EE 4BD4 Lecture 21 - McMaster University
... electrical cardiac stimulation cardiac • First electrostatic charges and later a-c and d-c currents • 1932 Alfred Hyman developed the first device to stimulate the heart electronically. Delivered 3 mA pulses directly to heart using needle electrodes • Coined the term pacemaker • 1947 Beck reported a ...
... electrical cardiac stimulation cardiac • First electrostatic charges and later a-c and d-c currents • 1932 Alfred Hyman developed the first device to stimulate the heart electronically. Delivered 3 mA pulses directly to heart using needle electrodes • Coined the term pacemaker • 1947 Beck reported a ...
Left Bundle Branch Block
... Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is an abnormality of the electrical conduction of the heart. There are two main conducting pathways in the heart, the left and the right bundle. In LBBB, the left conducting pathway no longer functions so electrical conduction is maintained through the right bundle. L ...
... Left bundle branch block (LBBB) is an abnormality of the electrical conduction of the heart. There are two main conducting pathways in the heart, the left and the right bundle. In LBBB, the left conducting pathway no longer functions so electrical conduction is maintained through the right bundle. L ...
Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
... abnormalities like Tetrology of Fallot, coarctation of the aorta, tricuspid atresia and transposition of the great vessels. In severe cases, treatment would involve surgical removal or ablation of one of the pathways. ...
... abnormalities like Tetrology of Fallot, coarctation of the aorta, tricuspid atresia and transposition of the great vessels. In severe cases, treatment would involve surgical removal or ablation of one of the pathways. ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
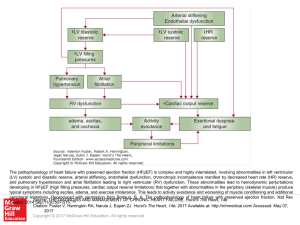
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
... The pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is complex and highly interrelated, involving abnormalities in left ventricular (LV) systolic and diastolic reserve, arterial stiffening, endothelial dysfunction, chronotropic incompetence manifest by decreased heart rate ...
Name:______ Per.______ Chapter 18: The Cardiovascular System
... _____________________. The first heart sound is a result of closure of the ______________________valves; closure of the ___________________ valves causes the second heart sound. The heart chambers that have just been filled when you hear the first heart sound are the ____________________. Immediatel ...
... _____________________. The first heart sound is a result of closure of the ______________________valves; closure of the ___________________ valves causes the second heart sound. The heart chambers that have just been filled when you hear the first heart sound are the ____________________. Immediatel ...
File
... • Etiology: the electrical impulse is formed in the SA node and conducted normally. • This is the normal rhythm of the heart; other rhythms that do not conduct via the typical pathway are called arrhythmias. ...
... • Etiology: the electrical impulse is formed in the SA node and conducted normally. • This is the normal rhythm of the heart; other rhythms that do not conduct via the typical pathway are called arrhythmias. ...
Heart Physiology part 1
... Without some unifying system to control them the heart would be an uncoordinated and inefficient pump ...
... Without some unifying system to control them the heart would be an uncoordinated and inefficient pump ...
Interpretation of Electrocardiogram findings
... rate drops below 45 beats per minute. Sinus Tachycardia 洞性頻脈 A rhythm in which more than the normal number of impulses arise from the sinus node. Rhythm is not of diagnostic significance unless the rate elevates above 130 beats per minute. Ectopic Atrial Rhythm, Atrioventricular Junctional Rhythm, W ...
... rate drops below 45 beats per minute. Sinus Tachycardia 洞性頻脈 A rhythm in which more than the normal number of impulses arise from the sinus node. Rhythm is not of diagnostic significance unless the rate elevates above 130 beats per minute. Ectopic Atrial Rhythm, Atrioventricular Junctional Rhythm, W ...
New Hope for Arrhythmias
... the ages of 50 to 70, and while many are not life-threatening, arrhythmias may require medical treatment and should be monitored by your physician. Left untreated, serious arrhythmias can lead to death. That’s why it’s important to research and understand all of your options when seeking help for an ...
... the ages of 50 to 70, and while many are not life-threatening, arrhythmias may require medical treatment and should be monitored by your physician. Left untreated, serious arrhythmias can lead to death. That’s why it’s important to research and understand all of your options when seeking help for an ...
Causes of Cardiac Arrhythmias
... the fibers that depolarizes first will repolarize first Causes: drugs, caffeine, smoking, lack of sleep, emotional irritations ...
... the fibers that depolarizes first will repolarize first Causes: drugs, caffeine, smoking, lack of sleep, emotional irritations ...
AED + CPR Save Lives
... that prevents the heart from pumping normal contraction rhythms in a heart having blood to all vital organs. dangerous arrhythmia or in cardiac arrest . ...
... that prevents the heart from pumping normal contraction rhythms in a heart having blood to all vital organs. dangerous arrhythmia or in cardiac arrest . ...
Electrocardiogram
... • Bundle of His • Located in the interventricular septum • Branches of the bundle of His carry electrical impulses to right and left ventricles and the Purkinje fibers ...
... • Bundle of His • Located in the interventricular septum • Branches of the bundle of His carry electrical impulses to right and left ventricles and the Purkinje fibers ...
