PG1005 Lecture 12 Kreb`s Citric Acid Cycle
... cytosol to the establishment of electron harvesting reactions in the mitochondrial matrix • To revise the general mechanisms of glucose uptake. • To describe the enzymatic reactions occurring at each step of Kreb’s Citric Acid Cycle (KCAC). (substrates, enzymes, products, reaction types) • To hig ...
... cytosol to the establishment of electron harvesting reactions in the mitochondrial matrix • To revise the general mechanisms of glucose uptake. • To describe the enzymatic reactions occurring at each step of Kreb’s Citric Acid Cycle (KCAC). (substrates, enzymes, products, reaction types) • To hig ...
28 Gluconeogenesis In animals, glucose is required by the brain
... and phospholipids), and some can be synthesized from fatty acids containing an odd number of carbons. Cows and other ruminants use a breakdown product of chlorophyll as a gluconeogenic substrate (in humans, this pathway is present but is far less important). In general, however, gluconeogenesis uses ...
... and phospholipids), and some can be synthesized from fatty acids containing an odd number of carbons. Cows and other ruminants use a breakdown product of chlorophyll as a gluconeogenic substrate (in humans, this pathway is present but is far less important). In general, however, gluconeogenesis uses ...
Lecture 27
... involved in methylation reactions. Methylation reactions catalyzed by SAM yield S-adenosylhomocysteine and a methylated acceptor molecule. S-adenosylhomocysteine is hydrolyzed to homocysteine. Homocysteine may be methylated to regenerate Met, in a B12 requiring reaction with N5-methyl-THF as the met ...
... involved in methylation reactions. Methylation reactions catalyzed by SAM yield S-adenosylhomocysteine and a methylated acceptor molecule. S-adenosylhomocysteine is hydrolyzed to homocysteine. Homocysteine may be methylated to regenerate Met, in a B12 requiring reaction with N5-methyl-THF as the met ...
Role of Carnitine in Lipid Metabolism
... In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the role of carnitine in the transport of longchain fatty acids into the matrix of the mitochondria was documented (2,3). Experimental work of the last 20 years has enhanced our knowledge of the role of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, carnitine acylcarnitine tran ...
... In the late 1950s and early 1960s, the role of carnitine in the transport of longchain fatty acids into the matrix of the mitochondria was documented (2,3). Experimental work of the last 20 years has enhanced our knowledge of the role of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I, carnitine acylcarnitine tran ...
anmol publications pvt. ltd.
... pyruvate to lactate (lactic acid) (e.g. in humans) or to ethanol plus carbon dioxide (e.g. in yeast). Other monosaccharides like galactose and fructose can be converted into intermediates of the glycolytic pathway. Aerobic In aerobic cells with sufficient oxygen, like most human cells, the pyruvate ...
... pyruvate to lactate (lactic acid) (e.g. in humans) or to ethanol plus carbon dioxide (e.g. in yeast). Other monosaccharides like galactose and fructose can be converted into intermediates of the glycolytic pathway. Aerobic In aerobic cells with sufficient oxygen, like most human cells, the pyruvate ...
ERT320 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING
... Chemical substances or combinations of chemical substances that are made by living things Can be broadly classified into three categories of sources: ...
... Chemical substances or combinations of chemical substances that are made by living things Can be broadly classified into three categories of sources: ...
2.1 Molecules to metabolim
... a metabolic pathway and breakdown each one into it’s component parts. This approach has been a very productive one. Our understanding of respiration (2.8) and photosynthesis (2.9) are good examples of the success of this approach. ...
... a metabolic pathway and breakdown each one into it’s component parts. This approach has been a very productive one. Our understanding of respiration (2.8) and photosynthesis (2.9) are good examples of the success of this approach. ...
Study Guide and Potential Essay Questions for Chapter 25
... hypothermia, Krebs’ cycle (TCA or citric acid cycle), lactic acid (lactate), metabolic rate, metabolic water, metabolism, minerals, mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane, NAD+/NADH + H+, nutrient, oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate-to-acetate step, reduction, substrate level phosphoryl ...
... hypothermia, Krebs’ cycle (TCA or citric acid cycle), lactic acid (lactate), metabolic rate, metabolic water, metabolism, minerals, mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane, NAD+/NADH + H+, nutrient, oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate-to-acetate step, reduction, substrate level phosphoryl ...
PowerPoint to accompany
... • lipase – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol • enterokinase – converts trypsinogen to trypsin • somatostatin – hormone that inhibits acid secretion by stomach • cholecystokinin – hormone that inhibits gastric glands, stimulates pancreas to release enzymes in pancreatic juice, stimulates ...
... • lipase – breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol • enterokinase – converts trypsinogen to trypsin • somatostatin – hormone that inhibits acid secretion by stomach • cholecystokinin – hormone that inhibits gastric glands, stimulates pancreas to release enzymes in pancreatic juice, stimulates ...
Liver
... -Chemically modifies the substances absorbed from the digestive tract before they reach the rest of the body -Removes toxins, pesticides, & carcinogens, converting them to less toxic forms -Regulates levels of steroid hormones -Produces most proteins found in plasma ...
... -Chemically modifies the substances absorbed from the digestive tract before they reach the rest of the body -Removes toxins, pesticides, & carcinogens, converting them to less toxic forms -Regulates levels of steroid hormones -Produces most proteins found in plasma ...
