CNS DEVELOPMENT - University of Kansas Medical Center
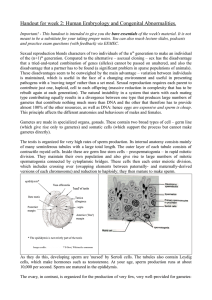
... Other cells lose contact with the basement membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limitin ...
... Other cells lose contact with the basement membrane and will migrate past the ependymal cells to form a new outer layer of densely packed cells collectively called the: Mantle layer: Cells that make up the mantle layer are: NEUROBLASTS. Note that mantle layer is still covered by the external limitin ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... close to that of humans, what we learn through ethical studies of nonhuman primates brings us closer to human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alon ...
... close to that of humans, what we learn through ethical studies of nonhuman primates brings us closer to human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alon ...
Nolte – Chapter 1 (Introduction to the Nervous
... (everything else). o Macroglia Oligodentrocytes produce internodes on multiple axons(upwards of 10) Astrocytes will sit inside these internodes at the nodes of Ranvier. ...
... (everything else). o Macroglia Oligodentrocytes produce internodes on multiple axons(upwards of 10) Astrocytes will sit inside these internodes at the nodes of Ranvier. ...
The Nervous System The master and
... The Nervous System The master _________________ and _________________ system of the body Method of communication? _________________ impulses The Three Overlapping Functions It uses millions of sensory receptors to _________________ _________________ called _________________ inside and outside the bo ...
... The Nervous System The master _________________ and _________________ system of the body Method of communication? _________________ impulses The Three Overlapping Functions It uses millions of sensory receptors to _________________ _________________ called _________________ inside and outside the bo ...
Neuro2
... 1) Neurons, Glia (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), Ependymal Cells, and CNS macrophages are the cells found in the CNS. 2) Cells lining the neural tube which are pseudostratisfied columnar epithelium make up the entire CNS (and obviously the cellular components). 3) A specific population of neurons ...
... 1) Neurons, Glia (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), Ependymal Cells, and CNS macrophages are the cells found in the CNS. 2) Cells lining the neural tube which are pseudostratisfied columnar epithelium make up the entire CNS (and obviously the cellular components). 3) A specific population of neurons ...
science guide 2016-Final2.indd
... what molecules are needed and how signals move throughout the brain. At the same time, he learns how diseases such as schizophrenia or Parkinson’s might alter these patterns. The Innovations and Discoveries • Sejnowski discovered the role of astrocytes, a type of brain cell, in producing unique brai ...
... what molecules are needed and how signals move throughout the brain. At the same time, he learns how diseases such as schizophrenia or Parkinson’s might alter these patterns. The Innovations and Discoveries • Sejnowski discovered the role of astrocytes, a type of brain cell, in producing unique brai ...
Slide ()
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
Click here to view a labelled image of the Knitted Retina
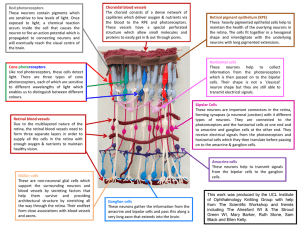
... to amacrine and ganglion cells at the other end. They receive electrical signals from the photoreceptors and horizontal cells which they then translate before passing on to the amacrine & ganglion cells. ...
... to amacrine and ganglion cells at the other end. They receive electrical signals from the photoreceptors and horizontal cells which they then translate before passing on to the amacrine & ganglion cells. ...
ppt - Le Moyne College
... things: surgically remove the tissue and/or use radiation to kill cancer cells. Why can’t brain tumors be treated like other cancers by using chemotherapy? • Does a brain tumor really involve brain tissue? • What kind of cells form the largest number found in the brain? ...
... things: surgically remove the tissue and/or use radiation to kill cancer cells. Why can’t brain tumors be treated like other cancers by using chemotherapy? • Does a brain tumor really involve brain tissue? • What kind of cells form the largest number found in the brain? ...
