Introduction to Neuroscience
... Neurons and glia The neuron doctrine Classification of neurons Anatomy of the brain (forebrain) Support and nourishment for the brain – ...
... Neurons and glia The neuron doctrine Classification of neurons Anatomy of the brain (forebrain) Support and nourishment for the brain – ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 39. The ____________________ division dominates control of many visceral organ effectors under normal, everyday conditions. 40. The ________________________ division serves as the emergency or stress system (fight or flight) in the body. 41. What is the difference between multipolar, bipolar, and un ...
... 39. The ____________________ division dominates control of many visceral organ effectors under normal, everyday conditions. 40. The ________________________ division serves as the emergency or stress system (fight or flight) in the body. 41. What is the difference between multipolar, bipolar, and un ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
Structure and Function of The Cell
... • The cells eventually group together to form tissues • Tissues come together to form organs • Organs form organ systems and organ system form the organism. Cells tissues organs organ systems ORGANISM ...
... • The cells eventually group together to form tissues • Tissues come together to form organs • Organs form organ systems and organ system form the organism. Cells tissues organs organ systems ORGANISM ...
C48 Nervous System
... system, vary depending on function. Glia or supporting cells – more numerous than neurons; provide structure in nervous system, protect, insulate, and assist. Features of neurons: Cell body – contains nucleus and other organelles Processes – increase distance over which cells can conduct o Den ...
... system, vary depending on function. Glia or supporting cells – more numerous than neurons; provide structure in nervous system, protect, insulate, and assist. Features of neurons: Cell body – contains nucleus and other organelles Processes – increase distance over which cells can conduct o Den ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
Study Guide
... The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping acro ...
... The part of the brain that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping acro ...
U of L adult stem cell research
... to walk across a rope, loses its footing and falls. Then a rat that had the same injury scurries across the rope without a problem, just weeks after an injection containing adult stem cells from a human nose that were transformed into nerve cells. The rats are part of a line of groundbreaking resear ...
... to walk across a rope, loses its footing and falls. Then a rat that had the same injury scurries across the rope without a problem, just weeks after an injection containing adult stem cells from a human nose that were transformed into nerve cells. The rats are part of a line of groundbreaking resear ...
Parkinson disease
... Lipofuscin: Lipofuscin are brown pigment granules representing lipidcontaining residues of lysosomal digestion and considered one of the aging or "wear and tear" pigments; found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, adrenals, nerve cells, and ganglion cells. PHF: Paired helical filaments (PHF) are abn ...
... Lipofuscin: Lipofuscin are brown pigment granules representing lipidcontaining residues of lysosomal digestion and considered one of the aging or "wear and tear" pigments; found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, adrenals, nerve cells, and ganglion cells. PHF: Paired helical filaments (PHF) are abn ...
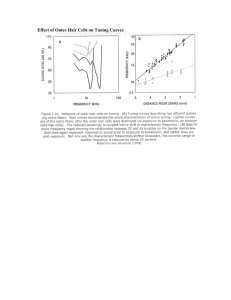
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... Converting a complex sound wave into electrode-stimulus patterns requires several steps. At left is a 100-millisecond portion of the waveform for the syllable "sa," including the junction between the "s" and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with t ...
... Converting a complex sound wave into electrode-stimulus patterns requires several steps. At left is a 100-millisecond portion of the waveform for the syllable "sa," including the junction between the "s" and "a." In this example, the input wave is filtered into four frequency bands (the band with t ...
graded potentials
... • P cells in the retina (also known as midget ganglion cells) project to the parvocellular layers (3-6) of LGN • M cells in the retina (also known as parasol cells) project to the magnocellular (ventral most) layers (1-2) of the LGN • Intercalated layers are termed koniocellular (dustlike or tiny ce ...
... • P cells in the retina (also known as midget ganglion cells) project to the parvocellular layers (3-6) of LGN • M cells in the retina (also known as parasol cells) project to the magnocellular (ventral most) layers (1-2) of the LGN • Intercalated layers are termed koniocellular (dustlike or tiny ce ...
The Neuron
... Supporting Cells Although neurons are typically defined as nerve cells, they are not actually the only cells in the nervous system. In fact, they are supported by a large number of other cells apply named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the support ...
... Supporting Cells Although neurons are typically defined as nerve cells, they are not actually the only cells in the nervous system. In fact, they are supported by a large number of other cells apply named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the support ...
Ageing and the nervous system
... • Dementia is a deterioration of intellectual functions affecting orientation, memory and judgement. The principal causes of Dementia are Alzheimer’s disease and multiple infarcts in the brain. • Alzheimer’s disease is degenerative condition of the brain in which some nerve cells gradually lose fun ...
... • Dementia is a deterioration of intellectual functions affecting orientation, memory and judgement. The principal causes of Dementia are Alzheimer’s disease and multiple infarcts in the brain. • Alzheimer’s disease is degenerative condition of the brain in which some nerve cells gradually lose fun ...
Introduction 1. Definition 1.1 Stem cells are those cells which are
... 1.1 Stem cells are those cells which are capable of dividing and renewing themselves for long period, unspecialized and capable of giving rise to specialized cell types. Comment: use the term differentiating into rather than giving rise to You might want to rephrase it as : stem cells are cells that ...
... 1.1 Stem cells are those cells which are capable of dividing and renewing themselves for long period, unspecialized and capable of giving rise to specialized cell types. Comment: use the term differentiating into rather than giving rise to You might want to rephrase it as : stem cells are cells that ...
Chapter 12- CNS and epidermis
... • The long-held belief that neurons were fully determined at birth is incorrect•Evidence for neuronal stem cells exists ...
... • The long-held belief that neurons were fully determined at birth is incorrect•Evidence for neuronal stem cells exists ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... Demyelinating Disease – Multiple sclerosis is characterized by sharply circumscribed plaques in which myelin is either gone or within foamy macrophages. Reactive astrocytes and preserved axons are also present. Trauma – Trauma can cause superficial contusions, hemorrhage at any site (epidural, subdu ...
... Demyelinating Disease – Multiple sclerosis is characterized by sharply circumscribed plaques in which myelin is either gone or within foamy macrophages. Reactive astrocytes and preserved axons are also present. Trauma – Trauma can cause superficial contusions, hemorrhage at any site (epidural, subdu ...
Neuronal Development
... If the neuropores do not close correctly, there will be neurological problems ...
... If the neuropores do not close correctly, there will be neurological problems ...
Neural stem cells - STEMCELL Technologies
... NSCs are located within two regions of the adult human and rodent brain (green): the subgranular zone of the hippocampus and the subventricular zone of the striatum2. Adult NSCs generate new neurons throughout life that integrate into hippocampal and olfactory circuits and are thought to be importan ...
... NSCs are located within two regions of the adult human and rodent brain (green): the subgranular zone of the hippocampus and the subventricular zone of the striatum2. Adult NSCs generate new neurons throughout life that integrate into hippocampal and olfactory circuits and are thought to be importan ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.