Cellular Respiration (Making ATP from food)
... 1. Open and close your hand as many times as possible for 30 seconds. Have your partner time and record the results…QUICKLY! After only a 5 second break repeat this step for a total of 5 trials. 2. After you have completed the 5 trials. Switch jobs with your partner, and record your partner’s 5 tria ...
... 1. Open and close your hand as many times as possible for 30 seconds. Have your partner time and record the results…QUICKLY! After only a 5 second break repeat this step for a total of 5 trials. 2. After you have completed the 5 trials. Switch jobs with your partner, and record your partner’s 5 tria ...
Cellular respiration
... glucose to produce fructose bisphosphate – Fructose bisphosphate is broken down into two G3P molecules – During the energy harvesting stage, the two G3P molecules are converted into two pyruvate molecules, resulting in four ATP and two NADH molecules ...
... glucose to produce fructose bisphosphate – Fructose bisphosphate is broken down into two G3P molecules – During the energy harvesting stage, the two G3P molecules are converted into two pyruvate molecules, resulting in four ATP and two NADH molecules ...
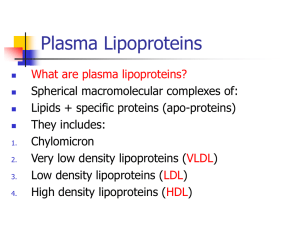
Plasma Lipoproteins
... The chylomicron remnant-, IDL-, and LDLderived cholesterol affects cellular cholesterol content in several ways. First, HMG CoA reductase is inhibited by high cholesterol, as a result of which, de novo cholesterol synthesis decreases. Second, synthesis of new LDL receptor protein is reduced by decre ...
... The chylomicron remnant-, IDL-, and LDLderived cholesterol affects cellular cholesterol content in several ways. First, HMG CoA reductase is inhibited by high cholesterol, as a result of which, de novo cholesterol synthesis decreases. Second, synthesis of new LDL receptor protein is reduced by decre ...
Cellular Respiration
... Total ATP Yield 02 ATP - glycolysis (substrate-level phosphorylation) 04 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - glycolysis 06 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - grooming phase 02 ATP - Krebs cycle (substrate-level phosphorylation) 18 ATP - converted from 6 NADH - Krebs cycle 04 ATP - converted from 2 FADH2 - Kreb ...
... Total ATP Yield 02 ATP - glycolysis (substrate-level phosphorylation) 04 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - glycolysis 06 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - grooming phase 02 ATP - Krebs cycle (substrate-level phosphorylation) 18 ATP - converted from 6 NADH - Krebs cycle 04 ATP - converted from 2 FADH2 - Kreb ...
Cellular Respiration
... Total ATP Yield 02 ATP - glycolysis (substrate-level phosphorylation) 04 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - glycolysis 06 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - grooming phase 02 ATP - Krebs cycle (substrate-level phosphorylation) 18 ATP - converted from 6 NADH - Krebs cycle 04 ATP - converted from 2 FADH2 - Kreb ...
... Total ATP Yield 02 ATP - glycolysis (substrate-level phosphorylation) 04 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - glycolysis 06 ATP - converted from 2 NADH - grooming phase 02 ATP - Krebs cycle (substrate-level phosphorylation) 18 ATP - converted from 6 NADH - Krebs cycle 04 ATP - converted from 2 FADH2 - Kreb ...
PT2009-1 Overcoming Peptide Problems by Design.indd
... unique with regard to its chemical and physical properties. While some peptides are difcult to synthesize, many peptides are relatively straightforward to synthesize but may still be difcult to purify after synthesis. A common problem with many peptides is insolubility in aqueous solution. For pur ...
... unique with regard to its chemical and physical properties. While some peptides are difcult to synthesize, many peptides are relatively straightforward to synthesize but may still be difcult to purify after synthesis. A common problem with many peptides is insolubility in aqueous solution. For pur ...
Chapter 20. Proteins
... During and after synthesis the primary sequence will associate in a fashion that leads to the most stable, "comfortable" structure for the protein. How a protein folds is largely dictated by the primary sequence of amino acids. Each amino acid in the sequence will associate with other amino acids to ...
... During and after synthesis the primary sequence will associate in a fashion that leads to the most stable, "comfortable" structure for the protein. How a protein folds is largely dictated by the primary sequence of amino acids. Each amino acid in the sequence will associate with other amino acids to ...
Lesson 4.2 Link Reaction and Krebs Cycle
... coenzyme A to produce Acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
... coenzyme A to produce Acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
Homework # 8 Energetics, Electron Transport
... Ques. 34. Starting with one acetyl-CoA molecule, how many NADH coenzymes enter the electron transport chains in going through the citric acid cycle? ...
