* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrocardiogram
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
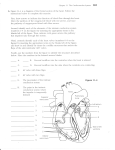
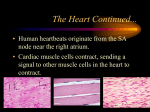
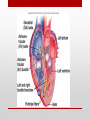
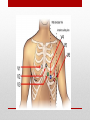
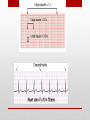
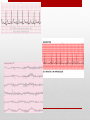
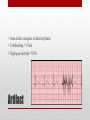
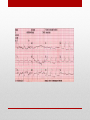
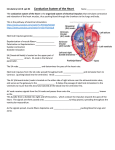
Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Allied Health II • Primarily from blood turbulence caused by closing of the heart valves • 4 heart sounds • 1st 2 are loud enough to be heard • Auscultation – listening to sounds within the body Heart Sounds • 1st sound • Louder and longer than the 2nd sound • Created by blood turbulence • Associated with the closure of the AV valves soon after ventricular systole begins Lubb (S1) • 2nd Sound • Shorter and not as loud as the first • Sound created by blood turbulence • Associated with closure of the semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole Dupp (S2) • Not normally loud enough to be heard • S3 associated with rapid ventricular filling • S4 associated with atrial contractions Heart Sounds (S3 and S4) • Lubb, dupp, pause, lubb, dupp, pause, lubb dupp, pause • As heart rate increases, pause interval shortens Cycle (at rest) • SA Node – located in right atrium • Natural pacemaker • Begin each wave of muscle contraction in the heart • Impulse in right atrium spreads over the muscles of both atria, causing them to contract simultaneously Electrical Activity • Atrioventricular Node • Impulses from SA node travel to AV node • Located on floor of right atrium, near septum • AV node transmits impulses on to the bundle of His. Electrical Activity • Bundle of His • Located in the interventricular septum • Branches of the bundle of His carry electrical impulses to right and left ventricles and the Purkinje fibers • Purkinje Fibers • Stimulation of purkinje fibers causes ventricles to contract simutaneously, forcing blood into aorta and pulmonary arteries Electrical Activity • Recording of the electrical changes that accompany each cardiac cycle • Composite of action potentials produced by all the heart muscle fibers during each heartbeat • Electrocardiograph – instrument used to record the changes of an electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) Electrocardiogram • First • Small upward wave • Represents atrial depolarization • Spreads from SA node throughout both atria • Atrial contraction P Wave • • • • • 2nd wave Begins as downward deflection Continues as a large, upright, triangular wave Ends as downward wave Represents onset of ventricular depolarization • Spread of wave through the ventricles • Ventricular contraction QRS Complex • Signifies ventricular repolarization • Relaxing & refilling of ventricles T Wave • • • • • • • • 10 Electrodes being placed Place limb leads 1st V1 – Right sternal border, 4th intercostal space V2 – Left sternal border, 4th intercostal space V4 – 5th intercostal space on left midclavicular line V3 – evenly placed between V2 and V4 V6 – left mid-axillary V5 – evenly spaced between V4 and V6 How to Apply the Leads • https://www.pinterest.com/pin/63472675973700293/ How to Apply the Leads • 6-second strip method • • • • Count number of QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10 30 big blocks = 6 seconds Less accurate Go-to method for irregular rhythms • Big block method • Count the number of big blocks in between 2 QRS waves and divide into 300 • More accurate • There are 300 big blocks in 1 minute How to Calculate the HR • A normal EKG (regular beats at 60-100bpm) is called = Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) • Sinus arrhythmia – rate increases with inhalation (common in children and some adults) • Ventricular Fibrillation – Vfib, life threatening! No cardiac output, ventricles are fluttering. Lethal if not reversed in 3-5 mins EKG • https://www.pinterest.com/pin/343188434080423067/ Possible Heart Rhythms • Interference seen on the monitor or rhythm strip • May look like wandering or fuzzy baseline • Can be caused by patient movement, poor electrode connection, improper grounding, faulty equipment Artifact • Some artifact can appear as lethal arrythmias • Toothbrushing = V-Tach • Tapping on electrode = V-Fib Artifact





















![Cardio Review 4 Quince [CAPT],Joan,Juliet](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008476689_1-582bb2f244943679cde904e2d5670e20-150x150.png)