04 Lecture - 3 Cardiac Arrhythmia-2-25-2
... Atrial tachycardia Atrial fibrilation Atrial flutter ...
... Atrial tachycardia Atrial fibrilation Atrial flutter ...
Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion Atrial fibrillation They are
... The main objectives of atrial fibrillation treatment are; to slow down the heart rate; to restore and maintain normal heart rhythm; and to prevent stroke. Defibrillator is a regular treatment for life threatening cardiac arrhythmias and fibrillation; it depolarizes the myocardium, ends the arrhythmi ...
... The main objectives of atrial fibrillation treatment are; to slow down the heart rate; to restore and maintain normal heart rhythm; and to prevent stroke. Defibrillator is a regular treatment for life threatening cardiac arrhythmias and fibrillation; it depolarizes the myocardium, ends the arrhythmi ...
Atrial Arrhythmias Atrial fibrillation
... is 100-160/min • Symptoms may occur with rapid heart rates including; weakness, fatigue, dizziness, or palpitations. • Sinus tachycardia is often temporary, occurring under stresses from exercise, strong emotions, fever, dehydration, thyrotoxicosis, anemia and heart failure. • If necessary, beta-blo ...
... is 100-160/min • Symptoms may occur with rapid heart rates including; weakness, fatigue, dizziness, or palpitations. • Sinus tachycardia is often temporary, occurring under stresses from exercise, strong emotions, fever, dehydration, thyrotoxicosis, anemia and heart failure. • If necessary, beta-blo ...
Electrocardiography
... Blocked Coronary Artery • depending on the amount of damage, conductive system may be impaired. • electrical impulses do not travel across dead tissue. ...
... Blocked Coronary Artery • depending on the amount of damage, conductive system may be impaired. • electrical impulses do not travel across dead tissue. ...
Conductivity and Rythm in Children - Easymed.club
... it could mean that the heart beats faster than normal (tachycardia), very fast (flutter), fast and with no regularity (fibrillation), slower than normal (bradycardia), or that it has isolated early beats (premature beats). While true arrhythmias are not very common, when they do occur they can be se ...
... it could mean that the heart beats faster than normal (tachycardia), very fast (flutter), fast and with no regularity (fibrillation), slower than normal (bradycardia), or that it has isolated early beats (premature beats). While true arrhythmias are not very common, when they do occur they can be se ...
4_control_of_heart_contraction
... • The heart is Myogenic so does not need impulses from the nervous system • This means that the cardiac muscle can generate its own contraction independently from the rest of the body • Contraction occurs in an organised manner and the heart acts as a functional unit ...
... • The heart is Myogenic so does not need impulses from the nervous system • This means that the cardiac muscle can generate its own contraction independently from the rest of the body • Contraction occurs in an organised manner and the heart acts as a functional unit ...
Cardiac Conduction System
... from the SA node travels here in about .04 seconds, this allows for the atria to contract and fill the ventricles with blood, then the AV node “fires” an impulse to the myocardium of the ventricles ...
... from the SA node travels here in about .04 seconds, this allows for the atria to contract and fill the ventricles with blood, then the AV node “fires” an impulse to the myocardium of the ventricles ...
Cardiac Arrhythmia www.AssignmentPoint.com Cardiac arrhythmia
... Most arrhythmias can be effectively treated. Treatments may include medications, medical procedures such as a pacemaker, and surgery. Medications for a fast heart rate may include beta blockers or agents that attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm such as procainamide. This later group may have mo ...
... Most arrhythmias can be effectively treated. Treatments may include medications, medical procedures such as a pacemaker, and surgery. Medications for a fast heart rate may include beta blockers or agents that attempt to restore a normal heart rhythm such as procainamide. This later group may have mo ...
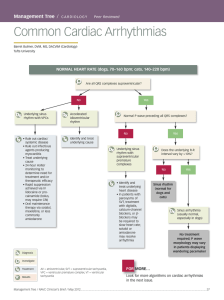
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
AV Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)
... A type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to a “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart located in the region of the AV node (part of the normal electrical conduction system of the heart). Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief, usually minutes in duratio ...
