How Cells Harvest Energy
... Energy given off by the electron transfers is used to pump H+ across the inner membrane into the outer compartment This creates a chemical/electrical gradient • A form of potential energy • An ATP-synthesizing enzyme uses this energy to make ATP ...
... Energy given off by the electron transfers is used to pump H+ across the inner membrane into the outer compartment This creates a chemical/electrical gradient • A form of potential energy • An ATP-synthesizing enzyme uses this energy to make ATP ...
The Digestive System
... - Protein digestion begins with pepsin (activation of pepsinogen by HCl) , resulting in peptides (small chains of protein). ...
... - Protein digestion begins with pepsin (activation of pepsinogen by HCl) , resulting in peptides (small chains of protein). ...
Fat Metabolism
... • When there is not enough insulin in the blood and it must break down fat for its energy. • Ketones build up in the blood and then spill over into the urine so that the body can get rid of them. Acetone can be exhaled through the lungs. This gives the breath a fruity odor. Ketones that build up in ...
... • When there is not enough insulin in the blood and it must break down fat for its energy. • Ketones build up in the blood and then spill over into the urine so that the body can get rid of them. Acetone can be exhaled through the lungs. This gives the breath a fruity odor. Ketones that build up in ...
Structure and function of human lactalbumin made lethal to tumor
... illuminating the structural, functional and therapeutic properties of protein complexes with oleic acid, which is summarized in this review. In vitro, both HAMLET and ELOA are produced by using ion-exchange columns preconditioned with oleic acid. However, the complex of human a-lactalbumin with olei ...
... illuminating the structural, functional and therapeutic properties of protein complexes with oleic acid, which is summarized in this review. In vitro, both HAMLET and ELOA are produced by using ion-exchange columns preconditioned with oleic acid. However, the complex of human a-lactalbumin with olei ...
Regulation of metabolic pathways at the cellular level
... • Velocity of transport of fatty acids into a mitochondrion: carnitine acyltransferase I is inhibited by malonyl-CoA • Consumption of AcCoA, FADH2 and NADH by subsequent reactions ...
... • Velocity of transport of fatty acids into a mitochondrion: carnitine acyltransferase I is inhibited by malonyl-CoA • Consumption of AcCoA, FADH2 and NADH by subsequent reactions ...
Utilization of fats and amino acids as fuels
... or to acetoacetyCoA, from which fats or ketone bodies can be made. These are called ketogenic amino acids. Only two of these (leucine and lycine) are not also glucogenic. Yes, you can get fats from proteins, either directly in the case of ketogenic amino acids or less directly through gluconeogenesi ...
... or to acetoacetyCoA, from which fats or ketone bodies can be made. These are called ketogenic amino acids. Only two of these (leucine and lycine) are not also glucogenic. Yes, you can get fats from proteins, either directly in the case of ketogenic amino acids or less directly through gluconeogenesi ...
Important metabolic pathways in poultry embryos prior to hatch
... During the incubation period, the avian embryo does not invest much metabolic resources into gut development until the end of the incubation period when rapid visceral growth and maturation occurs (Uni et al., 2003; Gilbert et al., 2007). The sooner the intestinal tract achieves its functional capac ...
... During the incubation period, the avian embryo does not invest much metabolic resources into gut development until the end of the incubation period when rapid visceral growth and maturation occurs (Uni et al., 2003; Gilbert et al., 2007). The sooner the intestinal tract achieves its functional capac ...
Amino Acids
... Polarity. The nonpolar amino acids are alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, and valine. Six of the polar amino acids are uncharged: these are asparagine, cysteine, glutamine, serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Five polar amino acids are charged; these ...
... Polarity. The nonpolar amino acids are alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, and valine. Six of the polar amino acids are uncharged: these are asparagine, cysteine, glutamine, serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Five polar amino acids are charged; these ...
Structure
... – It is the most abundant organic material on earth. – Cellulose is made up of long, straight glucose molecules. Cellulose is called a structural polysaccharide because it gives the plant cell its shape, is not soluble, and is very strong. – Cellulose is flexible when the plant cell is young. As the ...
... – It is the most abundant organic material on earth. – Cellulose is made up of long, straight glucose molecules. Cellulose is called a structural polysaccharide because it gives the plant cell its shape, is not soluble, and is very strong. – Cellulose is flexible when the plant cell is young. As the ...
Natural Gene Therapies in Down Syndrome
... septic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and total antioxidant status of serum were determined before and after dietary supplementation, using commercially available kits. In all the evaluable patients (n = 20), after 3.8 +/- 1.1 treatment cycles, thiol group serum concentrations and total antioxidant s ...
