Chapter_20_Heart_Review
... 3. Left ventricle has the thickest wall due to work load 4. Chambers of the heart, atria and ventricle 5. Heart separations – septums and conary sulcus 6. Cardiac circulation – coronary artery and coronary sinus 7. Valves of the heart – tricuspid, bicuspid (mitral), pulmonary, aortic 8. Blood flow t ...
... 3. Left ventricle has the thickest wall due to work load 4. Chambers of the heart, atria and ventricle 5. Heart separations – septums and conary sulcus 6. Cardiac circulation – coronary artery and coronary sinus 7. Valves of the heart – tricuspid, bicuspid (mitral), pulmonary, aortic 8. Blood flow t ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... electrical connection between atria and ventricles ...
... electrical connection between atria and ventricles ...
Ch 11 Heart Physiology
... heart muscle results in fibrillation Fibrillation—a rapid, uncoordinated the heart muscle ...
... heart muscle results in fibrillation Fibrillation—a rapid, uncoordinated the heart muscle ...
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Arrhythmogenic
... In ARVC, the normal heart muscle tissue is replaced by fibrous or fatty tissue. This disturbs the electrical conduction system of the heart, usually resulting in a ventricular premature contraction (VPC). A ventricular premature contraction occurs when an abnormal electrical impulse originates from ...
... In ARVC, the normal heart muscle tissue is replaced by fibrous or fatty tissue. This disturbs the electrical conduction system of the heart, usually resulting in a ventricular premature contraction (VPC). A ventricular premature contraction occurs when an abnormal electrical impulse originates from ...
Origin and Conduction of the Heart Beat
... or (sino-atrial node [SA node]) in mammals. This structure contains a group of nerve cells near the junction of and known as the or with an intrinsic rhythmic rate of 40 to 60 beats per minute. This is the area of heart beat initiation. A wave of nervous excitation in the SA node causes the atria to ...
... or (sino-atrial node [SA node]) in mammals. This structure contains a group of nerve cells near the junction of and known as the or with an intrinsic rhythmic rate of 40 to 60 beats per minute. This is the area of heart beat initiation. A wave of nervous excitation in the SA node causes the atria to ...
Arrhythmia
... On physical exam, he has a regular tachycardia at 180, and monitor shows a regular, narrow-complex tachycardia. He denies chest pain. Midway through transport, he becomes less responsive, and his blood pressure drops as he starts sweating profusely. ...
... On physical exam, he has a regular tachycardia at 180, and monitor shows a regular, narrow-complex tachycardia. He denies chest pain. Midway through transport, he becomes less responsive, and his blood pressure drops as he starts sweating profusely. ...
Physiologic Basis and Mechanism of Cardiac Arrhythmias by Dr
... From SA node—Sinus arrhythmias From atrial muscle—atrial arrhythmias From AV node—junctional or nodal arrhythmias From ventricles---ventricular arrhythmias First three are known as SVT or supraventricular tachy arrhythmias. ...
... From SA node—Sinus arrhythmias From atrial muscle—atrial arrhythmias From AV node—junctional or nodal arrhythmias From ventricles---ventricular arrhythmias First three are known as SVT or supraventricular tachy arrhythmias. ...
Lucia is an 8 year old girl who is a patient of Dr. Paulson who
... However, after 16 days at Children’s she walked out neurologically normal. It really is a miracle! Turns out she had Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) where she can go into an arrhythmia if her heart rate gets too high. She now is on a beta blocker and has an implantable d ...
... However, after 16 days at Children’s she walked out neurologically normal. It really is a miracle! Turns out she had Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) where she can go into an arrhythmia if her heart rate gets too high. She now is on a beta blocker and has an implantable d ...
Slide ()
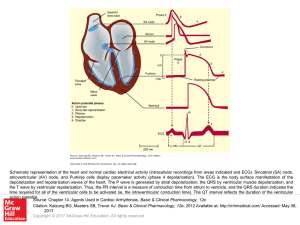
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
PBL- Case 1: Cardiac Arrhythmias Pre
... High prevalence of CAD, CHF and valvular disease and calcification (common in older patients) puts them at higher risk of atrial fibrillation. Cardiac valvular stenosis or regurgitation caused by either rheumatic or age related degenerative changes increases left atrial pressure and results in the e ...
... High prevalence of CAD, CHF and valvular disease and calcification (common in older patients) puts them at higher risk of atrial fibrillation. Cardiac valvular stenosis or regurgitation caused by either rheumatic or age related degenerative changes increases left atrial pressure and results in the e ...
• ECG paper: small box = 0.04 seconds • Normal PR interval = 0.12
... Review basic facts and principles, such as: ...
... Review basic facts and principles, such as: ...
Ventricular Fibrillation
... Supraventricular Arrythmias Arrhythmias that begin above the ventricles, such as in the upper chambers or atria. ...
... Supraventricular Arrythmias Arrhythmias that begin above the ventricles, such as in the upper chambers or atria. ...
Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)
... PVCs, or premature ventricular contractions, are “extra” heart beats that start in the lower portion of the heart. Nearly all of the 100,000 heart beats that occur each day start from the top part of the heart (the atria) that holds the “pacemaker” cells, which establish the heart rate. The normal p ...
... PVCs, or premature ventricular contractions, are “extra” heart beats that start in the lower portion of the heart. Nearly all of the 100,000 heart beats that occur each day start from the top part of the heart (the atria) that holds the “pacemaker” cells, which establish the heart rate. The normal p ...
Name_____________________________________ Per_____
... Explain how impulses travel through each of the following areas of the heart. 1) Sinoatrial node ...
