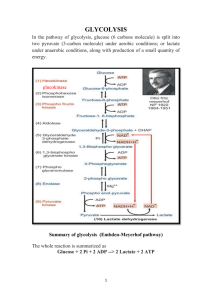
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... 1. It is the only pathway that is taking place in all the cells (cytoplasm) of the body. 2. Glycolysis is the only source of energy in erythrocytes. 3. In strenuous exercise, when muscle tissue lacks enough oxygen, anaerobic glycolysis forms the major source of energy for muscles. 4. The glycolytic ...
... 1. It is the only pathway that is taking place in all the cells (cytoplasm) of the body. 2. Glycolysis is the only source of energy in erythrocytes. 3. In strenuous exercise, when muscle tissue lacks enough oxygen, anaerobic glycolysis forms the major source of energy for muscles. 4. The glycolytic ...
Protein Similarities II
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
... The "lighter" amino acids aren't necessary to the electron-carrying function; at least, they don't have to be precisely the same for the protein to work. This isn't at all unlikely. For instance, there is an alpha helix going up the left side of the image above. It probably has to be an alpha helix ...
Digestive System Function Anatomy Anatomy Digestive Processes
... – enzymes, bile salts, mucus, etc. released by exocrine glands into GI tract ...
... – enzymes, bile salts, mucus, etc. released by exocrine glands into GI tract ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... •Debranching of limit dextran occurs in two steps. •1st, 3 X 1,4 linked glucose residues are transferred to non-reducing end of glycogen ...
... •Debranching of limit dextran occurs in two steps. •1st, 3 X 1,4 linked glucose residues are transferred to non-reducing end of glycogen ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... – enzymes, bile salts, mucus, etc. released by exocrine glands into GI tract ...
... – enzymes, bile salts, mucus, etc. released by exocrine glands into GI tract ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... •Debranching of limit dextran occurs in two steps. •1st, 3 X 1,4 linked glucose residues are transferred to non-reducing end of glycogen ...
... •Debranching of limit dextran occurs in two steps. •1st, 3 X 1,4 linked glucose residues are transferred to non-reducing end of glycogen ...
Life, 6th Edition
... Water: Structure and Properties Cohesion of water molecules results in a high surface tension. Water’s high heat of vaporization assures cooling when it evaporates. Solutions are substances dissolved in water. Concentration is the amount of a given substance in a given amount of solution. Most ...
... Water: Structure and Properties Cohesion of water molecules results in a high surface tension. Water’s high heat of vaporization assures cooling when it evaporates. Solutions are substances dissolved in water. Concentration is the amount of a given substance in a given amount of solution. Most ...
Unit 1: The Nature of Life
... 1. When hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor, it is an energy-releasing reaction in which energy is given off as heat. 2H2 + O2 2H2O 2. Reversing this reaction would require the addition of large amounts of energy. 3. In order to stay alive, organisms need to carry out reactions th ...
... 1. When hydrogen gas reacts with oxygen to produce water vapor, it is an energy-releasing reaction in which energy is given off as heat. 2H2 + O2 2H2O 2. Reversing this reaction would require the addition of large amounts of energy. 3. In order to stay alive, organisms need to carry out reactions th ...
as a PDF
... autumn to early spring (through December and the following three or four months). The leaves contribute widely to general diets of the people living in the region ...
... autumn to early spring (through December and the following three or four months). The leaves contribute widely to general diets of the people living in the region ...
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
... high-energy electrons and a hydrogen ion are added to an “empty” electron-carrier NAD+ to make the high-energy electron-carrier molecule NADH – Because two G3P molecules are produced per glucose molecule, two NADH carrier molecules are formed ...
... high-energy electrons and a hydrogen ion are added to an “empty” electron-carrier NAD+ to make the high-energy electron-carrier molecule NADH – Because two G3P molecules are produced per glucose molecule, two NADH carrier molecules are formed ...
Rearrange the sentences into the correct sequence
... The alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas detect a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood. ...
... The alpha cells of the Islets of Langerhans in the pancreas detect a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY
... Since glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate molecules from each glucose molecule, both of which are then converted to acetyl CoA, one glucose molecule will drive two turns of the Krebs Cycle, producing a total of 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2. So far, cellular respiration has produced from one glucose molecu ...
... Since glycolysis produces 2 pyruvate molecules from each glucose molecule, both of which are then converted to acetyl CoA, one glucose molecule will drive two turns of the Krebs Cycle, producing a total of 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2. So far, cellular respiration has produced from one glucose molecu ...
Untitled
... the structures that they form in water, or water-based solutions (referred to as aqueous, or water-containing). As we discussed on the previous slide, lipids will arrange themselves in water in the way that minimizes the amount of hydrophobic surface that is exposed. Since biological lipids are amph ...
... the structures that they form in water, or water-based solutions (referred to as aqueous, or water-containing). As we discussed on the previous slide, lipids will arrange themselves in water in the way that minimizes the amount of hydrophobic surface that is exposed. Since biological lipids are amph ...