... Ques. 34. Starting with one acetyl-CoA molecule, how many NADH coenzymes enter the electron transport chains in going through the citric acid cycle? ...
Cellular Respiration & Fermentation
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
Respiration
... • Even glycolysis would stop if no Reduced NAD is reoxidised. • Rather, each pyruvate molecule produced in glycolysis takes hydrogen ions from Reduced NAD – to form Lactic Acid. ...
... • Even glycolysis would stop if no Reduced NAD is reoxidised. • Rather, each pyruvate molecule produced in glycolysis takes hydrogen ions from Reduced NAD – to form Lactic Acid. ...
Postexercise nutrient intake timing in humans is critical to recovery
... nutrient ingestion timing has been investigated for glycogen metabolism, little is known about similar effects for protein dynamics. Each subject (n ⫽ 10) was studied twice, with the same oral supplement (10 g protein, 8 g carbohydrate, 3 g fat) being administered either immediately (EARLY) or 3 h ( ...
... nutrient ingestion timing has been investigated for glycogen metabolism, little is known about similar effects for protein dynamics. Each subject (n ⫽ 10) was studied twice, with the same oral supplement (10 g protein, 8 g carbohydrate, 3 g fat) being administered either immediately (EARLY) or 3 h ( ...
Enzymes and food flavor : a review
... The development of soy sauce fermentation, centuries ago, is probably one of the first processes where traditional biotechnology had a stronger impact on flavor than in preservation. More recent developments of protein hydrolysates from vëgetals, soy bean, wheat or yeasts are 'specifically related t ...
... The development of soy sauce fermentation, centuries ago, is probably one of the first processes where traditional biotechnology had a stronger impact on flavor than in preservation. More recent developments of protein hydrolysates from vëgetals, soy bean, wheat or yeasts are 'specifically related t ...
Diabetes? - H and N Herbs
... help maintain glucose control in diabetes. It is best when taken with meals because the fiber prevents the absorption of some carbohydrates and allows more effective use of carbohydrates that are absorbed. Ingesting up to 30 g of both soluble and non-soluble fiber is recommendedeven in non-diabetics ...
... help maintain glucose control in diabetes. It is best when taken with meals because the fiber prevents the absorption of some carbohydrates and allows more effective use of carbohydrates that are absorbed. Ingesting up to 30 g of both soluble and non-soluble fiber is recommendedeven in non-diabetics ...
Ch6
... • Energy harvested in stepwise process • Electrons transferred to electron carriers, which represent reducing power (easily transfer electrons to molecules) – Raise energy level of recipient molecule • NAD+/NADH, NADP+/NADPH, and FAD/FADH2 ...
... • Energy harvested in stepwise process • Electrons transferred to electron carriers, which represent reducing power (easily transfer electrons to molecules) – Raise energy level of recipient molecule • NAD+/NADH, NADP+/NADPH, and FAD/FADH2 ...
The Urea Cycle
... mitochondrial matrix by the enzymatic activities of glutaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is the enzyme that takes the ammonia, bicarbonate and 2 molecules of ATP to produce carbamoyl phosphate. This enzyme activates bicarbonate by the same method used by biotin c ...
... mitochondrial matrix by the enzymatic activities of glutaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is the enzyme that takes the ammonia, bicarbonate and 2 molecules of ATP to produce carbamoyl phosphate. This enzyme activates bicarbonate by the same method used by biotin c ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic fuel, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules • In the citric acid cycle ...
Bacterial Metabolism
... and the photosynthetic bacteria (or phototrophs) (Table 4-1). These are discussed below. ...
... and the photosynthetic bacteria (or phototrophs) (Table 4-1). These are discussed below. ...
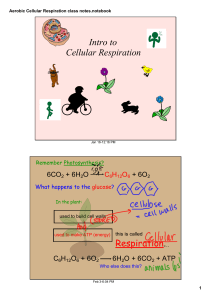
Aerobic Cellular Respiration class notes.notebook
... During Cellular Respiration if oxygen is present aerobic respiration will occur. Location: mitochondria of a cell. ...
... During Cellular Respiration if oxygen is present aerobic respiration will occur. Location: mitochondria of a cell. ...
Enzymatic properties of the N- and C
... As is the case for HK I, the mitochondrial binding domain (amino acid residues 1–18) at the N-terminus of HK II appears to mediate the specific activity of HK II. Furthermore, N-terminal and Δ18N constructs show higher affinity for ATP than the C-terminal half. Many lines of evidence suggest that G ...
... As is the case for HK I, the mitochondrial binding domain (amino acid residues 1–18) at the N-terminus of HK II appears to mediate the specific activity of HK II. Furthermore, N-terminal and Δ18N constructs show higher affinity for ATP than the C-terminal half. Many lines of evidence suggest that G ...