Chapter 5 The Structure & Function of Molecules
... – Are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings ...
... – Are lipids characterized by a carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings ...
Slides PPT - The University of Sydney
... genome) with the same promoter and regulatory regions! How is this possible? ...
... genome) with the same promoter and regulatory regions! How is this possible? ...
Biomolecule Review Worksheet
... The structure of DNA resembles that of a twisted ladder. This twisted ladder of DNA is called a ‘double helix.’ The rails of the DNA ladder are made from alternating sugars and phosphates (sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar…). In DNA, the sugar is called deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are m ...
... The structure of DNA resembles that of a twisted ladder. This twisted ladder of DNA is called a ‘double helix.’ The rails of the DNA ladder are made from alternating sugars and phosphates (sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphate-sugar…). In DNA, the sugar is called deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are m ...
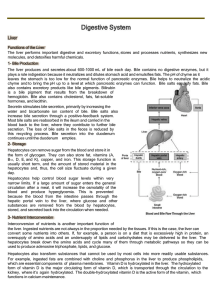
Functions of the Liver The liver performs important digestive and
... convert some nutrients into others. If, for example, a person is on a diet that is excessively high in protein, an oversupply of amino acids and an undersupply of lipids and carbohydrates may be delivered to the liver. The hepatocytes break down the amino acids and cycle many of them through metabol ...
... convert some nutrients into others. If, for example, a person is on a diet that is excessively high in protein, an oversupply of amino acids and an undersupply of lipids and carbohydrates may be delivered to the liver. The hepatocytes break down the amino acids and cycle many of them through metabol ...
Chapter 5 Quiz: Cellular respiration and fermentation Mark your
... It provides the cell with a mechanism to regenerate the oxidized form of electron carriers, allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
... It provides the cell with a mechanism to regenerate the oxidized form of electron carriers, allowing glycolysis to continue. ...
Classification of Enzymes - Lectures For UG-5
... -Second part is the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.This part ends with the suffix “ase”. Example: Lactate dehydrogenase ...
... -Second part is the type of reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.This part ends with the suffix “ase”. Example: Lactate dehydrogenase ...
Macromolecule (biomolecule) Review Worksheet
... called a ‘double helix.’ The rails of the DNA ladder are made from alternating sugars and phosphates (sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphatesugar…). In DNA, the sugar is called deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are made of four different kinds of bases, with one base hanging off of the sugar portion of ...
... called a ‘double helix.’ The rails of the DNA ladder are made from alternating sugars and phosphates (sugar-phosphate-sugar-phosphatesugar…). In DNA, the sugar is called deoxyribose. The rungs of the ladder are made of four different kinds of bases, with one base hanging off of the sugar portion of ...
Exam II
... 5. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Hydrogen bonding to a histidine residue assists stabilization of the Fe2+ -O2 complex in both hemoglobin and myoglobin. b. Myoglobin is a single polypeptide chain folded about a heme prosthetic group. c. The iron in both hemoglobin and myoglobin has ...
... 5. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Hydrogen bonding to a histidine residue assists stabilization of the Fe2+ -O2 complex in both hemoglobin and myoglobin. b. Myoglobin is a single polypeptide chain folded about a heme prosthetic group. c. The iron in both hemoglobin and myoglobin has ...
Biological membranes: the basics and why they are
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
... • Flexible phospholipid bilayer interspersed with protein molecules • Fluid – some parts move freely, if not anchored by other cell components • Mosaic – patchwork networks of proteins ...
Document
... 2. How do humans get the nitrogen they need? Plants can take up these forms of nitrogen and use it to make their molecules (see below). Heterotrophs (like humans) get their nitrogen FROM EATING plants or other heterotrophs. 3. Give examples (3) of some molecules your body needs nitrogen to make. Pro ...
... 2. How do humans get the nitrogen they need? Plants can take up these forms of nitrogen and use it to make their molecules (see below). Heterotrophs (like humans) get their nitrogen FROM EATING plants or other heterotrophs. 3. Give examples (3) of some molecules your body needs nitrogen to make. Pro ...
