Gene Cloning
... of an eukaryotic gene, and cloning long fragments is difficult, it is sometimes desirable to work only with the expressed sequences (exons) ...
... of an eukaryotic gene, and cloning long fragments is difficult, it is sometimes desirable to work only with the expressed sequences (exons) ...
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
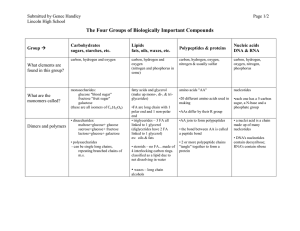
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
Chapter 2
... • Promoter is the specific region of the DNA that bound to RNA polymerase for efficient transcription. • Two highly conserved, separate nucleotide blocks make up the promoter of the E. coli lac operon. • These blocked are designated -10 and -35 upstream of the mRNA start site +1. •Mutations in the ...
... • Promoter is the specific region of the DNA that bound to RNA polymerase for efficient transcription. • Two highly conserved, separate nucleotide blocks make up the promoter of the E. coli lac operon. • These blocked are designated -10 and -35 upstream of the mRNA start site +1. •Mutations in the ...
Prokaryotes, Viruses, and Protistans
... Viral DNA usually becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome. ...
... Viral DNA usually becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome. ...
DNA Technology and its Applications
... to change the information it contains. By changing this information, genetic engineering changes the type or amount of proteins an organism is capable of producing, thus enabling it to make new substances or perform new functions. ...
... to change the information it contains. By changing this information, genetic engineering changes the type or amount of proteins an organism is capable of producing, thus enabling it to make new substances or perform new functions. ...
bio-of-cells-lent-restriction-enzymes-information-for-exam
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
Figure 1 - genomics-lab
... (P1 being for instance allele specific), a third primer, P3 is designed to bind specifically to a site on the target sequence downstream of the P1 binding. P3 is labeled with two fluorophores, a reporter dye (R) is attached at the 5' end, and a quencher dye (D), which has a different emission wavele ...
... (P1 being for instance allele specific), a third primer, P3 is designed to bind specifically to a site on the target sequence downstream of the P1 binding. P3 is labeled with two fluorophores, a reporter dye (R) is attached at the 5' end, and a quencher dye (D), which has a different emission wavele ...
The Human Genome Project
... • identify crime and catastrophe victims • establish paternity and other family relations • identify endangered and protected species as an aid to wildlife officials (prosecution of poachers) • detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food • match organ donors with ...
... • identify crime and catastrophe victims • establish paternity and other family relations • identify endangered and protected species as an aid to wildlife officials (prosecution of poachers) • detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air, water, soil, and food • match organ donors with ...
Mutations in the code
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
Sections 5.3-5.5 - BridgesToLiteracy.com
... phospholipids, and steroids. -lipids will be seen on CH. 7,39, and 42 -on Ch. 42, such lipids like cholesterol can cause cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart attack, and stroke. proteins they have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions. such as enzymatic prot ...
... phospholipids, and steroids. -lipids will be seen on CH. 7,39, and 42 -on Ch. 42, such lipids like cholesterol can cause cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart attack, and stroke. proteins they have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions. such as enzymatic prot ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 08. The opine synthesized by Nop. Ti plasmid is acetosyringone. 09. pBR 322 is constructed from pUC. 10. Sodium alginate is used as fusogent. III. Complete the following 11. Hot air oven is used for …………. of glassware. 12. PEG refers to ………… 13. Agrobacterium tumefasciens causes a disease called ……… ...
... 08. The opine synthesized by Nop. Ti plasmid is acetosyringone. 09. pBR 322 is constructed from pUC. 10. Sodium alginate is used as fusogent. III. Complete the following 11. Hot air oven is used for …………. of glassware. 12. PEG refers to ………… 13. Agrobacterium tumefasciens causes a disease called ……… ...
Biochemistry
... molecule of DNA. The DNA molecule is the same in every cell of the same animal and it is inherited from a combination of the parents’ DNA. Each organism and each individual has a different DNA. The only exception is with identical twins. A single strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleoti ...
... molecule of DNA. The DNA molecule is the same in every cell of the same animal and it is inherited from a combination of the parents’ DNA. Each organism and each individual has a different DNA. The only exception is with identical twins. A single strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. A nucleoti ...
DNA Sequence Analysis
... 1. DNA sequence databases contain genomic sequence data,which includes information at the level of the untranslated sequence, introns and exons, mRNA, cDNA , and translations. 2. Untranslated regions(UTRs): occur in both DNA and RNA; they are portions of the sequence flanking the CDS that are not tr ...
... 1. DNA sequence databases contain genomic sequence data,which includes information at the level of the untranslated sequence, introns and exons, mRNA, cDNA , and translations. 2. Untranslated regions(UTRs): occur in both DNA and RNA; they are portions of the sequence flanking the CDS that are not tr ...
Polymerase chain reaction
... PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It is called “polymerase” because the only enzyme used in this reaction is DNA polymerase. It is called “chain” because the products of the first reaction become substrates of the following one, and so on. ...
... PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It is called “polymerase” because the only enzyme used in this reaction is DNA polymerase. It is called “chain” because the products of the first reaction become substrates of the following one, and so on. ...
... The inherited instructions that are passed from parent to offspring exist in the form of a code. This code is contained in _______ molecules. The DNA molecules must be accurately replicated before being passed on. Once the coded information is passed on, it is used by a cell to make ______________. ...
Types of Restriction Endonucleases | NEB
... Type II enzymes cut DNA at defined positions close to or within their recognition sequences. They produce discrete restriction fragments and distinct gel banding patterns, and they are the only class used in the laboratory for routine DNA analysis and gene cloning. Rather than forming a single famil ...
... Type II enzymes cut DNA at defined positions close to or within their recognition sequences. They produce discrete restriction fragments and distinct gel banding patterns, and they are the only class used in the laboratory for routine DNA analysis and gene cloning. Rather than forming a single famil ...
Lesson 3 | DNA and Genetics
... Directions: Write the correct term in the boxes to the right of each definition. Then unscramble the letters in the shaded boxes to spell a seventh term. ...
... Directions: Write the correct term in the boxes to the right of each definition. Then unscramble the letters in the shaded boxes to spell a seventh term. ...
DNA fingerprinting and the 16S
... DNA has been amplified. If it has not, then the primers did not bind to the DNA of the sample, and it is therefore highly unlikely that the DNA of an organism which a given set of primers represents, is present. On the other hand, appearance of DNA by PCR will allow precise identification of the sou ...
... DNA has been amplified. If it has not, then the primers did not bind to the DNA of the sample, and it is therefore highly unlikely that the DNA of an organism which a given set of primers represents, is present. On the other hand, appearance of DNA by PCR will allow precise identification of the sou ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.