
Astronomy Assignment #5: Newton`s Universal Law of Gravitation
... If the Earth was 3 A.U. from the Sun (instead of 1 A.U.), would the gravity force between the Earth and the Sun be less or more than it is now? By how many times? If Mercury was 0.2 A.U. from the Sun (instead of 0.4 A.U.), would the gravity force between Mercury and the Sun be less or more than it i ...
... If the Earth was 3 A.U. from the Sun (instead of 1 A.U.), would the gravity force between the Earth and the Sun be less or more than it is now? By how many times? If Mercury was 0.2 A.U. from the Sun (instead of 0.4 A.U.), would the gravity force between Mercury and the Sun be less or more than it i ...
Out of this World
... travelling around another. - It takes the Earth one year to travel, or revolve, in a circle around the Sun counter-clockwise. - This motion allows us to see different constellations during different seasons. ...
... travelling around another. - It takes the Earth one year to travel, or revolve, in a circle around the Sun counter-clockwise. - This motion allows us to see different constellations during different seasons. ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary212
... 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 year 5. apparent magnitude- measure of how bright the object appears from Earth 6. luminosity7. Star- l ...
... 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 year 5. apparent magnitude- measure of how bright the object appears from Earth 6. luminosity7. Star- l ...
Terrestrial Planets
... •Space Probes: Magellan which mapped out the planet. •Known as Earths Sister b/c of simiar composition, size, and density. •Atmosphere consists of CO2, Nitrogen, and Sulfuric Acid which causes a great greenhouse effect; 737K during day, 288K at night. ...
... •Space Probes: Magellan which mapped out the planet. •Known as Earths Sister b/c of simiar composition, size, and density. •Atmosphere consists of CO2, Nitrogen, and Sulfuric Acid which causes a great greenhouse effect; 737K during day, 288K at night. ...
Unit 1: Earth History 1. Distinguish among eons
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
... 4. Explain the factors that determine if a planet will have a strong magnetic field/atmosphere? 5. Explain Kepler’s Laws. Calculate a planets period of rotation (using GRASS). 6. Compare and contr ...
Early Observers (The Beginnings of Astronomy)
... What is a year? What they saw The time it takes for a group of stars (constellation) to return to the same part of the sky at a certain time of day What we know: Time required for the Earth to revolve around the sun. ...
... What is a year? What they saw The time it takes for a group of stars (constellation) to return to the same part of the sky at a certain time of day What we know: Time required for the Earth to revolve around the sun. ...
File - Mrs. MacGowan 6-2
... Things in space that emit (give off) light – sun and stars Things in space that reflect light – moons, planets, comets, asteroids The planets in our solar system are broken up into rock planets and gas planets (you will need to know the correct order as well!) My Very Educated Mother Just Served Us ...
... Things in space that emit (give off) light – sun and stars Things in space that reflect light – moons, planets, comets, asteroids The planets in our solar system are broken up into rock planets and gas planets (you will need to know the correct order as well!) My Very Educated Mother Just Served Us ...
Practice Questions: This is a series of practice tests that you should
... 1. The Sun’s interior temperature is cooler than its outside temperature 2. It is estimated that the Sun is at its half life and has 5 billion years left 3. As the Sun converts hydrogen gas into helium gas, it releases energy 4. Solar flares occur in the interior of the Sun 58. Which statements are ...
... 1. The Sun’s interior temperature is cooler than its outside temperature 2. It is estimated that the Sun is at its half life and has 5 billion years left 3. As the Sun converts hydrogen gas into helium gas, it releases energy 4. Solar flares occur in the interior of the Sun 58. Which statements are ...
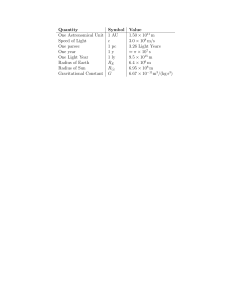
Quantity Symbol Value One Astronomical Unit 1 AU 1.50 × 10
... Part I. 1. Describe qualitatively the funny way that the planets move in the sky relative to the stars. Give a qualitative explanation as to why they move this way. 2. Draw a set of pictures approximately to scale showing the sun, the earth, the moon, α-centauri, and the milky way and the spacing b ...
... Part I. 1. Describe qualitatively the funny way that the planets move in the sky relative to the stars. Give a qualitative explanation as to why they move this way. 2. Draw a set of pictures approximately to scale showing the sun, the earth, the moon, α-centauri, and the milky way and the spacing b ...
Note: Bring the solved worksheet on Sunday, 21 st February 2016
... 5. Which best describes Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune? a. outer planets ...
... 5. Which best describes Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune? a. outer planets ...
Chapter 19 I. The Sun, Earth and Moon A. Sun is our closest star B
... II. During this process small celestial bodies also formed A. Comets- long tails and icy centers 1. orbits around Sun usually very long B. Asteroids- made from different elements C. Meteorites- sometimes strike the Earth Chapter 20 I. The Life and Death of Stars A. What are stars? 1. Stars are huge ...
... II. During this process small celestial bodies also formed A. Comets- long tails and icy centers 1. orbits around Sun usually very long B. Asteroids- made from different elements C. Meteorites- sometimes strike the Earth Chapter 20 I. The Life and Death of Stars A. What are stars? 1. Stars are huge ...
Chapter 1 - Humble ISD
... • Earth is between __________________________ • Partial when only part of Moon is in shadow • Total when it all is in shadow • Solar eclipse: Moon is between ________________________ • Partial when only part of Sun is blocked • Total when it all is blocked • Annular when Moon is too far from Earth f ...
... • Earth is between __________________________ • Partial when only part of Moon is in shadow • Total when it all is in shadow • Solar eclipse: Moon is between ________________________ • Partial when only part of Sun is blocked • Total when it all is blocked • Annular when Moon is too far from Earth f ...
STUDY GUIDE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... Why was Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift originally rejected by geologists? a. Wegener did not have any data to support his hypothesis. b. The continents of South America and Africa do not fit well together. c. Wegener could not explain how the continents could move through the ocean floor. ...
... Why was Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift originally rejected by geologists? a. Wegener did not have any data to support his hypothesis. b. The continents of South America and Africa do not fit well together. c. Wegener could not explain how the continents could move through the ocean floor. ...
Gravity - Pulling it all Together
... bench 50 cm apart. Calculate the magnitude of the gravitational force each exerts on the other. (1.0x10-6 N) ...
... bench 50 cm apart. Calculate the magnitude of the gravitational force each exerts on the other. (1.0x10-6 N) ...
Midterm Review Sheet
... Earth’s structure – know the different layers, with emphasis on lithosphere Differentiation Sources of central heat in planets Convection (including conditions required for convection) Earth’s magnetic field Magnet ...
... Earth’s structure – know the different layers, with emphasis on lithosphere Differentiation Sources of central heat in planets Convection (including conditions required for convection) Earth’s magnetic field Magnet ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.