ASD-Atrial Septal Defect
... Premature Ventricular Contractions, PVCs Premature Atrial Contractions, PACs ...
... Premature Ventricular Contractions, PVCs Premature Atrial Contractions, PACs ...
The Electrocardiogram
... Before the heart can contract it must be stimulated. This is accomplished through a specialized network of cells called the conduction system. There are numerous “pacemaker” cells to stimulate the heart to contract. ...
... Before the heart can contract it must be stimulated. This is accomplished through a specialized network of cells called the conduction system. There are numerous “pacemaker” cells to stimulate the heart to contract. ...
N120 Quiz #1 (20 Items): REVIEW BLUEPRINT
... Sinus tachycardia has a normal sinus rhythm, but the SA node fires at a rate greater than 100 beats/minute as a result of vagal inhibition or sympathetic stimulation. o Clinical associations. Sinus tachycardia is associated with physiologic and psychologic stressors such as exercise, fever, pain, hy ...
... Sinus tachycardia has a normal sinus rhythm, but the SA node fires at a rate greater than 100 beats/minute as a result of vagal inhibition or sympathetic stimulation. o Clinical associations. Sinus tachycardia is associated with physiologic and psychologic stressors such as exercise, fever, pain, hy ...
The Cardiovascular System: Part 1
... 1) Describe the structures of the heart that are responsible for regulating the movement of blood from one chamber to the next. 2) The pathway by which action potentials from the sinoatrial node travel through the heart is important for the normal function of the heart. Describe the conduction pathw ...
... 1) Describe the structures of the heart that are responsible for regulating the movement of blood from one chamber to the next. 2) The pathway by which action potentials from the sinoatrial node travel through the heart is important for the normal function of the heart. Describe the conduction pathw ...
Grade 11 Biology Worksheet -2 ( Circulatory system) a)Give one
... 2) Capillaries are found in _______ circulatory system and _____________ and in the open one. 3) The parasympathetic nerve fibres supplying the heart ____________ cardiac activity. 4) The ‘dub’ sound of heart is caused due to the closure of _______________. 5) The mitral valve has __________ cusps, ...
... 2) Capillaries are found in _______ circulatory system and _____________ and in the open one. 3) The parasympathetic nerve fibres supplying the heart ____________ cardiac activity. 4) The ‘dub’ sound of heart is caused due to the closure of _______________. 5) The mitral valve has __________ cusps, ...
Atrial Tachycardia Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter AV Nodal Reentrant
... frequently in the aftermath of a heart attack or myocardial infarction. Scar tissue in the ventricles will alter many local electrical properties and set up conditions favorable to formation of a local electrical circuit. Under specific circumstances, the circuit can be activated leading to a rapid ...
... frequently in the aftermath of a heart attack or myocardial infarction. Scar tissue in the ventricles will alter many local electrical properties and set up conditions favorable to formation of a local electrical circuit. Under specific circumstances, the circuit can be activated leading to a rapid ...
Atrial Tachycardia
... frequently in the aftermath of a heart attack or myocardial infarction. Scar tissue in the ventricles will alter many local electrical properties and set up conditions favorable to formation of a local electrical circuit. Under specific circumstances, the circuit can be activated leading to a rapid ...
... frequently in the aftermath of a heart attack or myocardial infarction. Scar tissue in the ventricles will alter many local electrical properties and set up conditions favorable to formation of a local electrical circuit. Under specific circumstances, the circuit can be activated leading to a rapid ...
HT, LDL , DM, etc
... unexpected loss of heart function, breathing and consciousness. Sudden cardiac arrest usually results from an electrical disturbance in your heart that disrupts its pumping action, stopping blood flow to the rest of your body. Sudden cardiac arrest is different from a heart attack, which occurs when ...
... unexpected loss of heart function, breathing and consciousness. Sudden cardiac arrest usually results from an electrical disturbance in your heart that disrupts its pumping action, stopping blood flow to the rest of your body. Sudden cardiac arrest is different from a heart attack, which occurs when ...
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... depend on ____________ _____________ impulses, specialized tissue causes _______________ in only one direction (_______ to _______); enforces contraction rate of approximately 75 beats per minute (even if all nerve connections are severed, the heart continues to beat rhythmically) cardiac conduction ...
... depend on ____________ _____________ impulses, specialized tissue causes _______________ in only one direction (_______ to _______); enforces contraction rate of approximately 75 beats per minute (even if all nerve connections are severed, the heart continues to beat rhythmically) cardiac conduction ...
Properties of Cardiac Muscle
... Frank Starling Law of the Heart • This law states that with in limits the force of ventricular contraction is directly proportional to the end-diastolic length of the cardiac muscle fibers which inturn is closely related to ...
... Frank Starling Law of the Heart • This law states that with in limits the force of ventricular contraction is directly proportional to the end-diastolic length of the cardiac muscle fibers which inturn is closely related to ...
Presentation
... Sinus Bradycardia - Occurs when you have a regular rhythm and normal waveforms, but the rate is slower than 60 bpm. ...
... Sinus Bradycardia - Occurs when you have a regular rhythm and normal waveforms, but the rate is slower than 60 bpm. ...