Peroxisomes: family of versatile organelles
... (C2) groups. Instead, it produces chain-shortened fatty acids (C6-C14) which can be used inside or outside peroxisomes for synthesis of some compounds or exported to mitochondria for further oxidation down to acetyl group. ...
... (C2) groups. Instead, it produces chain-shortened fatty acids (C6-C14) which can be used inside or outside peroxisomes for synthesis of some compounds or exported to mitochondria for further oxidation down to acetyl group. ...
Document
... One of the most widely occuring steroids, was first isolated in 1770. Contains 8 chiral C atoms, this means that 28 or 256 stereoisomers are possible, but only one of them is cholesterol. ...
... One of the most widely occuring steroids, was first isolated in 1770. Contains 8 chiral C atoms, this means that 28 or 256 stereoisomers are possible, but only one of them is cholesterol. ...
A defined growth medium for Clostridium difficile
... acids and vitamins Growth of all five test strains reached maximum after an incubation period of 20-22 h in BDM and m-BHI. The maximum OD,,, values were 0-80-0-88 in BDM and 0.73-0.84 in m-BHI. T o identify amino acid requirements for good growth of the five strains, experiments were performed using ...
... acids and vitamins Growth of all five test strains reached maximum after an incubation period of 20-22 h in BDM and m-BHI. The maximum OD,,, values were 0-80-0-88 in BDM and 0.73-0.84 in m-BHI. T o identify amino acid requirements for good growth of the five strains, experiments were performed using ...
©2011 The Simple Homeschool – Simple Days Unit Studies
... One more interesting factoid about cellulose is that insects use a form of it to create chitin; this is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
... One more interesting factoid about cellulose is that insects use a form of it to create chitin; this is a major component of the exoskeleton of arthropods. ...
Presentation 2013-201307040352
... organ in the body, around 8–15 ml O2 min/100 g heart, with the capacity to increase up to 70 ml under exercise conditions. Everyday the heart ...
... organ in the body, around 8–15 ml O2 min/100 g heart, with the capacity to increase up to 70 ml under exercise conditions. Everyday the heart ...
Dr. Walaa AL - Jedda – 2016 Metabolism of Glycogen Glycogen: is
... 2-Muscle glycogen on the other hand, is to act as readily available source of intermediates of glycolysis for provision of energy within the muscle itself. Muscle glycogen cannot directly contribute to blood glucose level. 3-Inherited deficiency of enzymes in the pathway of glycogen metabolism produ ...
... 2-Muscle glycogen on the other hand, is to act as readily available source of intermediates of glycolysis for provision of energy within the muscle itself. Muscle glycogen cannot directly contribute to blood glucose level. 3-Inherited deficiency of enzymes in the pathway of glycogen metabolism produ ...
CHAPTER 17: DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... that drain the pelvic floor may intrude into the anal canal as hemorrhoids. Constipation or diarrhea may follow from osmotic and secretory disturbances as well as transport problems originating in the myenteric plexus and muscularis externa. Digestion has two paramount functions: releasing nutrients ...
... that drain the pelvic floor may intrude into the anal canal as hemorrhoids. Constipation or diarrhea may follow from osmotic and secretory disturbances as well as transport problems originating in the myenteric plexus and muscularis externa. Digestion has two paramount functions: releasing nutrients ...
Gelatinization of Starch
... osmotic pressure if stored in sufficient quantities to be useful. Polymerized sugars reduce the number of molecules present and hence the osmotic effects. Free polymers are too thick to allow cell to function Thus, plants store energy into starch granules ...
... osmotic pressure if stored in sufficient quantities to be useful. Polymerized sugars reduce the number of molecules present and hence the osmotic effects. Free polymers are too thick to allow cell to function Thus, plants store energy into starch granules ...
AP Biology Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Guided Notes
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to __________, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an __________ _______ during cellular respiration • Each _______ ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to __________, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an __________ _______ during cellular respiration • Each _______ ...
Chapter 6
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
Derived copy of Bis2A 07.1 Glycolysis
... its isomers. (This change from phosphoglucose to phosphofructose allows the eventual split of the sugar into two three-carbon molecules.). Step 3. The third step is the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate, catalyzed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase. A second ATP molecule donates a high-energy p ...
... its isomers. (This change from phosphoglucose to phosphofructose allows the eventual split of the sugar into two three-carbon molecules.). Step 3. The third step is the phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate, catalyzed by the enzyme phosphofructokinase. A second ATP molecule donates a high-energy p ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF ENERGY
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
... – the cells are packed full of mitochondria, – the inner mitochondrial membrane contains an uncoupling protein, which allows H+ to flow back down its concentration gradient without generating ATP, and – ongoing oxidation of stored fats generates additional ...
