* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion Atrial fibrillation They are
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
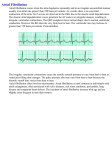
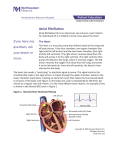
Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion Atrial fibrillation They are characterized by rapid atrial contractions that only incompletely pump blood into the ventricles. This result into irregular and often rapid heart rhythm, the arrhythmias result from abnormal electrical impulses in the heart, multiple impulses travels through the atria at the same time. Blood tends to stagnate in the incompletely emptied atria and is therefore more likely to clot. When clot moves to the left ventricle, they may be embolized to the brain causing stroke. Symptoms Common symptoms includes palpitations, which are sensations of a racing, uncomfortable, irregular heart beat; decreased blood pressure; weakness; lightheadedness; confusion; shortness of breath and chest pain. Some patients are with no symptoms until the condition is discovered during a physical exam. Causes; Hyperthyroidism; alcohol use; pulmonary embolism; pneumonia Heart conditions predisposing one to a fibrillation are: heart valve disease which may arise as a result of infection, injuries, degeneration, or congenital abnormality, infections such as infective endocarditis, and rheumatic fever; hypertrophy of the left ventricle caused by stress, heart muscle injury, disease, or neurohormones; cardiomyopathy – a chronic disease of the heart muscle, in which the muscle is abnormally enlarged, thickened. The weakened heart muscle losses it’s power to pump blood effectively, resulting to irregular heartbeats; SA node malfunction; and pericarditis which is the accumulation of fluid between the heart’s pericardia mostly caused by viral infections. Treatment The main objectives of atrial fibrillation treatment are; to slow down the heart rate; to restore and maintain normal heart rhythm; and to prevent stroke. Defibrillator is a regular treatment for life threatening cardiac arrhythmias and fibrillation; it depolarizes the myocardium, ends the arrhythmia and allows normal sinus rhythm to be restored by the heart’s natural pacemaker. An artificial pacemaker is an electronic device that prevents slow heartbeats, and may reduce the likelihood of atrial fibrillation in a small number of patients. The artificial pacemaker takes the place of the "natural pacemaker," the SA node, supplying electrical impulses to keep the heart beating in a normal rhythm when the SA node no longer can. It can be used in conjunction with radiofrequency ablation of the AV node, that creates a complete block between the atria and ventricle, the ventricle becomes dependent on the artificial pacemaker on the atria. Drugs – Digoxin (Lanoxin) The primary beneficial effect of digoxin is thought to be an increase in myocardial contractility – known as positive inotropic effect. This occurs in addition to the inhibition of sodium – potassium adenosine triphosphate pump. The effect of the inhibition of this enzyme – complex results in an increase in cellular sodium and calcium concentration – leading to an enhanced myocardial contraction. Digoxin also acts on the cholinergic stimulation via the vagus nerve of the PNS, this leads to increased diastolic filling between heartbeats, in addition to a reduced heart rate. Vagal tone is also believed to increase sensitivity of cardiac baroreceptors, which reduces sympathetic stimulation from the SNS. Specific to atrial fibrillation, negative dromotropic effect decreases automaticity at the SA node, decreased AV nodal conduction, reduced conductivity at the bundle of his, and prolongation of the atrial and ventricular refractory periods. Digoxin also leads to a better tolerance of exercise, improved quality of life, and improved symptoms controls, among others. Sources: http://www.emedicinehealth.com/atrial_fibrillation/page8_em.htm http://en.wikipedia.org Pharmacology and the Nursing process 6th edition Fundamentals of anatomy and physiology 8th edition Haron Kirikiru Wk 4 discussion