Chapter 21 - Bakersfield College
... Fatty acids • The human body is capable of synthesizing most fatty acids from carbohydrates or other fatty acids. ...
... Fatty acids • The human body is capable of synthesizing most fatty acids from carbohydrates or other fatty acids. ...
A1985AAT2400001
... & Research cancer in Western countries at a time Bacterial Metabolism Research when optimism was high following the Laboratory confirmation of the link between smokPorton Down, Salisbury ing and lung cancer. The work has been Wiltshire SP4 OJG repeated many times, and it is now acEngland cepted that ...
... & Research cancer in Western countries at a time Bacterial Metabolism Research when optimism was high following the Laboratory confirmation of the link between smokPorton Down, Salisbury ing and lung cancer. The work has been Wiltshire SP4 OJG repeated many times, and it is now acEngland cepted that ...
Chapter 15 Lecture Notes: Metabolism
... Energy is released from ATP when it is converted to ADP. This energy is used by organisms to drive energy-requiring reactions or physical processes that would otherwise not occur spontaneously. One way that energy can be released from ATP is by reacting it with H2O to form ADP, inorganic phosphate, ...
... Energy is released from ATP when it is converted to ADP. This energy is used by organisms to drive energy-requiring reactions or physical processes that would otherwise not occur spontaneously. One way that energy can be released from ATP is by reacting it with H2O to form ADP, inorganic phosphate, ...
Aminoacids
... – 1.Charge +/• Asp/Glu have typically one negative charge • Lsy/Arg have typically one positive charge • These charges attract each other form an ion pair or salt bridge • There is also the net charge of the protein ...
... – 1.Charge +/• Asp/Glu have typically one negative charge • Lsy/Arg have typically one positive charge • These charges attract each other form an ion pair or salt bridge • There is also the net charge of the protein ...
Chapter 3 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Lipids are a diverse group of macromolecules that are insoluble in water. • Fats and oils are well-known lipids used for energy storage and other purposes. • Phospholipids are components of the membranes that surround cells. • Steroids, which have a different structure from most lipids, are used a ...
... • Lipids are a diverse group of macromolecules that are insoluble in water. • Fats and oils are well-known lipids used for energy storage and other purposes. • Phospholipids are components of the membranes that surround cells. • Steroids, which have a different structure from most lipids, are used a ...
(3.1.1.5a) Nucleic Acids
... of proteins. Proteins have to have a special shape in order to do their job. For example, proteins that serve as enzymes have to have their active site, the groove that the substrate fits in. That shape is determined by the order of the amino acids and the way their side chains cause them to coil up ...
... of proteins. Proteins have to have a special shape in order to do their job. For example, proteins that serve as enzymes have to have their active site, the groove that the substrate fits in. That shape is determined by the order of the amino acids and the way their side chains cause them to coil up ...
Chapter 13 - Cell Metabolism
... Stage 3 • Pyruvate is moved to the mitochondria • In the presence of O2 it is converted to 1 molecule of CO2 and the remaining 2 C’s are attached to Coenzyme A, creating Acetyl CoA using pyruvate dehydrogenase complex • Also generates a molecule of NADH ...
... Stage 3 • Pyruvate is moved to the mitochondria • In the presence of O2 it is converted to 1 molecule of CO2 and the remaining 2 C’s are attached to Coenzyme A, creating Acetyl CoA using pyruvate dehydrogenase complex • Also generates a molecule of NADH ...
Chapter 5 Summary
... carbohydrates. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Lactose, maltose, and sucrose are disaccharides and consist of at least one glucose molecule. Lactose consists of glucose bonded to galactose, sucrose consists of glucose bonded to fructose, and maltose consists of ...
... carbohydrates. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Lactose, maltose, and sucrose are disaccharides and consist of at least one glucose molecule. Lactose consists of glucose bonded to galactose, sucrose consists of glucose bonded to fructose, and maltose consists of ...