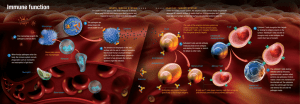
Topic 6.3 Defence against infectious disease
... sites – variable regions. The order of amino acids in the variable region determines the shape of the binding site ...
... sites – variable regions. The order of amino acids in the variable region determines the shape of the binding site ...
Do vaccines overwhelm the immune system?
... system to do what it is naturally meant to do – develop antibodies that can fight disease and keep your child healthy – vaccines make your child’s immune system even stronger! It’s natural for your child to be exposed to many different forms of bacteria and viruses every day, whether through eating, ...
... system to do what it is naturally meant to do – develop antibodies that can fight disease and keep your child healthy – vaccines make your child’s immune system even stronger! It’s natural for your child to be exposed to many different forms of bacteria and viruses every day, whether through eating, ...
microbio 14
... vacuoles, (6) intracellular traffic, and finally (7) exocytosis into either blood or subepithelial connective tissue What host-derived molecule causes death and sloughing of ciliary epitheliumin in particular? TNF-α, produced in response to peptidoglycan and LPS [tissue necrosis factor] ...
... vacuoles, (6) intracellular traffic, and finally (7) exocytosis into either blood or subepithelial connective tissue What host-derived molecule causes death and sloughing of ciliary epitheliumin in particular? TNF-α, produced in response to peptidoglycan and LPS [tissue necrosis factor] ...
DEFINING HYPERSENSITIVITY
... and are deposited in tissues, typically near basement membranes in places such as blood vessels, glomeruli, skin, joints, pleura, and pericardium. Larger immune complexes are quickly phagocytized by macrophages and removed, but small to intermediate complexes formed with antigen excess may escape re ...
... and are deposited in tissues, typically near basement membranes in places such as blood vessels, glomeruli, skin, joints, pleura, and pericardium. Larger immune complexes are quickly phagocytized by macrophages and removed, but small to intermediate complexes formed with antigen excess may escape re ...
Presentation slides - Yale School of Medicine
... Dendritic cells initiate antigenspecific immune responses • most efficient of all APCs ...
... Dendritic cells initiate antigenspecific immune responses • most efficient of all APCs ...
Immunity
... Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tissues where they are needed. ...
... Phagocytes are large white cells that can engulf and digest foreign invaders. They include monocytes, which circulate in the blood, and macrophages, which are found in tissues throughout the body, as well as neutrophils, cells that circulate in the blood but move into tissues where they are needed. ...
7. Protein Function
... either in monomeric (membraneboudn form) or a secreted form that is a cross-linked pentamer. IgA, found principaly in secretions (saliva, tears and milk), can be a monomer, dimer or trimer. ...
... either in monomeric (membraneboudn form) or a secreted form that is a cross-linked pentamer. IgA, found principaly in secretions (saliva, tears and milk), can be a monomer, dimer or trimer. ...
Notes: Chapter 39 Reading Guide (page 1022
... • B-cells mature into plasma cells and make antibodies against the specific pathogen • Memory B-cells and T-cells hang around in case the pathogen shows up again later – Quick response next time ...
... • B-cells mature into plasma cells and make antibodies against the specific pathogen • Memory B-cells and T-cells hang around in case the pathogen shows up again later – Quick response next time ...
Chapter 18 Quantitative and Thought Questions 18.1 Both would be
... destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins, or recruit NK cells in ADCC. The reason for these defects is that the sites to which compleme ...
... destroys cells directly (via the membrane attack complex) as well as by facilitating phagocytosis. 18.4 Antibodies would bind normally to antigen but may not be able to activate complement, act as opsonins, or recruit NK cells in ADCC. The reason for these defects is that the sites to which compleme ...
Chapter 19 Disorders of the Immune System Hypersensitivity Reactions
... • Histocompatibility antigens: Self antigens on cell surfaces • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC): Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens • Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
... • Histocompatibility antigens: Self antigens on cell surfaces • Major histocompatibility complex (MHC): Genes encoding histocompatibility antigens • Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex: MHC genes in humans ...
Q9 Describe how the body defends against infection
... o T cells à activated by the presentation of a microorganisms via the Major Histocompatibility complex MHC of an Antigen Presenting Cell. Several subtypes: § CD4 T cell • CD4 Th1 à activated by the ...
... o T cells à activated by the presentation of a microorganisms via the Major Histocompatibility complex MHC of an Antigen Presenting Cell. Several subtypes: § CD4 T cell • CD4 Th1 à activated by the ...
Immunity AIM: How does the immune system protect the body
... a. They are produced by the body in response to the presence of foreign substances. b. They may be produced in response to an antigen. c. They are nonspecific, acting against any foreign substance in the body. d. They may be produced by white blood cells. ...
... a. They are produced by the body in response to the presence of foreign substances. b. They may be produced in response to an antigen. c. They are nonspecific, acting against any foreign substance in the body. d. They may be produced by white blood cells. ...
Supplementary methods
... Antigen retrieval was performed, except in samples to determine Actin (clone HHF35) and Ly-6G/6C(Gr1). For PCNA, laminin and Nfib staining, sections were incubated at 95ºC in 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 15 min, followed by a 5 min cool down in the same buffer and 3 successive 5 min incubation ...
