* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HT, LDL , DM, etc
Baker Heart and Diabetes Institute wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
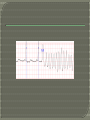
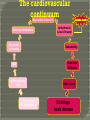
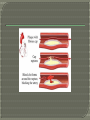
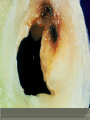
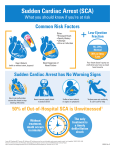
“natural death from cardiac causes heralded by abrupt loss of consciousness” Sudden cardiac arrest is the sudden, unexpected loss of heart function, breathing and consciousness. Sudden cardiac arrest usually results from an electrical disturbance in your heart that disrupts its pumping action, stopping blood flow to the rest of your body. Sudden cardiac arrest is different from a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to a portion of the heart is blocked. However, a heart attack can sometimes trigger an electrical disturbance that leads to sudden cardiac arrest. Sudden cardiac arrest is a medical emergency. If not treated immediately, it causes sudden cardiac death. With fast, appropriate medical care, survival is possible. Administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) — or even just compressions to the chest — can improve the chances of survival until emergency personnel arrive. The cardiovascular continuum Myocardial infarction Coronary thrombosis Myocardial ischaemia Arrhythmia & Loss of muscle Remodelling Ventricular dilatation CAD Atherosclerosis LVH Risk factors (HT, LDL, DM, etc) Heart failure Endstage heart disease CONGENITAL Electrical Heart muscle Valvar arterial ACQUIRED Atheromatous coronary disease Hypertension Post viral Rheumatic heart disease Rare < 15 years of age 15-35 years:congenital electrical atheromatous >35 years atheromatous hypertension For those identified to be high risk for SCD Per cent proportional risk reduction A 28 % Reduction in LDL-C significantly reduces cardiovascular events Major corronary events Coronary deaths Cardiovascular All-cause deaths deaths •0 •-5 •-10 •-15 -21 % •-20 •-25 •-30 -29 % -27 % -31 % •-35 Meta-analysis illustrating the beneficial effects of statin therapy LaRosa et al, JAMA 1999; 282: 2340-2346 Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)