Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Summary
... (a) In respiration, glucose is broken down, hydrogen ions and electrons are removed by dehydrogenase enzymes and ATP is released. (b) The role of ATP is to transfer of energy and to phosphorylate molecules in respiration. (c) Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway. The breakdown of glucose to p ...
... (a) In respiration, glucose is broken down, hydrogen ions and electrons are removed by dehydrogenase enzymes and ATP is released. (b) The role of ATP is to transfer of energy and to phosphorylate molecules in respiration. (c) Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway. The breakdown of glucose to p ...
Unit 2 Metabolism and Survival Summary
... glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm is called glycolysis. The phosphorylation of intermediates in glycolysis in an energy investment phase leading to the direct generation of more ATP in an energy pay-off stage giving a net gain of ATP. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is broken down to an acety ...
... glucose to pyruvate in the cytoplasm is called glycolysis. The phosphorylation of intermediates in glycolysis in an energy investment phase leading to the direct generation of more ATP in an energy pay-off stage giving a net gain of ATP. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is broken down to an acety ...
Medical Biology Cellular Metabolism
... RBCs contain no mitochondria, so there is. The RBC is highly dependent upon glucose as its energy source. ATP is obtained only from breakdown of glucose with the production of lactate (anaerobic glycolysis). Glucose is transported through RBC membrane by facilitated diffusion. One molecule of glucos ...
... RBCs contain no mitochondria, so there is. The RBC is highly dependent upon glucose as its energy source. ATP is obtained only from breakdown of glucose with the production of lactate (anaerobic glycolysis). Glucose is transported through RBC membrane by facilitated diffusion. One molecule of glucos ...
Topic 6.1 2016 PP
... consume are much too large to be absorbed by the cells of the body, particularly the villi of the small intestine where absorption of molecules takes place. • As you will recall from topic 2 on the biological molecules, they are large molecules that need to be broken down into simpler components. Fo ...
... consume are much too large to be absorbed by the cells of the body, particularly the villi of the small intestine where absorption of molecules takes place. • As you will recall from topic 2 on the biological molecules, they are large molecules that need to be broken down into simpler components. Fo ...
phospholipids
... • There are at least two isozymes of PGH2 Synthase (COX-1 and COX-2) • COX-1 is constitutively expressed at low levels in many cell types • Specifically, COX-1 is known to be essential for maintaining the integrity of the gastrointestinal ...
... • There are at least two isozymes of PGH2 Synthase (COX-1 and COX-2) • COX-1 is constitutively expressed at low levels in many cell types • Specifically, COX-1 is known to be essential for maintaining the integrity of the gastrointestinal ...
chapter 19 addendum
... Treat this with mild acid, and the first amino acid is cleaved off, rearranging to form a phenylthiohydantoin. This can be compared to a standard, and the amino acid identified. Each amino acid is removed from the N terminus and identified this way… and the process is automated on a machine. ...
... Treat this with mild acid, and the first amino acid is cleaved off, rearranging to form a phenylthiohydantoin. This can be compared to a standard, and the amino acid identified. Each amino acid is removed from the N terminus and identified this way… and the process is automated on a machine. ...
Reading Guide for Week 4
... to harvest energy and produce precursor metabolites (through catabolism) that are then used by the cell to synthesize subunits which are used to build macromolecules which are used to build cell structures (through anabolism) all driven by the activity of enzymes. 3. A brief look at the diversity of ...
... to harvest energy and produce precursor metabolites (through catabolism) that are then used by the cell to synthesize subunits which are used to build macromolecules which are used to build cell structures (through anabolism) all driven by the activity of enzymes. 3. A brief look at the diversity of ...
Limits of Human Performance
... • ATP broken down to ADP and Pi – A buildup of ADP and Pi stimulate metabolism • A buildup of ADP also inhibits the breakdown of ATP • ATP ADP + Pi ...
... • ATP broken down to ADP and Pi – A buildup of ADP and Pi stimulate metabolism • A buildup of ADP also inhibits the breakdown of ATP • ATP ADP + Pi ...
Chapter 16 Citric Acid Cycle
... So not feely soluble enzymes, but highly organized with channeling of intermediates to make more efficient D. Some mutations in TCA cycle lead to Cancer You can read details if interested 16.4 The Glyoxylate Cycle The two steps PEP to pyruvate and pyruvate to acetyl CoA are strongly exothermic, and ...
... So not feely soluble enzymes, but highly organized with channeling of intermediates to make more efficient D. Some mutations in TCA cycle lead to Cancer You can read details if interested 16.4 The Glyoxylate Cycle The two steps PEP to pyruvate and pyruvate to acetyl CoA are strongly exothermic, and ...
7-cellular-respiration
... If ATP is not being used then the high concentration will inhibit the activity of phosphofructokinase which will slow down glycolysis. If ATP concentration decreases the enzyme will no longer be inhibited and glycolysis will speed up. ...
... If ATP is not being used then the high concentration will inhibit the activity of phosphofructokinase which will slow down glycolysis. If ATP concentration decreases the enzyme will no longer be inhibited and glycolysis will speed up. ...
Biology 12: Digestive System Review
... glucose to be taken into liver cells (and muscle cells) and then convert to glycogen adipose tissue uses glucose to form fat ii) blood glucose concentration is low. (2 marks) pancreas releases glucagon into blood glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver ...
