dna and protein synthesis - YISS
... DNA Profiling can solve crimes • The pattern of the DNA profile is then compared with those of the victim and the suspect. • If the profile matches the suspect it provides strong evidence that the suspect was present at the crime scene (NB:it does not prove they committed the crime). • If the profi ...
... DNA Profiling can solve crimes • The pattern of the DNA profile is then compared with those of the victim and the suspect. • If the profile matches the suspect it provides strong evidence that the suspect was present at the crime scene (NB:it does not prove they committed the crime). • If the profi ...
Study Union Final Exam Review BSC 2010
... b. Any mistakes are corrected during the proofreading process. c. Individual amino acids can have more than one codon, but each codon only translates one amino acid d. The same 20 amino acids are used repeatedly. but in different combinations, to create different proteins, accounting for the necessa ...
... b. Any mistakes are corrected during the proofreading process. c. Individual amino acids can have more than one codon, but each codon only translates one amino acid d. The same 20 amino acids are used repeatedly. but in different combinations, to create different proteins, accounting for the necessa ...
DNA – Structure and Replication
... • DNA consists of two strands – made up of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules • The two strands are attached to each other by nitrogenous bases • DNA contains 4 bases: ...
... • DNA consists of two strands – made up of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules • The two strands are attached to each other by nitrogenous bases • DNA contains 4 bases: ...
Slide 1
... Cloning, in theory, allows you to turn any cell into an animal. So instead of injecting DNA into an egg, you can shoot DNA into cells in a petri dish, allow them to grow and look among millions of cells for the type of genetic alteration you want. Since it is so much easier to manipulate cells than ...
... Cloning, in theory, allows you to turn any cell into an animal. So instead of injecting DNA into an egg, you can shoot DNA into cells in a petri dish, allow them to grow and look among millions of cells for the type of genetic alteration you want. Since it is so much easier to manipulate cells than ...
Timeline
... nucleotides. The extra two phosphates (P~P) are removed by DNA polymerase and supply the energy for their condensation into the strand. DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Special Points As you know, bacteria usually replicate by binary fission. • The ring of DNA is attached at one point to the cell memb ...
... nucleotides. The extra two phosphates (P~P) are removed by DNA polymerase and supply the energy for their condensation into the strand. DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Special Points As you know, bacteria usually replicate by binary fission. • The ring of DNA is attached at one point to the cell memb ...
GENETICS EXAM 3 FALL 2004 Student Name
... 15. Which of the following is the most effective way to identify clones in a library that contain a specific gene? a) Screen the library with a radioactive probe. b) Isolate the DNA from randomly selected library clones and hybridize Southern blots containing their DNAs with a radioactive probe. c) ...
... 15. Which of the following is the most effective way to identify clones in a library that contain a specific gene? a) Screen the library with a radioactive probe. b) Isolate the DNA from randomly selected library clones and hybridize Southern blots containing their DNAs with a radioactive probe. c) ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis - Liceo da Vinci
... bonds to each other but not to cytosine or guanine. Similarly, cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds to each other in the double helix, but not to adenine or thymine. You may have noticed that every base pair contains one purine and one pyrimidine. This is related to the structure of each b ...
... bonds to each other but not to cytosine or guanine. Similarly, cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds to each other in the double helix, but not to adenine or thymine. You may have noticed that every base pair contains one purine and one pyrimidine. This is related to the structure of each b ...
MajadaDNAReplicationandProteinSynthesisActivity
... 6. Have students model translation by having them pretend to be ribosomes and putting the amino acids in the correct order according to the mRNA sequence of ribonucleotides. Use the attached RNA decoder, or provide one of your own. You can introduce additional factors like tRNA and models of the ri ...
... 6. Have students model translation by having them pretend to be ribosomes and putting the amino acids in the correct order according to the mRNA sequence of ribonucleotides. Use the attached RNA decoder, or provide one of your own. You can introduce additional factors like tRNA and models of the ri ...
To begin with, all the DNA polymerases either the five types in
... an enzyme called peptidyl transferase. This contradicts the rule that says all the enzymes are proteins. This enzyme connects the amino acids together by a peptide bond. ...
... an enzyme called peptidyl transferase. This contradicts the rule that says all the enzymes are proteins. This enzyme connects the amino acids together by a peptide bond. ...