... septic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and total antioxidant status of serum were determined before and after dietary supplementation, using commercially available kits. In all the evaluable patients (n = 20), after 3.8 +/- 1.1 treatment cycles, thiol group serum concentrations and total antioxidant s ...
Lecture 32: Protein (Part-I)
... for understanding its functions. In prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, protein is the main molecule to perform many functions; such as enzymes to catalyze to various chemical reactions, adaptor molecule for different ligands, messenger molecule to relay the signal within the cell to produce factors t ...
... for understanding its functions. In prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, protein is the main molecule to perform many functions; such as enzymes to catalyze to various chemical reactions, adaptor molecule for different ligands, messenger molecule to relay the signal within the cell to produce factors t ...
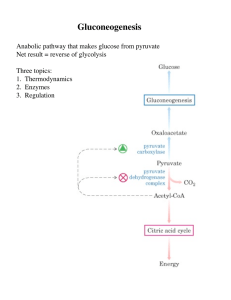
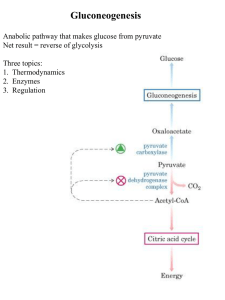
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
... Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low blood sugar ...
Review of Analytical Methods Part 1: Spectrophotometry
... • Oxaloacetate and pyruvate are measured with their corresponding dehydrogenase enzymes, MD and LD ...
... • Oxaloacetate and pyruvate are measured with their corresponding dehydrogenase enzymes, MD and LD ...
- Journal of Hepatology
... plasma, including cholesterol esters [5,6], triacylglycerols [4–7], diacylglycerols [4], sphingomyelins [4], various bile salts [8–10], together with lactate [9,11,12] and glutamate [11,13]. In addition, cysteine-glutathione disulfide and both oxidized and reduced glutathione were all reported to be ...
... plasma, including cholesterol esters [5,6], triacylglycerols [4–7], diacylglycerols [4], sphingomyelins [4], various bile salts [8–10], together with lactate [9,11,12] and glutamate [11,13]. In addition, cysteine-glutathione disulfide and both oxidized and reduced glutathione were all reported to be ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... The unifying feature of lipids is that they mix poorly, if at all, with water Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, waxes, and steroids © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc ...
... The unifying feature of lipids is that they mix poorly, if at all, with water Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, waxes, and steroids © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc ...
Glycolysis
... Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal cascades. Liver cells have major roles in metabolism, i ...
... Local control of metabolism involves regulatory effects of varied concentrations of pathway substrates or intermediates, to benefit the cell. Global control is for the benefit of the whole organism, & often involves hormone-activated signal cascades. Liver cells have major roles in metabolism, i ...
Glycolysis
... the keto in pyruvate to a hydroxyl, yielding lactate, as NADH is oxidized to NAD+. Lactate, in addition to being an end-product of fermentation, serves as a mobile form of nutrient energy, & possibly as a signal molecule in mammalian organisms. Cell membranes contain carrier proteins that facilitate ...
... the keto in pyruvate to a hydroxyl, yielding lactate, as NADH is oxidized to NAD+. Lactate, in addition to being an end-product of fermentation, serves as a mobile form of nutrient energy, & possibly as a signal molecule in mammalian organisms. Cell membranes contain carrier proteins that facilitate ...
Science Course Outline Template
... emphasis on how we, as humans, convert foods to useful energy. This course also aims to provide a solid context for new learning material by providing clinical, medical and everyday applications that correspond to the central themes and topics. Practicals are designed to reinforce the core bioch ...
... emphasis on how we, as humans, convert foods to useful energy. This course also aims to provide a solid context for new learning material by providing clinical, medical and everyday applications that correspond to the central themes and topics. Practicals are designed to reinforce the core bioch ...
LFT- GIT
... Serum Albumin • Albumin is present in higher concentrations than other plasma proteins ( ~ 40 g/L in normal adults). • Albumin is synthesized in the liver & has a half-life of 20 days. • Very small amounts of albumin cross the glomerular capillary wall. Accordingly, no more than traces of albumin m ...
... Serum Albumin • Albumin is present in higher concentrations than other plasma proteins ( ~ 40 g/L in normal adults). • Albumin is synthesized in the liver & has a half-life of 20 days. • Very small amounts of albumin cross the glomerular capillary wall. Accordingly, no more than traces of albumin m ...