* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mapping the Body.indd
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
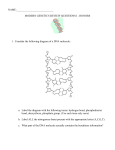
FINAL TEST for A&P Cell Biology Review (lessons 1-24) Name __________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT MOLECULES: 1) Which of these is the most important feature of the water molecule when it comes to understanding cell chemistry? a) It is polar. b) It is a liquid. c) It has 8 protons. d) It can be represented with a ball and stick model. 2) When a hydrogen leaves a water molecule, the oxygen keeps its electron, making the molecule into OH-. What is OH- called? a) the hydrogen ion b) the hydronium ion c) the hydroxide ion d) deuterium 3) What is H+ called? a) electron b) proton c) neutron d) hydrogen ion e) both a and d f) both b and d 4) The carbon atom is amazing. It can bond with dozens of atoms in hundreds of different ways. This makes it the “backbone” of many organic molecules. What allows it to form so many different molecules? a) It can make 4 bonds and shares its electrons easily. b) Its outer electron shell is completely full, so it is happy. c) It can bond to hydrogen. d) All of these. 5) What is COOH? a) carbonate ion 6) The molecule CH4 is: a) non-polar b) fatty acid molecule b) flammable c) methane c) methane d) none of these e) all of these f) none of these 7) An amino acid molecule has this element, which sets it apart from other organic molecules: a) oxygen b) hydrogen c) carbon d) nitrogen e) iron f) none of these 8) The molecule called glycerol has a backbone of 3 carbon atoms and functions like a: a) clip b) hanger c) cable d) tail e) head 9) The bond that joins two amino acids is called: a) an ionic bond b) a hydrogen bond c) a covalent bond d) a peptide bond 10) When water molecules are floating around as a liquid, they are kept together by what attractive force? a) ionic bonding b) hydrogen bonding c) covalent bonding d) magnetism ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11) Structure A isn’t really round, but we draw it as a circle. It is called the _______. body part 12) Part of this molecule, located at B, joins the top part to the bottom parts. This is: a) the carboxyl group b) glycosamine c) a peptide bond d) glycerol Use this picture for questions 11-20. 13) C and D are called the _________. 14) E is pointing to one of those “points.” What is located at each point? a) a carbon atom b) an oxygen atom c) a free electron d) a fatty acid 15) Notice that C is straight and D is bent a little. Why is D bent? a) It is saturated. b) It is unsaturated. c) It has missing carbon atoms. 16) The area marked F is a molecule that makes the top part “love” water. What is F? a) carboxyl group b) phosphate c) glycerol d) the R group e) hydroxide ion 17) C and D are: a) hydrophobic b) hydrophilic 18) How many carbon atoms does C have? a) 10 c) neither b) 12 c) 14 19) Where would you be most likely to find this molecule? a) in a membrane b) in or near a ribosome c) around DNA d) 16 d) in the cytoskeleton e) in the cytosol 20) When C and D were attached to the top part, this process was called: a) ionic bonding b) peptide bonding c) dehydration synthesis d) oxidative phosphorylation e) methylation QUESTIONS ABOUT MEMBRANES AND TRANSPORT ACROSS THEM 21) Phospholipid molecules will automatically form a sphere if they are put into water, because: a) their electrons are attracted to each other b) hydrogen bonding will occur c) the hydrophobic tails get together and make a “no-water” zone d) none of these 22) Which one of these structures is acidic on the inside? a) liposome b) lysosome c) vesicle d) vacuole 23) Which one of these structures is often filled with just water or air? a) liposome b) lysosome c) vesicle d) vacuole 24) Which one is made by the ER to transport proteins to the Golgi? b) lysosome c) vesicle d) vacuole 25) Active transport requires: a) vesicles b) ion channels 26) Which of these can be a trigger for an ion channel? a) voltage b) pressure c) messenger molecule a) liposome c) aquaporin d) light d) diffusion d) all of these e) energy e) none of these 27) Aquaporin is a channel that transports ________ across the plasma membrane. 