Proving that DNA Replication is Semiconservative
... N-labeled DNA. Now that the parental DNA was labeled, Meselson and Stahl abruptly changed the medium to one containing 14N as the sole nitrogen source. From this point on, all the DNA synthesized by the bacteria would incorporate 14N, rather than 15N, so that the daughter DNA strands would contain o ...
... N-labeled DNA. Now that the parental DNA was labeled, Meselson and Stahl abruptly changed the medium to one containing 14N as the sole nitrogen source. From this point on, all the DNA synthesized by the bacteria would incorporate 14N, rather than 15N, so that the daughter DNA strands would contain o ...
Big Idea 1
... 1.D: The origin of living systems is explained by natural processes. The process of evolution explains the diversity and unity of life. A number of experimental investigations have provided evidence that the conditions early in the Earth’s history provided an environment capable of generating comple ...
... 1.D: The origin of living systems is explained by natural processes. The process of evolution explains the diversity and unity of life. A number of experimental investigations have provided evidence that the conditions early in the Earth’s history provided an environment capable of generating comple ...
Second messengers
... AAs lead to similar protein structure and function. These sequences are referred to as primary structure • Primary structure is the most elementary determinant of protein shape and also is critical for determining sites where proteins are cleaved by various enzymes (proteases). • Proteins adopt spec ...
... AAs lead to similar protein structure and function. These sequences are referred to as primary structure • Primary structure is the most elementary determinant of protein shape and also is critical for determining sites where proteins are cleaved by various enzymes (proteases). • Proteins adopt spec ...
DNA SEQUENCING DNA sequencing
... Single-molecule templates Some of the clonally amplified methods protocols are cumbersome to implement and require a large amount of genomic DNA material (3–20 μg). The preparation of single-molecule templates is more straightforward and requires less starting material (<1 μg). More importantly, th ...
... Single-molecule templates Some of the clonally amplified methods protocols are cumbersome to implement and require a large amount of genomic DNA material (3–20 μg). The preparation of single-molecule templates is more straightforward and requires less starting material (<1 μg). More importantly, th ...
nucleic acid,nursing2015 ppt
... primers present to start the addition of new nucleotides. Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA Primer. DNA polymerase can then add the new nucleotides ...
... primers present to start the addition of new nucleotides. Primase is the enzyme that synthesizes the RNA Primer. DNA polymerase can then add the new nucleotides ...
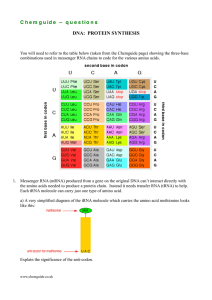
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Molecules of life
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
... larger structure ◦ Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
Ch. 16 – Control of Gene Expression Sample Questions
... A.Have their transcription occurring in the cytoplasm and translation in the nucleus. B.Have their transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm. C.Have only operons to assist in gene expression. D.Carry out protein synthesis only in the presence of the cAMP molecule. E.Use ...
... A.Have their transcription occurring in the cytoplasm and translation in the nucleus. B.Have their transcription occurring in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm. C.Have only operons to assist in gene expression. D.Carry out protein synthesis only in the presence of the cAMP molecule. E.Use ...
Cell Cycle PowerPoint
... • Cell division is the process by smaller which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells (IDENTICAL CELLS!). ...
... • Cell division is the process by smaller which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells (IDENTICAL CELLS!). ...
Molecular Genetics II (cont.) Mutation
... nonsense - a change that results in a stop codon replacing a normal amino acid codon silent - a change in a base pair that results in no change in an amino acid frameshift - due to an insertion or deletion of one or more base pairs in DNA Frameshift mutations result in a change in the reading frame ...
... nonsense - a change that results in a stop codon replacing a normal amino acid codon silent - a change in a base pair that results in no change in an amino acid frameshift - due to an insertion or deletion of one or more base pairs in DNA Frameshift mutations result in a change in the reading frame ...
Genetics - Mobile County Public Schools
... Explain the structure of eukaryotic chromosomes, including transposons, introns, and exons. Compare spermatogenesis and oogenesis using charts. Describe occurrences and effects of sex linkage, autosomal linkage, crossover, multiple alleles, and polygenes Describe the structure and function of DNA, i ...
... Explain the structure of eukaryotic chromosomes, including transposons, introns, and exons. Compare spermatogenesis and oogenesis using charts. Describe occurrences and effects of sex linkage, autosomal linkage, crossover, multiple alleles, and polygenes Describe the structure and function of DNA, i ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.