BIE 5810 - Chapter 5, Part I
... (1) Efficiency = 14,600 cal_ = 28% for lactic acid fermentation 52,000 cal (2) Efficiency in utilizing total energy potentially available from glucose: E= 14,600 cal__ = 2% (typical of fermentations) 686,.000 cal 1. (p. 139) TCA cycle main functions: 1. provide e (NADH) for electron transport chain ...
... (1) Efficiency = 14,600 cal_ = 28% for lactic acid fermentation 52,000 cal (2) Efficiency in utilizing total energy potentially available from glucose: E= 14,600 cal__ = 2% (typical of fermentations) 686,.000 cal 1. (p. 139) TCA cycle main functions: 1. provide e (NADH) for electron transport chain ...
The Digestive System
... – Na+ cotransported with sugars and amino acids – Cl- exchanged for bicarbonate reversing chloride-bicarbonate exchange that occurs in the stomach – iron and calcium absorbed as needed • iron absorption is stimulated by liver hormone hepcidin • absorptive cells bind ferrous ions (Fe2+) and internali ...
... – Na+ cotransported with sugars and amino acids – Cl- exchanged for bicarbonate reversing chloride-bicarbonate exchange that occurs in the stomach – iron and calcium absorbed as needed • iron absorption is stimulated by liver hormone hepcidin • absorptive cells bind ferrous ions (Fe2+) and internali ...
Slide 1
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
complete
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
... get them in our diet? • How are proteins digested and absorbed into the blood? How do other tissues and organs get the amino acids out of the blood? • What are plasma proteins and why are they important? Be able to give an example of a plasma protein. • Learn how amino acids can be used in • The syn ...
macromolecules
... nitrogen and phosphorus Monomer: Nucleotide (sugar, phosphate & nitrogen base) Polymer: Nucleic Acid Structure: Long chains of nucleotides found in a twisted or folded structure ...
... nitrogen and phosphorus Monomer: Nucleotide (sugar, phosphate & nitrogen base) Polymer: Nucleic Acid Structure: Long chains of nucleotides found in a twisted or folded structure ...
Other Pathways of Carbohydrate Metabolism Gluconeogenesis
... In fed state, glucose → glycogen and acetyl-CoA (fatty acid biosynthesis and fat storage) In fasted state, glycogen and protein → glucose Pathways are controlled by allosteric effectors and covalent modifications (hormonal control) of: hexokinase glucose-6-phosphatase phosphofructokinase-2/fructose- ...
... In fed state, glucose → glycogen and acetyl-CoA (fatty acid biosynthesis and fat storage) In fasted state, glycogen and protein → glucose Pathways are controlled by allosteric effectors and covalent modifications (hormonal control) of: hexokinase glucose-6-phosphatase phosphofructokinase-2/fructose- ...
Kreb`s Cycle - Montgomery College
... 7 A molecule of ATP is made from each 1,3-biphosphoglycerate as the phosphate added in step 6 is transferred to ADP 8 The molecule is reorganized through the relocation of the phosphate group ...
... 7 A molecule of ATP is made from each 1,3-biphosphoglycerate as the phosphate added in step 6 is transferred to ADP 8 The molecule is reorganized through the relocation of the phosphate group ...
Dietary n-6 and n-3 fatty acids in immunity and - Direct-MS
... and organ-specific differences for antioxidants, and suggested that the kidney, in terms of its fatty acid composition, is more resistant to dietary n-3 fatty acid influences. Fernandes et al. (1996) have also shown that feeding fish oil to the NZB x NZW F1 mouse increases programmed cell death of l ...
... and organ-specific differences for antioxidants, and suggested that the kidney, in terms of its fatty acid composition, is more resistant to dietary n-3 fatty acid influences. Fernandes et al. (1996) have also shown that feeding fish oil to the NZB x NZW F1 mouse increases programmed cell death of l ...
Mislocalization and inhibition of acetyl
... activates STAT6 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 6), which subsequently induces IGF inhibitory genes. It was not previously known how the binding of chromeceptin with MFP-2 blocks adipogenesis and activates STAT6. The results of the present study show that the chromeceptin–MFP-2 com ...
... activates STAT6 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 6), which subsequently induces IGF inhibitory genes. It was not previously known how the binding of chromeceptin with MFP-2 blocks adipogenesis and activates STAT6. The results of the present study show that the chromeceptin–MFP-2 com ...
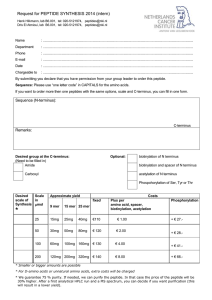
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
cell surface lipids and adhesion
... incorporated into the plasmalemmae of these neural retina cells. About 20 % of the plasmalemmal content of fatty acids can be turned over in 30'. Incorporation is mainly into phosphatidyl choline, serine and ethanolamine in both Rt and Ra positions. The plasmalemmae contain the enzymes to effect the ...
... incorporated into the plasmalemmae of these neural retina cells. About 20 % of the plasmalemmal content of fatty acids can be turned over in 30'. Incorporation is mainly into phosphatidyl choline, serine and ethanolamine in both Rt and Ra positions. The plasmalemmae contain the enzymes to effect the ...
Organic Chemistry for Biology
... carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and protein. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of cell membranes and waterproofing. Nucleic ...
... carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and protein. Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of cell membranes and waterproofing. Nucleic ...
Intro-Cell-Physiology
... – Plasma membrane encompasses the functional cell unit – Membranes segregate most other individual components of the cell • Nucleus • Organelles ...
... – Plasma membrane encompasses the functional cell unit – Membranes segregate most other individual components of the cell • Nucleus • Organelles ...