... glucose to be taken into liver cells (and muscle cells) and then convert to glycogen adipose tissue uses glucose to form fat ii) blood glucose concentration is low. (2 marks) pancreas releases glucagon into blood glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver ...
6 Digestive System Provincial KEY
... • glucose to be taken into liver cells (and muscle cells) and then convert to glycogen • adipose tissue uses glucose to form fat ii) blood glucose concentration is low. (2 marks) • pancreas releases glucagon into blood • glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver ...
... • glucose to be taken into liver cells (and muscle cells) and then convert to glycogen • adipose tissue uses glucose to form fat ii) blood glucose concentration is low. (2 marks) • pancreas releases glucagon into blood • glycogen is converted to glucose in the liver ...
Amino Acids 14.5 * 14.8
... The two Amino Acids are joined together by an peptide bond. (the linking of two amino acids) Produces dipeptide. ...
... The two Amino Acids are joined together by an peptide bond. (the linking of two amino acids) Produces dipeptide. ...
Digestion
... occurs before food enters the stomach triggered by sight, smell or thought of food PNS nerve fibers traveling down the vagus nerve stimulates the mucous cells, chief cells, parietal cells, and G cells ...
... occurs before food enters the stomach triggered by sight, smell or thought of food PNS nerve fibers traveling down the vagus nerve stimulates the mucous cells, chief cells, parietal cells, and G cells ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... 14. Which of the following cofactors is required for the conversion of succinate to fumarate in the citric acid cycle? A) ATP B) Biotin C) FAD D) NAD+ E) NADP+ 15. The conversion of 1 mol of pyruvate to 3 mol of CO2 via pyruvate dehydrogenase and the citric acid cycle also yields _____ mol of NADH, ...
... 14. Which of the following cofactors is required for the conversion of succinate to fumarate in the citric acid cycle? A) ATP B) Biotin C) FAD D) NAD+ E) NADP+ 15. The conversion of 1 mol of pyruvate to 3 mol of CO2 via pyruvate dehydrogenase and the citric acid cycle also yields _____ mol of NADH, ...
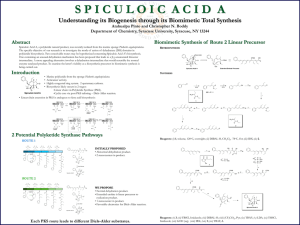
Total Synthesis of Spiculoic Acid A
... Spiculoic Acid A, a polyketide natural product, was recently isolated from the marine sponge Plakortis angulospiculatus. The specific objective of our research is to investigate the mode of action of dehydratase (DH) domains in polyketide biosynthesis. Two conceivable routes may be hypothesized conc ...
... Spiculoic Acid A, a polyketide natural product, was recently isolated from the marine sponge Plakortis angulospiculatus. The specific objective of our research is to investigate the mode of action of dehydratase (DH) domains in polyketide biosynthesis. Two conceivable routes may be hypothesized conc ...
e is nline ion any er.`
... chemical interest, because of the novelty of the compounds present, and human health interest because the arsenicals occur in many common foods. The highest arsenic concentrations are found in seafoods, and many studies have reported on the type of arsenic compounds present in such foods.1 The vast ...
... chemical interest, because of the novelty of the compounds present, and human health interest because the arsenicals occur in many common foods. The highest arsenic concentrations are found in seafoods, and many studies have reported on the type of arsenic compounds present in such foods.1 The vast ...
lec3.Preferencial energy. mac2010-09
... Released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis (especially the branched-chain amino acids which cannot be degraded by the liver, and are preferentially metabolized in muscle) Degraded to pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates energy production or fatty acid synthesis ...
... Released into the blood for all tissues to use in protein synthesis (especially the branched-chain amino acids which cannot be degraded by the liver, and are preferentially metabolized in muscle) Degraded to pyruvate, acetyl CoA, or TCA cycle intermediates energy production or fatty acid synthesis ...
New Product Highlights Monoclonal Anti
... Isotype: rat IgG2a Species Cross Reactivity: Human and mouse Shh Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is an important cell signaling molecule expressed during embryonic development. Shh is involved in the patterning of the developing embryonic nervous system, somite and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is releas ...
... Isotype: rat IgG2a Species Cross Reactivity: Human and mouse Shh Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is an important cell signaling molecule expressed during embryonic development. Shh is involved in the patterning of the developing embryonic nervous system, somite and limb. The N-terminal peptide of Shh is releas ...
3.2 Metabolism of cardiac muscle cell
... covers the remnant 30 %. Lactate is utilized as an energy substrate under the condition of increased muscular activity, during which the lactate concentration in blood augments rapidly. Ketone bodies and aminoacids are utilized exclusively under special pathological conditions (e.g. in diabetic keto ...
... covers the remnant 30 %. Lactate is utilized as an energy substrate under the condition of increased muscular activity, during which the lactate concentration in blood augments rapidly. Ketone bodies and aminoacids are utilized exclusively under special pathological conditions (e.g. in diabetic keto ...
Biochemistry
... A *Transport of fatty acids from the cytosol to the mitochondria B Transport of fatty acids from the fat depots to the tissues C Participation in one of the reactions of beta-oxidation of fatty acids D Fatty acid activation E Intracellular lipolysis activation ...
... A *Transport of fatty acids from the cytosol to the mitochondria B Transport of fatty acids from the fat depots to the tissues C Participation in one of the reactions of beta-oxidation of fatty acids D Fatty acid activation E Intracellular lipolysis activation ...