28) Name a vitamin that can diffuse right through the plasma membrane, without using a channel: ______ (Hint: The vitamins are A, B, C, D, E, and K 29) When something moves “down its concentration gradient,” it moves: a) from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration b) from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration c) from areas of high concentration to areas of equilibrium 30) Which of these would NOT be found in a plasma membrane? a) MHC1 b) lipid rafts c) oligosaccharides d) flippase __________ e) ion pumps f) polymerase Here are the answers to the next five questions. Match them to the right questions. OSMOSIS DIFFUSION FACILITATED DIFFUSION ACTIVE TRANSPORT PASSIVE TRANSPORT 31) Food coloring gradually spreading out to fill a glass of water: __________________ 32) Endocytosis and exocytosis are examples of: ______________________ 33) Ions passing through channels to enter a cell: ________________________ 34) Water moving across a plant cell membrane to rehydrate the cell: ___________________ 35) Aquaporins and ion channels are examples of: ________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT PROTEINS 36) All of these statements are true except one. Which one is false? a) Amino acids can be right or left handed. b) Amino acids are identical except for their R group. c) Amino acids contain a nitrogen atom. d) Amino acids found in nature are all right handed. e) Amino acids can be recycled. e) Amino acids get their “personality” from their R group. 37) Nitrogen usually wants to make how many bonds? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 e) 5 f) 8 38) True or False? The secondary structure of a protein is the way it folds up into a 3-dimensional shape. 39) True or False? The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino acids. 40) True or False? Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of seconary structures. MORE QUESTIONS ABOUT PROTEINS 41) Which of these is NOT a protein gadget? a) cytoskeleton b) enzymes c) ribosomes d) ATP synthase machine e) ion pumps f) flagella 42) Which one of these is NOT a possible shape for a protein? a) alpha helix b) double helix c) beta sheet d) zinc finger 43) The cytoskeleton has how many different sizes of cables? a) 2 b) 3 44) The smallest of the cytoskeleton cables are called: a) microfilaments c) 4 b) microtubules c) keratin d) cilia 45) Some enzymes act like scissors or staplers. The things that they cut or staple are called: a) antibodies b) substrates c) active sites d) polypeptides e) receptors _________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT CARBOHYDRATES 46) Which of these is NOT a monsaccharide? a) sucrose b) glucose c) fructose d) galactose 47) How do you join two monosaccharides to make a disaccharide? a) peptide bond b) ionic bond c) dehydration synthesis d) Trick question-- you can’t. 48) People who are lactose intolerant can’t digest this milk sugar (lactose) because: a) Their stomachs are not acidic enough. b) They don’t make the correct enzyme for breaking it apart. c) They are drinking it too fast. d) They are drinking the wrong kind of milk. 49) Animals can’t digest the cellulose that forms the walls of plant cells. So how can cows live on grass? a) They are the exception to the rule, and they make a special digestion enzyme. b) The bacteria that live in their gut can digest cellulose. c) The cellulose actually doesn’t get digested, which is why farmers feed them corn. d) None of these. 50) Which of these carbohydrates can your body make? a) starch b) cellulose c) glycogen d) all of these _________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT PROKARYOTES 51-52) Which of these cell parts does a prokaryote NOT have? Choose 2. a) DNA b) ribosomes c) nucleus d) plasma membrane e) cell wall 53) What is a plasmid made of? a) protein Match the bacteria shape with its correct name. 54) Steptococcus _______ 55) Diplococcus _______ 56) Spirillum _______ 57) Spirochete______ 58) Staphylococcus ______ 59) Coccus ______ 60) Bacillus _______ b) DNA c) polysaccharides f) plasmid d) plasma g) mitochondria h) cytosol MORE QUESTIONS ABOUT PROKARYOTES 61) What is the significance of a plasmid? a) It means that the bacteria was damaged. c) It contains survival information. b) It is a remnant left behind after binary fission. d) It contains harmful mutations. 