... Antigen retrieval was performed, except in samples to determine Actin (clone HHF35) and Ly-6G/6C(Gr1). For PCNA, laminin and Nfib staining, sections were incubated at 95ºC in 10 mM citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 15 min, followed by a 5 min cool down in the same buffer and 3 successive 5 min incubation ...
T cells - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... induce an immune response. Molecular size, complexity, and physical form are intrinsic properties of immunogens. Molecular size is an important component of immunogenicity. For example, low-molecularweight compounds called haptens cannot induce an immune response but can bind to antibodies. Because ...
... induce an immune response. Molecular size, complexity, and physical form are intrinsic properties of immunogens. Molecular size is an important component of immunogenicity. For example, low-molecularweight compounds called haptens cannot induce an immune response but can bind to antibodies. Because ...
Abstract
... Department of Life Science, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, 1 Oryong-dong, Puk-ku, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Attacking of self-components by auto-reactive T cells and/or B cells causes a damage or loss of organ function resulting in diverse immune disorders. Autonomic neuropathies often cau ...
... Department of Life Science, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, 1 Oryong-dong, Puk-ku, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Attacking of self-components by auto-reactive T cells and/or B cells causes a damage or loss of organ function resulting in diverse immune disorders. Autonomic neuropathies often cau ...
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CANCER CARE AND CURE
... such as those of lung cancer. Some cancer cells such as those of Molt-4 lymphoblastic leukemia express hCG, but are not killed by anti-hCG antibodies alone or in presence of Complement. These cancer cells are completely eliminated by using the antibody conjugated to Curcumin, a totally safe compound ...
... such as those of lung cancer. Some cancer cells such as those of Molt-4 lymphoblastic leukemia express hCG, but are not killed by anti-hCG antibodies alone or in presence of Complement. These cancer cells are completely eliminated by using the antibody conjugated to Curcumin, a totally safe compound ...
ABO BLOOD GROUPS
... there are three alternative alleles for one gene Discovered by Karl Landersteiner in the early 1900’s Controlled by a gene located on c-some 9. One combination of alleles in the ABO system exhibits codominance. ...
... there are three alternative alleles for one gene Discovered by Karl Landersteiner in the early 1900’s Controlled by a gene located on c-some 9. One combination of alleles in the ABO system exhibits codominance. ...
Defense Against Disease
... Blood contains white blood cells which kill any micro-organisms within the body ...
... Blood contains white blood cells which kill any micro-organisms within the body ...
Document
... c. Antibody forming cells are isolated from the mouse's spleen. d. Monoclonal antibodies produced by fusing single antibody-forming cells to tumor cells grown in culture which results in a hybridoma. e. Each hybridoma produces large quantities of identical antibody molecules. f. Once a monoclonal an ...
... c. Antibody forming cells are isolated from the mouse's spleen. d. Monoclonal antibodies produced by fusing single antibody-forming cells to tumor cells grown in culture which results in a hybridoma. e. Each hybridoma produces large quantities of identical antibody molecules. f. Once a monoclonal an ...
1) if the response to an antigen
... of soluble antibodies in the body fluids, it is called: Humoral immunity. 2) if the response is through cytotoxic or killer T cells, then the immunity is known as cell-mediated. These two mechanisms complement each other. The challenge for the immune system is to be able to provide antibodies to int ...
... of soluble antibodies in the body fluids, it is called: Humoral immunity. 2) if the response is through cytotoxic or killer T cells, then the immunity is known as cell-mediated. These two mechanisms complement each other. The challenge for the immune system is to be able to provide antibodies to int ...
Immune System - Iowa State University
... 11) Humoral immunity involves the production of___________________. 12)___ _________ __________________________________proteins are the molecules on your macrophages are used to display antigen fragments for detection by your T-lymphocytes. 13) In the Adaptive Immune System ____________________overs ...
... 11) Humoral immunity involves the production of___________________. 12)___ _________ __________________________________proteins are the molecules on your macrophages are used to display antigen fragments for detection by your T-lymphocytes. 13) In the Adaptive Immune System ____________________overs ...
The Immune Response
... • The T-cells then bind to B-cells causing them to divide and produce plasma cells and memory B cells • Plasma cells secrete antibodies • Memory B cells and antibodies stay in the bloodstream and attack and mark the antigens quickly for destruction by macrophages the next time they enter the body • ...
... • The T-cells then bind to B-cells causing them to divide and produce plasma cells and memory B cells • Plasma cells secrete antibodies • Memory B cells and antibodies stay in the bloodstream and attack and mark the antigens quickly for destruction by macrophages the next time they enter the body • ...
Immune System
... White blood cells • Some WBCs mark pathogens for destruction while others engulf microbes during an immune response • And yet others produce antibodies ...
... White blood cells • Some WBCs mark pathogens for destruction while others engulf microbes during an immune response • And yet others produce antibodies ...
Monoclonal antibody

Monoclonal antibodies (mAb or moAb) are monospecific antibodies that are made by identical immune cells that are all clones of a unique parent cell, in contrast to polyclonal antibodies which are made from several different immune cells. Monoclonal antibodies have monovalent affinity, in that they bind to the same epitope.Given almost any substance, it is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to that substance; they can then serve to detect or purify that substance. This has become an important tool in biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. When used as medications, the non-proprietary drug name ends in -mab (see ""Nomenclature of monoclonal antibodies""), and many immunotherapy specialists use the word mab anacronymically.