Ch 11 Part 1 - Groch Biology
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
... Supporting cells found in the CNS are called neuroglia. ___ _______________ Neurons are mitotic. ___ ____________________ Schwann cells and satellite cells are found only in the CNS. ___ ________________ Ependymal cells show irritability and conductivity. ___ ____________________ Almost 50% of the v ...
Stem Cell Basics
... three primary germ layers of the embryo (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). Capable of integrating into all fetal tissues during development. (Mouse ES cells maintained in culture for long periods can still generate any tissue when they are reintroduced into an embryo to generate a chimeric animal.) ...
... three primary germ layers of the embryo (endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). Capable of integrating into all fetal tissues during development. (Mouse ES cells maintained in culture for long periods can still generate any tissue when they are reintroduced into an embryo to generate a chimeric animal.) ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... biologic essentials to keep cell alive Dendrites: fibers that project out of the cell body, receiving info from other ...
... biologic essentials to keep cell alive Dendrites: fibers that project out of the cell body, receiving info from other ...
- Catalyst
... Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (Oct-4 missing) • SKPs also express neural crest cell makers, but, surprisingly, not Ret ...
... Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc (Oct-4 missing) • SKPs also express neural crest cell makers, but, surprisingly, not Ret ...
Genes and Prenatal Development
... This explains why one drop of blood, skin cell or piece of hair can be used to test for DNA. ...
... This explains why one drop of blood, skin cell or piece of hair can be used to test for DNA. ...
Cell Specialization
... Examples of Cell Specialization 2. Red blood cells: – Carry oxygen throughout body – Flattened disks so that they can easily flow through blood vessels ...
... Examples of Cell Specialization 2. Red blood cells: – Carry oxygen throughout body – Flattened disks so that they can easily flow through blood vessels ...
PDF
... for regenerative medicine, but they also offer a means of studying cell differentiation, and hence development, ex vivo. Here, Stephen Duncan and co-workers analyse the differentiation of hESCs to probe the molecular mechanisms that underlie human hepatocyte differentiation (see p. 4143). Using a pr ...
... for regenerative medicine, but they also offer a means of studying cell differentiation, and hence development, ex vivo. Here, Stephen Duncan and co-workers analyse the differentiation of hESCs to probe the molecular mechanisms that underlie human hepatocyte differentiation (see p. 4143). Using a pr ...
to get the file - Chair of Computational Biology
... So does it occur in the cortex also? So far we haven’t seen it under normal conditions. It’s been claimed in other areas as well, and we’re not saying that it doesn’t happen at very, very low frequency or under damaged conditions, but we haven’t seen it. I’m still open to the idea, however, since we ...
... So does it occur in the cortex also? So far we haven’t seen it under normal conditions. It’s been claimed in other areas as well, and we’re not saying that it doesn’t happen at very, very low frequency or under damaged conditions, but we haven’t seen it. I’m still open to the idea, however, since we ...
Scientific Papers using Accutase/Accumax Efficient
... Assessment of six different collagenase-based methods to isolate feline pancreatic islets. Res Vet Sci 2009,Dec,01;87(3):367-72; Publication Type: Journal Article Research in veterinary science, Zini, Franchini, Guscetti, Osto, Kaufmann, Ackermann, Lutz, Reusch, Clinic for Small Animal Internal Medi ...
... Assessment of six different collagenase-based methods to isolate feline pancreatic islets. Res Vet Sci 2009,Dec,01;87(3):367-72; Publication Type: Journal Article Research in veterinary science, Zini, Franchini, Guscetti, Osto, Kaufmann, Ackermann, Lutz, Reusch, Clinic for Small Animal Internal Medi ...
the nervous system
... • An impulse begins when it is stimulated either by another neuron or the environment • The impulse is sent through many neurons and cells • The space between the cells is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help the impulse cross over the synapse ...
... • An impulse begins when it is stimulated either by another neuron or the environment • The impulse is sent through many neurons and cells • The space between the cells is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help the impulse cross over the synapse ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.