... A type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). This is related to a “short circuit” in the electrical connections of the heart located in the region of the AV node (part of the normal electrical conduction system of the heart). Episodes of fast heart rates tend to be brief, usually minutes in duratio ...
ECG - Derriford ED
... 2. What does the T wave on ECG represent? 3. Describe how to measure HR on 12 Lead ECG. 4. Which Heart Block presents with a prolonged P-R interval? 5. How can you tell the difference between an atrial or a ventricular premature conduction? 6. What HR may be on the cardiac monitor if patient is in P ...
... 2. What does the T wave on ECG represent? 3. Describe how to measure HR on 12 Lead ECG. 4. Which Heart Block presents with a prolonged P-R interval? 5. How can you tell the difference between an atrial or a ventricular premature conduction? 6. What HR may be on the cardiac monitor if patient is in P ...
Development of High Precession Dominant Frequency
... nutrients and oxygen to sustain the organs. Normal heartbeat requires precise synchronization of electrical impulses passing through portions of the heart tissue. When regular and rhythmic impulses are broken, cardiac arrhythmias occur. And ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation ( ...
... nutrients and oxygen to sustain the organs. Normal heartbeat requires precise synchronization of electrical impulses passing through portions of the heart tissue. When regular and rhythmic impulses are broken, cardiac arrhythmias occur. And ventricular tachycardia (VT) and ventricular fibrillation ( ...
RECENT TRENDS IN TREATMENT OF ARRHYTHMIAS
... little is known about it electrophysiologic properties, and more studies are still needed. Some of them e.g. pranolium may be of help in protection in patients who are at high risk of sudden coronary death. II. Non Pharmacologic Treatment. 1. Cardiac pace makers: are electronic devices that delivers ...
... little is known about it electrophysiologic properties, and more studies are still needed. Some of them e.g. pranolium may be of help in protection in patients who are at high risk of sudden coronary death. II. Non Pharmacologic Treatment. 1. Cardiac pace makers: are electronic devices that delivers ...
Heart Rate notes
... What Makes the Heart Beat? 2. AV Node (atrioventricular node) 1. Located in wall between right atrium and right ventricle 2. Delays spreading the electrical impulses for 0.1 seconds to ensure the atria are completely empty 3. Sends impulses to specialized muscle fibers and Purkinje fibers, which co ...
... What Makes the Heart Beat? 2. AV Node (atrioventricular node) 1. Located in wall between right atrium and right ventricle 2. Delays spreading the electrical impulses for 0.1 seconds to ensure the atria are completely empty 3. Sends impulses to specialized muscle fibers and Purkinje fibers, which co ...
Heart Physiology
... • Sinoatrial (SA) node – pacemaker "sinus rhythm". • Atrioventricular (AV) node • AV Bundle • Bundle branches • Purkinje fibers ...
... • Sinoatrial (SA) node – pacemaker "sinus rhythm". • Atrioventricular (AV) node • AV Bundle • Bundle branches • Purkinje fibers ...
Gabie Gomez - Labmongers2
... Class III: (Cordarone) Antiarrhymic drug that convert atrial fibrillation or flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conducti ...
... Class III: (Cordarone) Antiarrhymic drug that convert atrial fibrillation or flutter to normal sinus rhythm. Class IV:(Calan) Antiarrhymic drug that inhibit the movement of calcium through channels across the myocardial cell membrane and vascular smooth muscle. By reducing the calcium flow, conducti ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
... Postoperative automatic junctional tachycardia 8 hours after complete repair of AV septal defect in a 3-month-old infant. Using the V1−V2−V3 montage from a standard electrocardiographic recording device, the device cables corresponding to V1 and V2 are connected to the two temporary atrial epicardia ...
... Postoperative automatic junctional tachycardia 8 hours after complete repair of AV septal defect in a 3-month-old infant. Using the V1−V2−V3 montage from a standard electrocardiographic recording device, the device cables corresponding to V1 and V2 are connected to the two temporary atrial epicardia ...
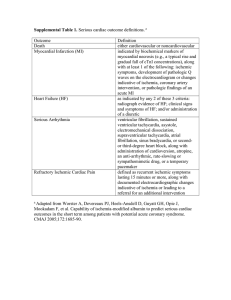
Supplemental Table 1
... ventricular fibrillation, sustained ventricular tachycardia, asystole, electromechanical dissociation, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, or secondor third-degree heart block, along with administration of cardioversion, atropine, an anti-arrhythmic, rate-slowing or ...
