Immunity
... and mechanisms that defend the host against infections by other organisms. •Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. ...
... and mechanisms that defend the host against infections by other organisms. •Innate immune systems provide immediate defense against infection, and are found in all classes of plant and animal life. ...
The Immune system - Locust Trace Veterinary Assistant Program
... • Drugs given to help treat this are antihistamines ...
... • Drugs given to help treat this are antihistamines ...
APC Mouse Anti-Human Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (CD143
... Store undiluted at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze. The monoclonal antibody was purified from tissue culture supernatant or ascites by affinity chromatography. The antibody was conjugated to APC under optimum conditions, and unconjugated antibody and free APC were r ...
... Store undiluted at 4°C and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze. The monoclonal antibody was purified from tissue culture supernatant or ascites by affinity chromatography. The antibody was conjugated to APC under optimum conditions, and unconjugated antibody and free APC were r ...
Anti-food polysaccharide antibody formation in Inflammatory
... Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 400 people per 100K populations in UK, which burdens the NHS with £720 million per annum (British Society of Gastroenterology, 2009). It has been shown that IBD patients produce an abnormally high level of ant ...
... Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting approximately 400 people per 100K populations in UK, which burdens the NHS with £720 million per annum (British Society of Gastroenterology, 2009). It has been shown that IBD patients produce an abnormally high level of ant ...
B. Cell-Mediated Immunity
... 5. Hapten – a small compound that is not antigenic unless it is attached to a carrier molecule. B. The Nature of Antibodies 1. Antibodies – proteins that are made in response to an antigen, that can recognize and bind to that antigen. 2. Highly specific for the antigen that stimulated their producti ...
... 5. Hapten – a small compound that is not antigenic unless it is attached to a carrier molecule. B. The Nature of Antibodies 1. Antibodies – proteins that are made in response to an antigen, that can recognize and bind to that antigen. 2. Highly specific for the antigen that stimulated their producti ...
File
... A mild disease was usually produced, followed by immunity to smallpox. Variolation was practiced in Europe, but was expensive and sometimes disease resulted (1 in 100 died), so many people were not treated. Edward Jenner, in 1796, deliberately introduced material from a cowpox lesion on a milkmaid t ...
... A mild disease was usually produced, followed by immunity to smallpox. Variolation was practiced in Europe, but was expensive and sometimes disease resulted (1 in 100 died), so many people were not treated. Edward Jenner, in 1796, deliberately introduced material from a cowpox lesion on a milkmaid t ...
Why Synthetic Peptide Vaccines?
... General Intro - MAbs Usage Today • Human and animal serum products are still used today; however, we now have new tools that allow for the development of totally human—monoclonal—antibody based therapeutic drugs. • There are now 12 monoclonal antibody based therapeutic products that are approved by ...
... General Intro - MAbs Usage Today • Human and animal serum products are still used today; however, we now have new tools that allow for the development of totally human—monoclonal—antibody based therapeutic drugs. • There are now 12 monoclonal antibody based therapeutic products that are approved by ...
Study guid Ch 15
... How are helper T cells activated? What kind of cell activates them and how does that cell present the antigenic peptide? What are the regions of the T cell receptor? What part of the receptor binds to and recognizes the antigen? Why do you think it’s important that this region is variable and unique ...
... How are helper T cells activated? What kind of cell activates them and how does that cell present the antigenic peptide? What are the regions of the T cell receptor? What part of the receptor binds to and recognizes the antigen? Why do you think it’s important that this region is variable and unique ...
Lecture notes
... The Y-shaped Ig molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains (held together by disulphide bonds) – two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The N-terminal regions of paired heavy and light chains form an antigen combining site. Each chain is composed of a sequence of globular ...
... The Y-shaped Ig molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains (held together by disulphide bonds) – two identical heavy chains and two identical light chains. The N-terminal regions of paired heavy and light chains form an antigen combining site. Each chain is composed of a sequence of globular ...
Lecture 5
... B - lymphocytes capable of producing antibodies that bind to the antigen present in secondary immune tissues (spleen, lymph nodes, Harderian glands, Peyer’s patches, Merkel’s diverticulum) start to divide. • Two populations: – Enlarge to become Plasma Cells actively producing antibodies (primary res ...
... B - lymphocytes capable of producing antibodies that bind to the antigen present in secondary immune tissues (spleen, lymph nodes, Harderian glands, Peyer’s patches, Merkel’s diverticulum) start to divide. • Two populations: – Enlarge to become Plasma Cells actively producing antibodies (primary res ...
File - LFHS AP Biology
... 3. Explain why only a few cell types have MHC II complexes on their cell surfaces: Only certain cells are Antigen-Presenting Cells that can bind to helper-T cells. 4. Explain what the term “clonal selection” refers to: The way only specific B and T-cells that recognize a particular antigen are stimu ...
... 3. Explain why only a few cell types have MHC II complexes on their cell surfaces: Only certain cells are Antigen-Presenting Cells that can bind to helper-T cells. 4. Explain what the term “clonal selection” refers to: The way only specific B and T-cells that recognize a particular antigen are stimu ...