62) Prokaryotes are often covered with hair-like fimbriae. What do the fimbriae do? a) Act like cilia and help the bacteria to move through liquids. b) Help the bacteria to stick to surfaces. c) Help the bacteria to find food. d) Help the bacteria not to dry out. 63) Prokaryotes are often surrounded by a capsule of sugary slime. What does this slime do? a) Help the bacteria not to dry out. b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? Gram positive bacteria have a thick cell wall made of peptidoglycan. 66) True or False? Gram positive bacteria have toxic sugars on their outer surface. 67) Which type of bacteria has an inner flagellum (inside the body rather than outside)? a) spirochete b) bacillus c) coccus d) all of these 68) Archaea are very similar to bacteria, and used to be classified as bacteria. However, they were given their own kingdom because they have so many features that are different from bacteria. All of the following are some of their different features except one. Which one is NOT a way in which archaea are different from bacteria? a) The structure of the phospholipids in their plasma membranes. b) The structure of their ribosomes. b) The winding of the DNA around histone spools. d) Their shapes and sizes. 69) Why do doctors need to know whether a bacteria is Gram positive or negative? a) So they can choose an appropriate antibiotic. b) So they can predict the outcome of the disease. c) So they can know which ones are good and which ones are bad. d) So they can tell the insurance company. 70) Penicillin (and others ending in “-cillin”) attack which part of a bacteria? a) ribosomes b) cell wall c) DNA d) plasma membrane ________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT TRANSLATION 71) What is A? a) DNA b) mRNA c) tRNA d) polypeptide e) miRNA 72) B is pointing to the ribosome. What is a ribosome made of? a) RNA b) mRNA c) DNA d) protein e) none of these 73) What is D? a) a protein gadget b) an enzyme c) tRNA 74) What are all the circles along C? a) enzymes b) tRNA c) amino acids d) an amino acid d) none of these 75) E is pointing to an anticodon. What does an anticodon do? a) joins amino acids using peptide bonds b) matches a 3-letter sequence on mRNA c) sticks to the plasma membrane d) carries a coded message from DNA e) acts like a “mailing label” f) none of these QUESTIONS ABOUT TRANSCRIPTION 76) What does RNA polymerase do? a) makes mRNA from DNA b) makes DNA from mRNA c) makes proteins from mRNA 77) Before mRNA is used it must be “edited” and parts of it are removed. All of these are ways in which mRNA is edited except one. Which one is NOT a way that mRNA is edited? a) an end cap is added to the front end b) a tail is added to the back end c) pieces called introns are taken out d) the sequence of nucleotids must be rearranged The next three questions refer to this list of words: adenine 78) What are these? a) amino acids b) nucleotides thymine c) bases cytosine guanine d) sugars uracil e) proteins 79) Which one is NOT found in DNA? _____________ 80) Which one is named after bird droppings? ______________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT MITOCHONDRIA AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION 81) Which is the correct order? (Think of the game board if you played the Cellular Respiration Game.) a) glycolysis→ Krebs Cycle→ ETC b) ETC→ Krebs Cycle→ glycolysis c) Krebs Cycle→ ETC→ glycolysis 82) What is the end result of glycolysis? (Again, think of the game board if you played the game.) a) Many ATPs are made. b) 2 pyruvates are made. c) 2 NADH trucks are filled. d) 2 ATPs are made. d) both b and c e) both b and d 83) Where does glycolysis occur? a) in the cytosol b) in the mitochondrial matrix c) in the nucleus d) all of these 84) The inner chamber of the mitochondria is called the ____________. 85) Mitochondria have several features that no other organelle has. One of these features is a circular ring of ________. 