... ventricular fibrillation, sustained ventricular tachycardia, asystole, electromechanical dissociation, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, sinus bradycardia, or secondor third-degree heart block, along with administration of cardioversion, atropine, an anti-arrhythmic, rate-slowing or ...
Heartbeat
... What Makes the Heart Beat? 2. AV Node (atrioventricular node) 1. Located in wall between right atrium and right ventricle 2. Delays spreading the electrical impulses for 0.1 seconds to ensure the atria are completely empty 3. Sends impulses to specialized muscle fibers and Purkinje fibers, which co ...
... What Makes the Heart Beat? 2. AV Node (atrioventricular node) 1. Located in wall between right atrium and right ventricle 2. Delays spreading the electrical impulses for 0.1 seconds to ensure the atria are completely empty 3. Sends impulses to specialized muscle fibers and Purkinje fibers, which co ...
Pre-Lecture Quiz
... 1. The sinoatrial (SA) node, with an inherent firing rate of 60 to 100 impulses per minute, is considered the primary pacemaker of the heart. 2. Afterload refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole. 3. Hypertension is defined as a systolic BP that ...
... 1. The sinoatrial (SA) node, with an inherent firing rate of 60 to 100 impulses per minute, is considered the primary pacemaker of the heart. 2. Afterload refers to the degree of stretch of the ventricular cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole. 3. Hypertension is defined as a systolic BP that ...
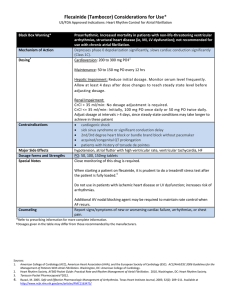
Flecainide Considerations for Use
... 2nd/3rd degree heart block or bundle brand block without pacemaker acquired/congenital QT prolongation patients with history of torsade de pointes hypotension, atrial flutter with high ventricular rate, ventricular tachycardia, HF PO: 50, 100, 150mg tablets Close monitoring of this drug is req ...
... 2nd/3rd degree heart block or bundle brand block without pacemaker acquired/congenital QT prolongation patients with history of torsade de pointes hypotension, atrial flutter with high ventricular rate, ventricular tachycardia, HF PO: 50, 100, 150mg tablets Close monitoring of this drug is req ...
cardio 2 - Iowa State University
... 2. A heartbeat originates with the depolarization of __________________________ cells at the ___________________________ also called the _______________________. The electrical signal is transmitted to the ____________________________ which connects the ____________________ and _____________________ ...
... 2. A heartbeat originates with the depolarization of __________________________ cells at the ___________________________ also called the _______________________. The electrical signal is transmitted to the ____________________________ which connects the ____________________ and _____________________ ...
Slide ()
... Positive signal-averaged electrocardiogram in a patient with sustained ventricular tachycardia. All three measured parameters are abnormal. Filtered QRS duration (DUR) is 136 ms, and the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage of the last 40 ms of the QS complex is 4.37 μV. LAS, low-amplitude signal. Reprodu ...
... Positive signal-averaged electrocardiogram in a patient with sustained ventricular tachycardia. All three measured parameters are abnormal. Filtered QRS duration (DUR) is 136 ms, and the root-mean-square (RMS) voltage of the last 40 ms of the QS complex is 4.37 μV. LAS, low-amplitude signal. Reprodu ...
Cardiac Arrhythmia - An-Najah National University
... Atrial fibrillation: the atria quiver rather than contract normally because of rapid and irregular electrical signals in the heart. Beside the abnormal heart beat, there is also a risk that blood will pool in the atria, possibly causing the formation of blood clots. ...
... Atrial fibrillation: the atria quiver rather than contract normally because of rapid and irregular electrical signals in the heart. Beside the abnormal heart beat, there is also a risk that blood will pool in the atria, possibly causing the formation of blood clots. ...
Atrial Flutter
... Definition: Well-organised but overly rapid contractions of the atrium of the heart ...
... Definition: Well-organised but overly rapid contractions of the atrium of the heart ...