Lecture 18, Mar 5
... Phospholipids and transmembrane proteins constitute the core structure of biological membranes. The core of typical biological membranes contains approximately 70% lipid and 30% transmembrane protein. Because biological membranes are fluid at normal temperatures and have a pattern of transmembrane p ...
... Phospholipids and transmembrane proteins constitute the core structure of biological membranes. The core of typical biological membranes contains approximately 70% lipid and 30% transmembrane protein. Because biological membranes are fluid at normal temperatures and have a pattern of transmembrane p ...
Student PPT Notes
... as substrate/enzyme levels increase, the rxn rate increases until active sites of all enzymes are being continuously occupied by a new substrate Genes that code for enzymes can turn ________________(i.e. marathon runners after high-carb pre-competition meals) Some enzymes only synthesized at _ ...
... as substrate/enzyme levels increase, the rxn rate increases until active sites of all enzymes are being continuously occupied by a new substrate Genes that code for enzymes can turn ________________(i.e. marathon runners after high-carb pre-competition meals) Some enzymes only synthesized at _ ...
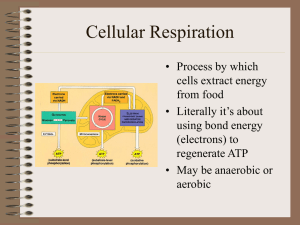
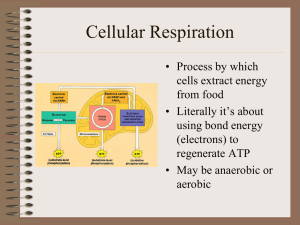
Cellular Respiration
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
Light RXNS: 1. What is the key event that starts off light reactions? 2.
... from the catabolism of one glucose molecule? (Assume ATP synthase can make 1 ATP from the motive force of 3.5 protons). 5. If you had to remove one of the membrane components involved in the elec ...
... from the catabolism of one glucose molecule? (Assume ATP synthase can make 1 ATP from the motive force of 3.5 protons). 5. If you had to remove one of the membrane components involved in the elec ...
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • 6C glucose split • to 2, 3C pyruvates • Yield 2 ATP • Yield 2 NADH • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
BI ACE_02 .
... Some amino acids have the additional carboxyl groups, and hence they are given the name of acidic amino acids. Some others that have additional amino groups are known as the basic amino acids. ...
... Some amino acids have the additional carboxyl groups, and hence they are given the name of acidic amino acids. Some others that have additional amino groups are known as the basic amino acids. ...
Macromolecules
... - Store genetic information and code for proteins -DNA—the nucleic acid, found in the nucleus of cells ...
... - Store genetic information and code for proteins -DNA—the nucleic acid, found in the nucleus of cells ...
Ch t 19 apter 19 The Citric Acid Cycle
... • The citric acid cycle is the source of starting materials for the biosynthesis of other compounds • If a component of the citric acid cycle is taken out for biosynthesis, it must be replaced • oxaloacetate, for example, is replaced by the carboxylation of pyruvate • A reaction that replenishes a c ...
... • The citric acid cycle is the source of starting materials for the biosynthesis of other compounds • If a component of the citric acid cycle is taken out for biosynthesis, it must be replaced • oxaloacetate, for example, is replaced by the carboxylation of pyruvate • A reaction that replenishes a c ...
biochem
... hyperventilate .Lab investigations reveal metabolic acidosis, increased anion gap and high lactate levels. These findings are best explained by low activity of ...
... hyperventilate .Lab investigations reveal metabolic acidosis, increased anion gap and high lactate levels. These findings are best explained by low activity of ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... - in fed state pyruvate produced from glycolysis (glucose) - in fed state 2/3 of carbon from pyruvate directed to fat synthesis for fuel storage (in adipose cells and lesser extent in liver) - aerobic muscle and heart pyruvate completely oxidized to CO2 for energy - pyruvate can be produced fr ...
... - in fed state pyruvate produced from glycolysis (glucose) - in fed state 2/3 of carbon from pyruvate directed to fat synthesis for fuel storage (in adipose cells and lesser extent in liver) - aerobic muscle and heart pyruvate completely oxidized to CO2 for energy - pyruvate can be produced fr ...
Appendix S6.
... dummy variables: KOALA study conventional, KOALA study alternative recruitment group vs. LISA study as reference), sex, maternal education, maternal smoking during pregnancy, exclusive breastfeeding for at least 3 months, but not for family history of atopy (asthma or allergy) to avoid overcorrectio ...
... dummy variables: KOALA study conventional, KOALA study alternative recruitment group vs. LISA study as reference), sex, maternal education, maternal smoking during pregnancy, exclusive breastfeeding for at least 3 months, but not for family history of atopy (asthma or allergy) to avoid overcorrectio ...