86) What is the Krebs “pre-step”? (It was right after the stop sign in the Cellular Respiration Game.) a) It provides acetyl CoAs for the Krebs Cycle. b) The pyruvate has a carbon chopped off then a CoA put onto it. c) It is a step where a molecule of carbon dioxide is made as a by-product. d) All of the above. e) Only a and b. 87) Which of the following is NOT true of the Krebs Cycle? a) It produces ATPs. b) It produces carbon dioxide. c) It breaks the bonds between the two carbon atoms in the acetyl-CoA molecule. d) It recharges NADH and FADH2. e) It requires oxygen to dispose of the “tired” electrons it produces. 88) What is the total number of ATPs that can be made from one glucose molecule (via cellular respiration)? a) 2 b) 4 c) 8 d) 12 e) 24 f) 32 g) 36 89) The electron transport chain has three proton pumps in its assembly line. Why do protons need to be pumped? a) So they can depolarize the membrane. b) So that they can be used to turn the ATP synthase motor. c) Because there are too many of them in the cytosol. 90) What role does oxygen play in the Electron Transport Chain? a) It creates a concentration gradient. b) It allows the cell to breathe. c) It receives “tired” electrons at the end of the line. d) It is a by-product formed by ATP synthase. QUESTIONS ABOUT SPERM, OVUM AND ZYGOTE 91) Which of these organelles does a mature sperm cell NOT have? a) nucleus b) centrioles c) acrosome d) mitochondria 92) What is a flagella made of? a) microtubules e) Golgi body b) microfilaments c) cilia f) plasma membrane d) muscle fibers 93) When the sperm gets to the ovum and starts burying into it, what organelle bursts and releases it contents? a) nucleus b) mitochondria c) Golgi body d) acrosome e) centrosome f) flagellum 94) What is the clear layer surrounding the ovum? a) plasma membrane b) corona radiata c) zona pellucida 95) The polar bodies are left over from what process? a) mitosis d) a layer of vesicles b) meiosis c) binary fission 96) When a sperm finally gets to the ovum’s plasma membrane, it triggers this response: a) depolarization b) oxidative phosphorylation c) neutralization d) conjugation 97) Which organelle is responsible for neutralizing toxins? a) lysosome b) peroxisome d) transcription e) methylation c) Golgi body d) ER 98) Which organelle is often called the “stomach” of the cell because it contains digestive enzymes? a) lysosome b) peroxisome c) Golgi body d) ER e) nucleus f) vacuole 99) This organelle consists of a network of tubes. It can manufacture pieces of phospholipid membrane to repair the plasma membrane. It can also make some hormones. a) rough ER b) smooth ER c) Golgi body d) lysosome e) ribosome f) peroxisome 100) What does MHC1 do? a) receives protein messages from other cells b) acts like channel allowing certain molecules to enter c) acts like an ID tag d) allows water to enter by osmosis _________________________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS ABOUT MITOSIS AND EPIGENETICS 101) What is responsible for forming the spindle? a) ribosomes b) nucleolus c) cytoskeleton d) centrosomes 102) What is the spindle made of? __________________ 103) Which of these stages finds the chromosomes in the middle? a) anaphase b) metaphase c) telophase d) prophase e) interphase 104) In which of these stages do most cells spend the most time? a) anaphase b) metaphase c) telophase d) prophase e) interphase 105) During which phase is DNA replicated? a) anaphase b) metaphase c) telophase e) interphase d) prophase 106) What is an Okazaki fragment? a) a piece of DNA that has broken off during a mutation c) a piece of DNA on the lagging strand 107) What reads the DNA during replication? a) RNA polymerase b) a piece of mRNA that is being translated d) a piece of DNA that no longer needed b) DNA polymerase c) ligase c) primase 108) Which of these can NOT be used as tags attached to a histone spool to control expression of DNA? a) methyl b) acetyl c) carboxyl d) phosphate 109) Which of these can stop mRNA from being used? a) tRNA b) miRNA c) mtDNA d) all of these 110) When DNA is in its normal, relaxed state (not bundled into chromosomes) it is called _______________.