ATP
... The energy stored in ATP is released when ATP is hydrolysed by enzymes into ADP Further hydrolysis of ADP into AMP releases a similar quantity of energy BUT hydrolysis of AMP releases much less energy than the other two The energy is stored in the molecule as a whole, although the breaking of the bo ...
... The energy stored in ATP is released when ATP is hydrolysed by enzymes into ADP Further hydrolysis of ADP into AMP releases a similar quantity of energy BUT hydrolysis of AMP releases much less energy than the other two The energy is stored in the molecule as a whole, although the breaking of the bo ...
Nucleotide Metabolism Nucleotide sources - Rose
... The first reaction of the purine synthesis pathway, catalyzed by ribose-5phosphate pyrophosphokinase, produces phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP). PRPP is not committed to purine biosynthesis; it is also used for other processes (such as pyrimidine biosynthesis, histidine biosynthesis, and nucleotid ...
... The first reaction of the purine synthesis pathway, catalyzed by ribose-5phosphate pyrophosphokinase, produces phosphoribosylpyrophosphate (PRPP). PRPP is not committed to purine biosynthesis; it is also used for other processes (such as pyrimidine biosynthesis, histidine biosynthesis, and nucleotid ...
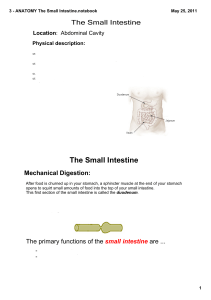
3 - ANATOMY The Small Intestine.notebook
... receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the Duodenum: the first section of the small intestines which is a short section that pancreatic and common bile ducts. receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the pancreatic and common The food is a highly acidic mush and needs to ...
... receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the Duodenum: the first section of the small intestines which is a short section that pancreatic and common bile ducts. receives secretions from the pancreas and liver via the pancreatic and common The food is a highly acidic mush and needs to ...
... The right of the author to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electron ...
Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration
... 6.6 Overview: Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in three main stages During the transport of electrons, a concentration gradient of H+ ions is formed across the inner membrane into the intermembrane space – The potential energy of this concentration gradient is used to make ATP by a process cal ...
... 6.6 Overview: Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in three main stages During the transport of electrons, a concentration gradient of H+ ions is formed across the inner membrane into the intermembrane space – The potential energy of this concentration gradient is used to make ATP by a process cal ...
R - MyCourses
... secondary structure describes 3D-objects formed through H-bonding interactions ...
... secondary structure describes 3D-objects formed through H-bonding interactions ...
Mitochondrial Cytopathies: A Primer
... on Coumadin. He was readmitted for a stroke several months later, and was again found to be in A-fib. His neurologist and cardiologist referred him to CCF Cardiology for placement of a pacemaker. In October 1996, after a 24 hour journey, he visited our cardiology department, and was told that a pace ...
... on Coumadin. He was readmitted for a stroke several months later, and was again found to be in A-fib. His neurologist and cardiologist referred him to CCF Cardiology for placement of a pacemaker. In October 1996, after a 24 hour journey, he visited our cardiology department, and was told that a pace ...
2 ATP - HCC Learning Web
... • The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic • Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration – Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 ...
... • The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic • Fermentation is a partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration – Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 ...
Title: Hormones of the Pancreas
... 1. Structure of insulin: MW 6.000, consisting of 51 AA as two amino acid chains linked by disulfide bridges (α chain – 21 AA, β chain – 30 AA ) 2. Metabolism of insulin : half-life 5 minutes, degraded in liver and kidneys, hepatic portal vein goes to liver where 40-50% is removed in one pass, kidney ...
... 1. Structure of insulin: MW 6.000, consisting of 51 AA as two amino acid chains linked by disulfide bridges (α chain – 21 AA, β chain – 30 AA ) 2. Metabolism of insulin : half-life 5 minutes, degraded in liver and kidneys, hepatic portal vein goes to liver where 40-50% is removed in one pass, kidney ...