Lecture 23 – SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION: G
... Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate OR F26BP is the allosteric regulator that activates glycolysis in the liver and whose concentration is controlled by hormone in response to blood glucose. Identify one glycolytic enzyme that uses ATP and one that produces ATP. uses ATP: hexokinase OR glucokinase OR phosphof ...
... Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate OR F26BP is the allosteric regulator that activates glycolysis in the liver and whose concentration is controlled by hormone in response to blood glucose. Identify one glycolytic enzyme that uses ATP and one that produces ATP. uses ATP: hexokinase OR glucokinase OR phosphof ...
ESSENTIAL VITAMINS
... folic acid, B6 and B12, are critical for proper methylation, a biochemical process that helps convert the problematic amino acid metabolite homocysteine into the amino acids methionine and cysteine. This process is vital for supporting cardiovascular and mental health, a healthy nervous system, regu ...
... folic acid, B6 and B12, are critical for proper methylation, a biochemical process that helps convert the problematic amino acid metabolite homocysteine into the amino acids methionine and cysteine. This process is vital for supporting cardiovascular and mental health, a healthy nervous system, regu ...
Code Questions Answers 1. Write the reactions of glycolysis
... Inside the mitochondria HMG CoA is formed using 3 acetyl CoA as ………………………….. acetoacetate and free acetyl CoA. Acetoacetate is the parent ketone body. It is subsequently reduced by NADH dependent --------------------------------------------- This is known as ketoacidisis. ...
... Inside the mitochondria HMG CoA is formed using 3 acetyl CoA as ………………………….. acetoacetate and free acetyl CoA. Acetoacetate is the parent ketone body. It is subsequently reduced by NADH dependent --------------------------------------------- This is known as ketoacidisis. ...
2. How we study biology • The scientific method requires controls
... - Catabolism is the metabolic process that transforms complex molecules into their smaller component parts. The recycling of parts of the organism is one aspect of catabolism. If you are starving, catabolism will breakdown your lipid stores to form ATP. Molecular digestion of food e.g. proteins into ...
... - Catabolism is the metabolic process that transforms complex molecules into their smaller component parts. The recycling of parts of the organism is one aspect of catabolism. If you are starving, catabolism will breakdown your lipid stores to form ATP. Molecular digestion of food e.g. proteins into ...
Chapter 4
... •High [NADH] is indirectly equivalent to high[ATP]. This means that the cell is high in “energy”. •High [NAD+] or [ADP or AMP] means that the cell is low in “energy”. •These molecules (and others) can act as allosteric effectors stimulating or inhibiting allosteric enzymes which are usually at the b ...
... •High [NADH] is indirectly equivalent to high[ATP]. This means that the cell is high in “energy”. •High [NAD+] or [ADP or AMP] means that the cell is low in “energy”. •These molecules (and others) can act as allosteric effectors stimulating or inhibiting allosteric enzymes which are usually at the b ...
Cytochromes
... ► Chemiosmotic Potential or Proton-Motive Force (PMF) The electrochemical potential difference between the two sides of the IMM, that engage in active transport of Protons is called Proton-Motive Force (PMF). ► Proton motive force is the energy of the proton ...
... ► Chemiosmotic Potential or Proton-Motive Force (PMF) The electrochemical potential difference between the two sides of the IMM, that engage in active transport of Protons is called Proton-Motive Force (PMF). ► Proton motive force is the energy of the proton ...
File
... assembled by ribosomes (this process is called translation). The protein that you will translate is ADH (antidiuretic hormone). In this activity you will assemble the amino acids that are the building blocks for this protein. You will then simulate how the ribosome “reads” the sequence of amino acid ...
... assembled by ribosomes (this process is called translation). The protein that you will translate is ADH (antidiuretic hormone). In this activity you will assemble the amino acids that are the building blocks for this protein. You will then simulate how the ribosome “reads” the sequence of amino acid ...
Lecture content: How do amino acids differ from carbohydrates and
... (Ch22.2 Biosynthesis of amino acids) (Ch22.4 Biosynthesis and degradation of nucleotides) ...
... (Ch22.2 Biosynthesis of amino acids) (Ch22.4 Biosynthesis and degradation of nucleotides) ...
ESTAS SON ALGUNAS RESPUESTAS TÍPICAS A PREGUNTAS
... Draw and label a diagram of the digestive system. Award [1] for each structure correctly drawn and labelled. esophagus attached to both mouth and stomach; stomach j-shaped sac attached to esophagus and u-shaped portion of small intestine; large intestine wider diameter than small intestine, at ...
... Draw and label a diagram of the digestive system. Award [1] for each structure correctly drawn and labelled. esophagus attached to both mouth and stomach; stomach j-shaped sac attached to esophagus and u-shaped portion of small intestine; large intestine wider diameter than small intestine, at ...
video slide
... – Is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods – Can be used as surgical thread CH2O H ...
... – Is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods – Can be used as surgical thread CH2O H ...