Cellular Respiration Review
... #21. Name the 3 carbon molecule that forms when glucose is split in half during glycolysis. #22. Name the 6 carbon molecule that forms during the first step of the Krebs cycle. #23. Fermentation is said to be ________________ because it happens “NOT IN AIR” or without oxygen. 24. Compare NADH and FA ...
... #21. Name the 3 carbon molecule that forms when glucose is split in half during glycolysis. #22. Name the 6 carbon molecule that forms during the first step of the Krebs cycle. #23. Fermentation is said to be ________________ because it happens “NOT IN AIR” or without oxygen. 24. Compare NADH and FA ...
File - Wk 1-2
... equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aerobic pathway). Pyruvic acid from glycolysis first needs to be converted to acetyl CoA before it can enter into the citric acid cycle. This ...
... equivalents for the electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) occurs in the mitacholdria of the cell and occurs in the presence of oxygen (aerobic pathway). Pyruvic acid from glycolysis first needs to be converted to acetyl CoA before it can enter into the citric acid cycle. This ...
BY 330 Spring 2015Worksheet 4 Name the substrate ligand and
... The law of mass action describes enzymes that can work in more than one direction. Whichever direction the equilibrium lies, is the direction that enzyme will work in. For example, if there is too much product present, these enzymes will work in reverse and if there is too much substrate present, th ...
... The law of mass action describes enzymes that can work in more than one direction. Whichever direction the equilibrium lies, is the direction that enzyme will work in. For example, if there is too much product present, these enzymes will work in reverse and if there is too much substrate present, th ...
Digestion Digesiton
... …Essentially the processes organisms use to obtain the essential biomolecules from the food they eat ...
... …Essentially the processes organisms use to obtain the essential biomolecules from the food they eat ...
03-232 Biochemistry
... key intermediates and their products. Feel free to draw a well-labeled diagram. Choice B: When cellular levels of O2 are limiting during strenuous exercise, glycolysis becomes the main source of energy. Describe what additional step(s) in either yeast or mammalian cells is (are) needed to allow cont ...
... key intermediates and their products. Feel free to draw a well-labeled diagram. Choice B: When cellular levels of O2 are limiting during strenuous exercise, glycolysis becomes the main source of energy. Describe what additional step(s) in either yeast or mammalian cells is (are) needed to allow cont ...
Concept 1 - Phillips Scientific Methods
... CO2 production occurs in the Kreb’s cycle, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial matrix; therefore, it would be impossible to produce CO2 in the cytoplasm fraction with glucose. The Kreb’s cycle requires pyruvate, not glucose, as a reactant, which explains why CO2 could not be produced in the ...
... CO2 production occurs in the Kreb’s cycle, which takes place in the inner mitochondrial matrix; therefore, it would be impossible to produce CO2 in the cytoplasm fraction with glucose. The Kreb’s cycle requires pyruvate, not glucose, as a reactant, which explains why CO2 could not be produced in the ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... II. Glycolysis: The first reactions. . . a. Occurs in the _____________________________________ b. _____________________ is broken down in to 2 molecules of pyruvate c. Uses ________ ATP to start, then makes ______ ATP, so net gain= ____________ d. Uses NAD+ and FAD which are coenzymes made from Vit ...
... II. Glycolysis: The first reactions. . . a. Occurs in the _____________________________________ b. _____________________ is broken down in to 2 molecules of pyruvate c. Uses ________ ATP to start, then makes ______ ATP, so net gain= ____________ d. Uses NAD+ and FAD which are coenzymes made from Vit ...
Mapping the Body.indd
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...
Bioc 462a Lecture Notes
... There are 20 different amino acids found in proteins and they differ by the nature of the R group. The nonionic form shown above does not occur in water, rather the zwitterion occurs. Note that the-carbon is asymmetric (has four different substituents) meaning that amino acids occur as enantiomers ...
... There are 20 different amino acids found in proteins and they differ by the nature of the R group. The nonionic form shown above does not occur in water, rather the zwitterion occurs. Note that the-carbon is asymmetric (has four different substituents) meaning that amino acids occur as enantiomers ...
Biochemistry
... The key problems: The structure of protein amino acids. The classification of amino acids according to both the polarity and the structural features of their side chains (e. g. polar, nonpolar; aliphatic, aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of a ...
... The key problems: The structure of protein amino acids. The classification of amino acids according to both the polarity and the structural features of their side chains (e. g. polar, nonpolar; aliphatic, aromatic; sulfur-containing; charged, uncharged; acidic, basic). The amphoteric properties of a ...
Nutrient PPT
... Vitamins, minerals and water do not directly give us energy. They do not have calories. ...
... Vitamins, minerals and water do not directly give us energy. They do not have calories. ...