Title: Hormones of the Pancreas
... 1. Structure of insulin: MW 6.000, consisting of 51 AA as two amino acid chains linked by disulfide bridges (α chain – 21 AA, β chain – 30 AA ) 2. Metabolism of insulin : half-life 5 minutes, degraded in liver and kidneys, hepatic portal vein goes to liver where 40-50% is removed in one pass, kidney ...
... 1. Structure of insulin: MW 6.000, consisting of 51 AA as two amino acid chains linked by disulfide bridges (α chain – 21 AA, β chain – 30 AA ) 2. Metabolism of insulin : half-life 5 minutes, degraded in liver and kidneys, hepatic portal vein goes to liver where 40-50% is removed in one pass, kidney ...
The Concentration of Phosphatidylethanolamine in
... Next, we performed tolerance tests for glucose, insulin, pyruvate, and glycerol (Fig. 1). Pemt+/+ and Pemt2/2 mice that were fed a chow diet were similarly sensitive to insulin (Fig. 1A). There was a slightly improved glucose tolerance in Pemt2/2 mice compared with Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 1B). This impro ...
... Next, we performed tolerance tests for glucose, insulin, pyruvate, and glycerol (Fig. 1). Pemt+/+ and Pemt2/2 mice that were fed a chow diet were similarly sensitive to insulin (Fig. 1A). There was a slightly improved glucose tolerance in Pemt2/2 mice compared with Pemt+/+ mice (Fig. 1B). This impro ...
Scholarly Interest Report
... My current interest is the theoretical basis for ammonia detoxication in vertebrate liver. This ammonia may be of either hepatic or extrahe- patic origin. Liver tissue is the site of gluconeogenesis in higher vertebrates and, during this process, amino acids are deaminated, forming ammonia. Extrahep ...
... My current interest is the theoretical basis for ammonia detoxication in vertebrate liver. This ammonia may be of either hepatic or extrahe- patic origin. Liver tissue is the site of gluconeogenesis in higher vertebrates and, during this process, amino acids are deaminated, forming ammonia. Extrahep ...
NEURAL TUBE DEFECT ROLE OF FOLIC ACID
... therefore cells are not able to methylate important compounds like proteins, lipids and myelin. • Thus, folate deficiency or genetically rooted error in folate metabolism can cause developmental defects through disturbances of DNA biosynthesis and/or the methylation cycle ...
... therefore cells are not able to methylate important compounds like proteins, lipids and myelin. • Thus, folate deficiency or genetically rooted error in folate metabolism can cause developmental defects through disturbances of DNA biosynthesis and/or the methylation cycle ...
Hydrocarbons and Fuels - Deans Community High School
... Each OH group in the glycerol can combine chemically with one carboxylic fatty acid molecule. The resulting molecules are fats and oils. Question: What is the name of this reaction? They are described as triglycerides. (tri esters) The hydrocarbon chain in each can be from 4 to 24 C’s long. The C’s ...
... Each OH group in the glycerol can combine chemically with one carboxylic fatty acid molecule. The resulting molecules are fats and oils. Question: What is the name of this reaction? They are described as triglycerides. (tri esters) The hydrocarbon chain in each can be from 4 to 24 C’s long. The C’s ...
Separation of Racemic Mixtures of Amino Acids Using Chiral Eluents
... Usually, increasing the concentration of organic modifier in the eluent in the reversed phase chromatography leads to reduction of the retention times of the solutes because of an increasing solvent strength. The influence of methanol as modifier was investigated with the aliphatic amino acids Val, ...
... Usually, increasing the concentration of organic modifier in the eluent in the reversed phase chromatography leads to reduction of the retention times of the solutes because of an increasing solvent strength. The influence of methanol as modifier was investigated with the aliphatic amino acids Val, ...