File
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
Document
... Lymphocytes (white blood cells) - T-Cells: identify pathogens by its markers or “antigens” - B-cells: produce antibodies or proteins that destroy the pathogen ...
... Lymphocytes (white blood cells) - T-Cells: identify pathogens by its markers or “antigens” - B-cells: produce antibodies or proteins that destroy the pathogen ...
Washing - immunology.unideb.hu
... Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) derives its name from its first known site of origin, the prostate gland. Serum concentrations of PSA are elevated in patients with prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) and prostatitis. In addition, PSA serum levels appear to correlate with the volume a ...
... Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) derives its name from its first known site of origin, the prostate gland. Serum concentrations of PSA are elevated in patients with prostate cancer, benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) and prostatitis. In addition, PSA serum levels appear to correlate with the volume a ...
Hypersensitivity Reaction Types
... types, it is not antibody mediated but rather is a type of cell-mediated response. CD8 cytotoxic T cells and CD4 helper T cells recognise antigen in a complex with either type I or II major histocompatibility complex. The antigen-presenting cells in this case are macrophages and they release interle ...
... types, it is not antibody mediated but rather is a type of cell-mediated response. CD8 cytotoxic T cells and CD4 helper T cells recognise antigen in a complex with either type I or II major histocompatibility complex. The antigen-presenting cells in this case are macrophages and they release interle ...
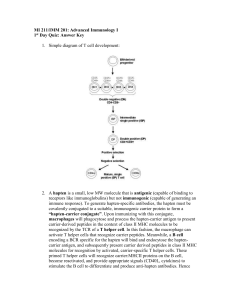
Adv
... 2. A hapten is a small, low MW molecule that is antigenic (capable of binding to receptors like immunoglobulins) but not immunogenic (capable of generating an immune response). To generate hapten-specific antibodies, the hapten must be covalently conjugated to a suitable, immunogenic carrier protein ...
... 2. A hapten is a small, low MW molecule that is antigenic (capable of binding to receptors like immunoglobulins) but not immunogenic (capable of generating an immune response). To generate hapten-specific antibodies, the hapten must be covalently conjugated to a suitable, immunogenic carrier protein ...
Chapter 37 - Leon County Schools
... the graph below, predict what probably bk Using happened to the memory B cell count after the First Exposure to Antigen X ...
... the graph below, predict what probably bk Using happened to the memory B cell count after the First Exposure to Antigen X ...
Figure-17 This diagram illustrates the various effector mechanism
... Figure-26 A summary of the various methods which parasites have evolved to avoid host defence mechanisms. DAF = decay accelerating factor. ...
... Figure-26 A summary of the various methods which parasites have evolved to avoid host defence mechanisms. DAF = decay accelerating factor. ...
IMMUNITY CELLULAR AND HUMORAL IMMUNITY
... proliferate to form daughter lymphocytes, processed in the same way as themselves. These B-cells then develop into short-lived plasma cells. (clones by mitosis) The plasma cells produce antibodies and release them into the circulation at the lymph nodes and blood. 3. Memory Some of the activated B-c ...
... proliferate to form daughter lymphocytes, processed in the same way as themselves. These B-cells then develop into short-lived plasma cells. (clones by mitosis) The plasma cells produce antibodies and release them into the circulation at the lymph nodes and blood. 3. Memory Some of the activated B-c ...
Crabtree_DOM_ResearchDay_Abstract
... immunization. Hematopoietic cell-specific PTPN22 encodes Lymphoid Phosphatase (Lyp), which regulates lymphocyte antigen receptor and Pattern Recognition Receptor (PRR) signaling. A PTPN22 variant R620W (LypW) predisposes to autoimmune and infectious disease, and confers altered signaling through ant ...
... immunization. Hematopoietic cell-specific PTPN22 encodes Lymphoid Phosphatase (Lyp), which regulates lymphocyte antigen receptor and Pattern Recognition Receptor (PRR) signaling. A PTPN22 variant R620W (LypW) predisposes to autoimmune and infectious disease, and confers altered signaling through ant ...
Phospho-regulation of human Protein Kinase Aurora-A
... Fig. S3. Specificity of the phospho-Thr288 Aurora-A-specific monoclonal antibody pA7.2. Three independent lines of evidence testified to the specificity of the monoclonal phospho-specific antibody pA7.2. Firstly, the antibody selectively recognized the phosphorylated peptide in ELISA screening assay ...
... Fig. S3. Specificity of the phospho-Thr288 Aurora-A-specific monoclonal antibody pA7.2. Three independent lines of evidence testified to the specificity of the monoclonal phospho-specific antibody pA7.2. Firstly, the antibody selectively recognized the phosphorylated peptide in ELISA screening assay ...
Immunology: Specific Immunity
... Dual Nature of the immune system • Humoral and cell mediated – Humoral refers to body fluids • Specifically antibodies: protein molecules dissolved in blood, body fluids, and secretions. • B lymphocytes are the source of antibodies – Cell mediated refers to the direct involvement of cells to attack ...
... Dual Nature of the immune system • Humoral and cell mediated – Humoral refers to body fluids • Specifically antibodies: protein molecules dissolved in blood, body fluids, and secretions. • B lymphocytes are the source of antibodies – Cell mediated refers to the direct involvement of cells to attack ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.