... Explain how impulses travel through each of the following areas of the heart. 1) Sinoatrial node ...
pace-maker
... that trigger cardiac contraction, the sinoatrial node normally initiates it, simply because it generates impulses slightly faster than the other areas with pacemaker potential. Cardiac myocytes, like all muscle cells, have refractory periods following contraction during which additional contractions ...
... that trigger cardiac contraction, the sinoatrial node normally initiates it, simply because it generates impulses slightly faster than the other areas with pacemaker potential. Cardiac myocytes, like all muscle cells, have refractory periods following contraction during which additional contractions ...
Heart Conduction System
... • SA (Sinoatrial) Node (pacemaker)- - located in wall of Rt Atrium generates an electrical impulse that spreads out over both atria. • Both atria contract (syncytium) and stimulate the AV (atrioventricular) node to send an impulse. ...
... • SA (Sinoatrial) Node (pacemaker)- - located in wall of Rt Atrium generates an electrical impulse that spreads out over both atria. • Both atria contract (syncytium) and stimulate the AV (atrioventricular) node to send an impulse. ...
chapter ??
... For the practical you will be required to provide an answer for each ECG that includes the name of the ECG, what is the disorder, why it is abnormal, and give the rate when required. Be specific. Don’t overwrite with excess unnecessary information. We will review in class on _______.Until then go th ...
... For the practical you will be required to provide an answer for each ECG that includes the name of the ECG, what is the disorder, why it is abnormal, and give the rate when required. Be specific. Don’t overwrite with excess unnecessary information. We will review in class on _______.Until then go th ...
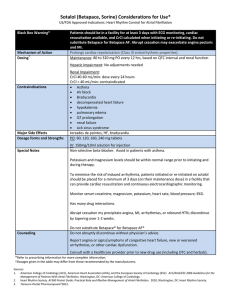
Sotalol Considerations for Use - American College of Cardiology
... CrCl 40-60 mL/min: dose every 24 hours CrCl < 40 mL/min: contraindicated Asthma AV block Bradycardia decompensated heart failure hypokalemia pulmonary edema QT prolongation renal failure sick sinus syndrome torsades de pointes, HF, bradycardia PO: 80, 120, 160, 240 mg tablets ...
... CrCl 40-60 mL/min: dose every 24 hours CrCl < 40 mL/min: contraindicated Asthma AV block Bradycardia decompensated heart failure hypokalemia pulmonary edema QT prolongation renal failure sick sinus syndrome torsades de pointes, HF, bradycardia PO: 80, 120, 160, 240 mg tablets ...
Control of the cardiac cycle
... Coordination of the heart • The sinoatrial node (SAN) (pacemaker) generates electrical activity at regular intervals. This causes the atrial cardiac muscles to contract (atrial systole) • The atrioventricular node (AVN) delays the electrical activity to allow blood to flow into the ventricles. • Th ...
... Coordination of the heart • The sinoatrial node (SAN) (pacemaker) generates electrical activity at regular intervals. This causes the atrial cardiac muscles to contract (atrial systole) • The atrioventricular node (AVN) delays the electrical activity to allow blood to flow into the ventricles. • Th ...
Slide ()
... of the mechanisms. A. Second-degree AV block is depicted with a 2:1 ratio. Alternate stimuli from the atria are blocked in the AV node, so the ventricles beat only half as fast as the atria. The only physical sign is a slow regular heartbeat with first sounds of equal intensity. B. Complete AV block ...
... of the mechanisms. A. Second-degree AV block is depicted with a 2:1 ratio. Alternate stimuli from the atria are blocked in the AV node, so the ventricles beat only half as fast as the atria. The only physical sign is a slow regular heartbeat with first sounds of equal intensity. B. Complete AV block ...
Familial Arrhythmia
... Cardiac arrhythmias are generally characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the heart that puts patients at high risk for embolic stroke and/or sudden cardiac death (SCD). Commonly recognized arrhythmic disorders include atrial fibrillation (AF), long QT syndrome (LQTS), catecholaminergic pol ...
... Cardiac arrhythmias are generally characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the heart that puts patients at high risk for embolic stroke and/or sudden cardiac death (SCD). Commonly recognized arrhythmic disorders include atrial fibrillation (AF), long QT syndrome (LQTS), catecholaminergic pol ...
Arrhythmias
... Preexcitation Syndrome – Wolff-Parkinson-White • AV conduction through the accessory pathway is faster than through the AV node ...
... Preexcitation Syndrome – Wolff-Parkinson-White • AV conduction through the accessory pathway is faster than through the AV node ...
Co-ordination of the Cardiac Cycle
... •Be able to interpret and explain electrocardiogram (ECG) traces, with reference to normal and abnormal heart activity ...
... •Be able to interpret and explain electrocardiogram (ECG) traces, with reference to normal and abnormal heart activity ...
Cardiac Arrhythmia Center - New York Hospital Queens
... As The Heart Hospital of Queens, we are committed to ensuring that the diagnostic and treatment options physicians prefer are available for their patients right here. In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Center’s Electrophysiology Laboratory, you will find the techniques and the technology to treat all types ...
... As The Heart Hospital of Queens, we are committed to ensuring that the diagnostic and treatment options physicians prefer are available for their patients right here. In the Cardiac Arrhythmia Center’s Electrophysiology Laboratory, you will find the techniques and the technology to treat all types ...
Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT)
... This is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to an abnormal “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart between the atria and the ventricles (heart chambers.) Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief - usually minutes in duration - but can be longer. Gene ...
... This is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to an abnormal “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart between the atria and the ventricles (heart chambers.) Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief - usually minutes in duration - but can be longer. Gene ...