Analysis of TETRAKETIDE a-PYRONE
... poorly understood. Recently, characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana genes and corresponding enzymes involved in exine formation has demonstrated the role of fatty acid derivatives as precursors of sporopollenin building units. Fatty acyl-CoA esters synthesized by ACYL-COA SYNTHETASE5 (ACOS5) are c ...
... poorly understood. Recently, characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana genes and corresponding enzymes involved in exine formation has demonstrated the role of fatty acid derivatives as precursors of sporopollenin building units. Fatty acyl-CoA esters synthesized by ACYL-COA SYNTHETASE5 (ACOS5) are c ...
WHERE DOES THE ENERGY TO GALLOP COME
... polysaccharides or chains of simple sugars e.g. starch and cellulose); fats (fats, oils, lipids); proteins. By far the most common sources of energy used by the body, especially during exercise, are carbohydrates and fats (protein is only usually used as an energy source in extreme circumstances (e. ...
... polysaccharides or chains of simple sugars e.g. starch and cellulose); fats (fats, oils, lipids); proteins. By far the most common sources of energy used by the body, especially during exercise, are carbohydrates and fats (protein is only usually used as an energy source in extreme circumstances (e. ...
Revision Questions What is the definition of energy and what are the
... Fat – Plasma FFA (from adipose tissue lipolysis) & intramuscular triglycerides Protein – Only small contribution to total energy production (2%) – can increase up to 5 – 15% during prolonged exercise Blood lactate – gluconeogenesis via Cori cycle. ...
... Fat – Plasma FFA (from adipose tissue lipolysis) & intramuscular triglycerides Protein – Only small contribution to total energy production (2%) – can increase up to 5 – 15% during prolonged exercise Blood lactate – gluconeogenesis via Cori cycle. ...
6. Respiration - WordPress.com
... Reduced NAD/FAD provide hydrogen atoms and, when oxidised, protons and electrons. These electrons pass along the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial. This provides the energy for the active transport of protons, pumping from the matrix into the intermembrane space before they flow th ...
... Reduced NAD/FAD provide hydrogen atoms and, when oxidised, protons and electrons. These electrons pass along the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial. This provides the energy for the active transport of protons, pumping from the matrix into the intermembrane space before they flow th ...
Sialic Acid Linkage Analysis Kit
... Unit Definition One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme required to catalyze the release of 1 µmole of pNP from pNP-α-Nacetylneuraminic acid per minute at pH 5.5 and 37°C. Storage The enzymes should be stored at 4°C ...
... Unit Definition One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme required to catalyze the release of 1 µmole of pNP from pNP-α-Nacetylneuraminic acid per minute at pH 5.5 and 37°C. Storage The enzymes should be stored at 4°C ...
Purine and pyrimidi..
... 3- CTP is required for synthesis of phospholipids that enter in the structure of cell membrane 4- enter in the synthesis of some coenzymes such as NAD, FAD, ...
... 3- CTP is required for synthesis of phospholipids that enter in the structure of cell membrane 4- enter in the synthesis of some coenzymes such as NAD, FAD, ...
biomolecules
... Lipids are diverse in structure and serve a variety of functions – They are used for energy storage – They form waterproof coverings on plant and animal bodies – They serve as the primary component of cellular membranes – Still others are hormones ...
... Lipids are diverse in structure and serve a variety of functions – They are used for energy storage – They form waterproof coverings on plant and animal bodies – They serve as the primary component of cellular membranes – Still others are hormones ...
respiration_how cell..
... converted to acetylCoA. Coenzyme A (CoA) is a large molecule (and a vitamin) that acts as a coenzyme. The conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA is an coupled oxidation-reduction reaction in which high energy electrons are removed from pyruvate and end up in NADH. The three carbon pyruvate is split int ...
... converted to acetylCoA. Coenzyme A (CoA) is a large molecule (and a vitamin) that acts as a coenzyme. The conversion of pyruvate to acetylCoA is an coupled oxidation-reduction reaction in which high energy electrons are removed from pyruvate and end up in NADH. The three carbon pyruvate is split int ...