Bugs 6 Photocop section 3-4.qxd
... © Elisenda Papiol and Maria Toth 2005. Bugs 6. Published by Macmillan Publishers Limited. ...
... © Elisenda Papiol and Maria Toth 2005. Bugs 6. Published by Macmillan Publishers Limited. ...
Astronomy Humble ISD Curriculum Year-At-A
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
... • Identify the characteristics of main sequence stars. • Characterize star formation in stellar nurseries from giant molecular clouds, to protostars, to the development of main sequence stars. • Evaluate the relationship between mass and fusion on the dying process and properties of stars. • Differe ...
Life2
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
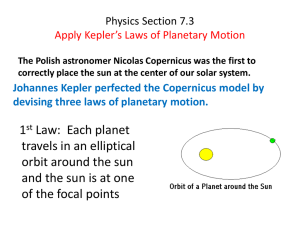
Physics Section 7.3 Apply Kepler*s Laws of Planetary
... year) is proportional to the cube of the average distance between the planet and the sun. T2 = ...
... year) is proportional to the cube of the average distance between the planet and the sun. T2 = ...
Name: ________________________ Date: Chapter 13: Earth
... solar system p. 492 constellation p. 493 moon p. 482 universe p. 498 crater p. 482 galaxy p. 498 1. The path that Earth takes as it moves around the sun is its _____________________________. 2. The sun is the center of our _________________________. 3. Everything that exists, including planets, star ...
... solar system p. 492 constellation p. 493 moon p. 482 universe p. 498 crater p. 482 galaxy p. 498 1. The path that Earth takes as it moves around the sun is its _____________________________. 2. The sun is the center of our _________________________. 3. Everything that exists, including planets, star ...
Use with the big book “A Tour of the Planets” Photocopy questions
... when they hear the answer to their question. Continue and discuss what the students observed. Students will notice that one particular group will place many of their color Post It Note in the book. (The Think and Search ...
... when they hear the answer to their question. Continue and discuss what the students observed. Students will notice that one particular group will place many of their color Post It Note in the book. (The Think and Search ...
The Stars
... billions of stars. To the naked eye, even the closest of these galaxies is no more than a dim, fuzzy spot. The sun is many thousands of times closer to the earth than any other star. Light from the sun takes a few minutes to reach the earth, but light from the next nearest star takes a few years t ...
... billions of stars. To the naked eye, even the closest of these galaxies is no more than a dim, fuzzy spot. The sun is many thousands of times closer to the earth than any other star. Light from the sun takes a few minutes to reach the earth, but light from the next nearest star takes a few years t ...
Patterns in the night sky - Laureate International College
... the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have moons that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the solar system. ...
... the Sun which means that they move in an orbit around the sun. Most planets also have moons that orbit around them. The sun, planets, moon, and other objects that orbit the sun make up the solar system. ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... Planet (IAU definitions of Planet, Dwarf Planet and Small Solar System Bodies) (1)A "planet” is a celestial body that: (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) ...
... Planet (IAU definitions of Planet, Dwarf Planet and Small Solar System Bodies) (1)A "planet” is a celestial body that: (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) ...
Our Solar System
... 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
... 7 known moons Triton largest moon Great Dark Spot thought to be a hole, similar to the hole in the ozone layer on Earth ...
Planets With Detectable Life - International Space Science Institute
... So now we have convinced ourselves that the stuff of life is plentiful in the galaxy and we have defined the constraints that a life-bearing planet must satisfy. In our solar system, we have found only one planet that has life on it, Earth, and another that is at least in the habitable zone of our s ...
... So now we have convinced ourselves that the stuff of life is plentiful in the galaxy and we have defined the constraints that a life-bearing planet must satisfy. In our solar system, we have found only one planet that has life on it, Earth, and another that is at least in the habitable zone of our s ...
Earth Science – Quiz 2
... 38. Compared to Earth's atmosphere, the atmosphere of Mars has surface pressures that are ________. A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane ...
... 38. Compared to Earth's atmosphere, the atmosphere of Mars has surface pressures that are ________. A) 3 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide B) 0.1 times those on Earth; major gases are water vapor and carbon dioxide C) one-half those on Earth; main gases are methane ...