Lecture 24
... Difference between phosphoglycerate mutase and phosphoglucomutase is the amino acid residue to which the phosphoryl group is attached. Serine in phosphoglucomutase as opposed to His imidazole ...
... Difference between phosphoglycerate mutase and phosphoglucomutase is the amino acid residue to which the phosphoryl group is attached. Serine in phosphoglucomutase as opposed to His imidazole ...
Metabolic Engineering for Production of Complex Lipids in Tobacco
... esterified to a glycerol backbone at the sn-1, sn-2 and sn-3 positions (Figure 3c). The fatty acids in a TAG molecule can differ, but are naturally a mixture of two or three different fatty acids. Most natural fats are composed of a mixture of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. In most organisms, TA ...
... esterified to a glycerol backbone at the sn-1, sn-2 and sn-3 positions (Figure 3c). The fatty acids in a TAG molecule can differ, but are naturally a mixture of two or three different fatty acids. Most natural fats are composed of a mixture of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. In most organisms, TA ...
Translation
... Specific codon always codes for the same amino acid • Redundant - For a given amino acid may have more than one codon for it. - Codons that specify the amino acid are called “synonyms” most of them differ only in the last base of the triplet UUU UUC ...
... Specific codon always codes for the same amino acid • Redundant - For a given amino acid may have more than one codon for it. - Codons that specify the amino acid are called “synonyms” most of them differ only in the last base of the triplet UUU UUC ...
Amino Acid Metabolism 1 Key Concepts
... into intestinal epithelial cells and then exported to the blood. The complete degradation of dietary proteins by these digestive proteases results from the distinct substrate specificities of the enzymes. Another source of free amino acids in the body comes from Figure 14. degradation of cellular pr ...
... into intestinal epithelial cells and then exported to the blood. The complete degradation of dietary proteins by these digestive proteases results from the distinct substrate specificities of the enzymes. Another source of free amino acids in the body comes from Figure 14. degradation of cellular pr ...
Amino Acids - Rose
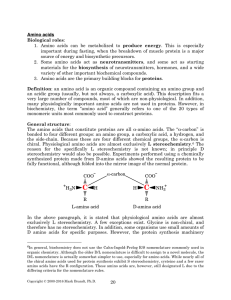
... 1. Amino acids can be metabolized to produce energy. This is especially important during fasting, when the breakdown of muscle protein is a major source of energy and biosynthetic precursors. 2. Some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, and some act as starting materials for the biosynthesis of neu ...
... 1. Amino acids can be metabolized to produce energy. This is especially important during fasting, when the breakdown of muscle protein is a major source of energy and biosynthetic precursors. 2. Some amino acids act as neurotransmitters, and some act as starting materials for the biosynthesis of neu ...
histidine and cysteine can enhance the metabolic reaction rates in
... theory of the genetic code. I have also shown in a separate letter [3] that not only histidine but other single amino acids such as cysteine, glutamic acid (or aspartic acid), lysine, and tyrosine (and their cognate anticodons, too) can act as the specific catalysts of various metabolic reactions in ...
... theory of the genetic code. I have also shown in a separate letter [3] that not only histidine but other single amino acids such as cysteine, glutamic acid (or aspartic acid), lysine, and tyrosine (and their cognate anticodons, too) can act as the specific catalysts of various metabolic reactions in ...
LESSON 11. СOMMUNICATION BETWEEN CELLS. MECHANISM
... receptors located either on the plasma membrane of cells or in the cytosol and nucleus. Hormones from different classes elicit their effects on target cells in different ways. 3. Water-soluble versus lipid-soluble hormones. On the basis of their physical properties, hormones fall into one of two cat ...
... receptors located either on the plasma membrane of cells or in the cytosol and nucleus. Hormones from different classes elicit their effects on target cells in different ways. 3. Water-soluble versus lipid-soluble hormones. On the basis of their physical properties, hormones fall into one of two cat ...
Complementation Analysis of Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
... [3H]palmitate concentration is thus virtually constant throughout the incubation period, and MAD:S activities are consistently <10% of control. The dependence of 3H20 formation on cell density is displayed in Fig. 1. 3H20 production was linear up to -60 Mg of cell protein per well, at which point th ...
... [3H]palmitate concentration is thus virtually constant throughout the incubation period, and MAD:S activities are consistently <10% of control. The dependence of 3H20 formation on cell density is displayed in Fig. 1. 3H20 production was linear up to -60 Mg of cell protein per well, at which point th ...