Study Questions - Nervous System
... 33. What forms the blood-brain barrier? What molecules can pass through this barrier easily? (11.7) 34. White portions of the CNS consist of ______________________ while grey portions consisr of ___________________.(p258) 35. Brain anatomy: ventricles, hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain, meninges, cere ...
... 33. What forms the blood-brain barrier? What molecules can pass through this barrier easily? (11.7) 34. White portions of the CNS consist of ______________________ while grey portions consisr of ___________________.(p258) 35. Brain anatomy: ventricles, hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain, meninges, cere ...
Neuro1
... Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All neurons and supporting cells are derived from the ectoderm. As the notochord develops in embryonic development, it included the overlying ectoderm to form a neuroectoderm that thickens and becomes a neural plate. ...
... Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All neurons and supporting cells are derived from the ectoderm. As the notochord develops in embryonic development, it included the overlying ectoderm to form a neuroectoderm that thickens and becomes a neural plate. ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... hence the disease cannot be cured. There is no effective drug for relieving symptoms, and no prospect of one in the near ...
... hence the disease cannot be cured. There is no effective drug for relieving symptoms, and no prospect of one in the near ...
Slide 1
... are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
... are responsible for the reception, transmission, processing of stimuli; the triggering of certain cell activities; the release of neurotransmitters and other informational molecules. ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
... Aim: 2 Parts of the nervous system: the CNS Synapse – _____ At end of axon a chemical is released, crosses the synapse and binds to the dendrite on the other side to begin again CNS – _____ PNS – _____ Brain coordinates all body activities except _____ 3 parts, 100 billion neurons o cerebrum – ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
WangCellTableHW_JW
... Communicate with endothelial cells via signals. Cells full of hemoglobin. Sort of bowl shaped. No nucleus or mitochondria. Large white blood cells. Flexible cell membranes Contractile muscle cells that respond to nerve endings Located on inner ventricular walls of heart. Very branched, thin cells. ...
... Communicate with endothelial cells via signals. Cells full of hemoglobin. Sort of bowl shaped. No nucleus or mitochondria. Large white blood cells. Flexible cell membranes Contractile muscle cells that respond to nerve endings Located on inner ventricular walls of heart. Very branched, thin cells. ...
Slide ()
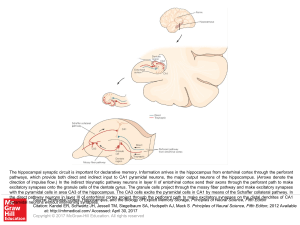
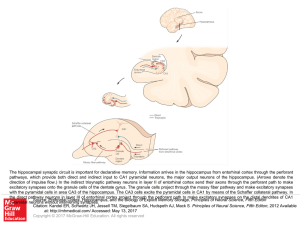
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Development
... • Nerve Growth Factor: Sympathetic & Ch14 basal forebrain neurons. • Neurotrophic Factors: BDNF, FGF, GDNF. • Each derived from cultured cells (sympathetic neurons, fibroblasts, glia, brain, etc.) and act on special receptors. ...
... • Nerve Growth Factor: Sympathetic & Ch14 basal forebrain neurons. • Neurotrophic Factors: BDNF, FGF, GDNF. • Each derived from cultured cells (sympathetic neurons, fibroblasts, glia, brain, etc.) and act on special receptors. ...
THERE ARE THREE PRINCIPLES: 1. Cells are the basic unit of life
... made of cells and their products 3. New cells are made by old cells dividing into two ...
... made of cells and their products 3. New cells are made by old cells dividing into two ...
FINAL241NSCC
... B. Name the region of the brain that initiates voluntary movement. ______________________________ C. The dopamine releasing neurons of Parkinson’s patients are damaged and eventually die. If dopamine normally binds to sodium-gated channels on post-synaptic neurons, then explain how AP initiation in ...
... B. Name the region of the brain that initiates voluntary movement. ______________________________ C. The dopamine releasing neurons of Parkinson’s patients are damaged and eventually die. If dopamine normally binds to sodium-gated channels on post-synaptic neurons, then explain how AP initiation in ...
Name
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
... 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS 16. a chemical which diffuses across the synapse in order to affect a postsynaptic neuron 17. stimulus strength NOT strong enough to cause a response 18. when these “ ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Carries information to another neuron or muscle cell. Often relatively long. Single (one per neuron). Conducts action potential ...
... Carries information to another neuron or muscle cell. Often relatively long. Single (one per neuron). Conducts action potential ...
Payton
... • ventricles produce 2x more neurons than necessary. unused neurons progressively die by apoptosis ◦ babies have more neurons than adults Neural development: new cells in the adult • there is neurogenesis in the adult brain. in rats: hippocampus (learning and memory) and olfactory bulb (sense of sme ...
... • ventricles produce 2x more neurons than necessary. unused neurons progressively die by apoptosis ◦ babies have more neurons than adults Neural development: new cells in the adult • there is neurogenesis in the adult brain. in rats: hippocampus (learning and memory) and olfactory bulb (sense of sme ...
histology of nervous tissue
... Dendrites – cellular process (extension) – carries impulses toward the cell body ...
... Dendrites – cellular process (extension) – carries impulses toward the cell body ...
Subventricular zone

The subventricular zone (SVZ) is a paired brain structure situated throughout the lateral walls of the lateral ventricles. It is composed of four distinct layers of variable thickness and cell density, as well as cellular composition. Along with the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus, the SVZ is one of two places where neurogenesis has been found to occur in the adult mammalian brain.