Relative sizes of astronomical objects
... This image represents the relative sizes of our Sun and Sirius (Alpha Canis Majoris), Pollux (Beta Geminorum) and Arcturus (Alpha Bootes). ‘Giant’ Jupiter is just 1 pixel in this perspective. Earth is invisible on this scale. ...
... This image represents the relative sizes of our Sun and Sirius (Alpha Canis Majoris), Pollux (Beta Geminorum) and Arcturus (Alpha Bootes). ‘Giant’ Jupiter is just 1 pixel in this perspective. Earth is invisible on this scale. ...
Planets and Other Space Rocks Notes
... • Its year is just under 165 Earth years, and its day is just over 19 hours. • The temperature at the top is −213℃. • It has a tilt, so it has seasons like Earth, but they are mild. ...
... • Its year is just under 165 Earth years, and its day is just over 19 hours. • The temperature at the top is −213℃. • It has a tilt, so it has seasons like Earth, but they are mild. ...
Outer Space Study Guide
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
... This is another exciting theme to learn about. In the next few years ordinary people can travel to space thanks to Virgin Galactic’s idea. Anyone can view space from their computer thanks to the ISS. LINK. To top things off you can even explore Mars from home. LINK Scientist have estimated Earth to ...
Terms - HULK SCIENCE
... Planets inside the asteroid belt (terrestrial) Planets outside the asteroid belt (gas) A force determined by mass that holds objects in orbit Planets made of land (inner planets) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars Planets made of gas (outer planets) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ...
... Planets inside the asteroid belt (terrestrial) Planets outside the asteroid belt (gas) A force determined by mass that holds objects in orbit Planets made of land (inner planets) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars Planets made of gas (outer planets) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ...
Students` solar system project - johnson
... Our solar system is made up of the sun and eight planets a planet is a large ball made of rock or gas. ...
... Our solar system is made up of the sun and eight planets a planet is a large ball made of rock or gas. ...
Conversations with the Earth
... • These Sun-like, habitable stars have just the right distance, constancy, and temperature to qualify in a forthcoming enlarged radio search. ...
... • These Sun-like, habitable stars have just the right distance, constancy, and temperature to qualify in a forthcoming enlarged radio search. ...
Chapter 5 and 6 Study Guide
... 6. When a ___hurricane___________________ moves from the ocean onto land, its strong winds and heavy rains can cause severe damage. 7. A hot, glowing ball of gases is a ___star____________. 8. To _revolve___________ means to move around another object. 9. The moon has eight main _phases_____________ ...
... 6. When a ___hurricane___________________ moves from the ocean onto land, its strong winds and heavy rains can cause severe damage. 7. A hot, glowing ball of gases is a ___star____________. 8. To _revolve___________ means to move around another object. 9. The moon has eight main _phases_____________ ...
Life in the Universe
... 1. Old enough to allow time for evolution (rules out high-mass stars ~1%) 2. Need to have stable orbits (might rule out binary/multiple star systems ~50%) 3. Size of habitable zone: region where a planet of the right size could support liquid water ...
... 1. Old enough to allow time for evolution (rules out high-mass stars ~1%) 2. Need to have stable orbits (might rule out binary/multiple star systems ~50%) 3. Size of habitable zone: region where a planet of the right size could support liquid water ...
Rare Earth hypothesis

In planetary astronomy and astrobiology, the Rare Earth Hypothesis argues that the origin of life and the evolution of biological complexity such as sexually reproducing, multicellular organisms on Earth (and, subsequently, human intelligence) required an improbable combination of astrophysical and geological events and circumstances. The hypothesis argues that complex extraterrestrial life is a very improbable phenomenon and likely to be extremely rare. The term ""Rare Earth"" originates from Rare Earth: Why Complex Life Is Uncommon in the Universe (2000), a book by Peter Ward, a geologist and paleontologist, and Donald E. Brownlee, an astronomer and astrobiologist, both faculty members at the University of Washington.An alternative view point was argued by Carl Sagan and Frank Drake, among others. It holds that Earth is a typical rocky planet in a typical planetary system, located in a non-exceptional region of a common barred-spiral galaxy. Given the principle of mediocrity (also called the Copernican principle), it is probable that the universe teems with complex life. Ward and Brownlee argue to the contrary: that planets, planetary systems, and galactic regions that are as friendly to complex life as are the Earth, the Solar System, and our region of the Milky Way are very rare.