Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Recall that the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number of an element Properties to be considered Atomic Radius (and Ionic Radius) ...
... Recall that the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number of an element Properties to be considered Atomic Radius (and Ionic Radius) ...
topic 1 sol review homework
... 5. Which of the following is the most active nonmetal? a) F b) Na c) Si d) Kr 6. Which of the following has the greatest tendency to gain electrons? a) P b) C c) Cl d) B 7. Which of the following has the least tendency to gain electrons? a) F b) I c) Br d) Cl 8. List two things that the elements lis ...
... 5. Which of the following is the most active nonmetal? a) F b) Na c) Si d) Kr 6. Which of the following has the greatest tendency to gain electrons? a) P b) C c) Cl d) B 7. Which of the following has the least tendency to gain electrons? a) F b) I c) Br d) Cl 8. List two things that the elements lis ...
The Quantum Atom (section 18)
... Excited gases emit line spectra: light at certain characteristic frequencies, not continuous spectra. They also absorb light only at these frequencies. Why? ...
... Excited gases emit line spectra: light at certain characteristic frequencies, not continuous spectra. They also absorb light only at these frequencies. Why? ...
Chemistry Name______________________________________
... electron before any orbital has two (electrons stay unpaired as long as possible) ...
... electron before any orbital has two (electrons stay unpaired as long as possible) ...
Midterm Exam 2
... Oxygen and nitrogen are two of the major components of the atmosphere as well as critical components for all biological system. Both elements exist as diatomic gases (X2) within the atmosphere. O2 is a reactive species which is often involved in oxidation. This process leads to the formation or rust ...
... Oxygen and nitrogen are two of the major components of the atmosphere as well as critical components for all biological system. Both elements exist as diatomic gases (X2) within the atmosphere. O2 is a reactive species which is often involved in oxidation. This process leads to the formation or rust ...
Atomic Spectra Bohr Model Notes
... Everything you ever wanted to know about where the electrons hang out! ...
... Everything you ever wanted to know about where the electrons hang out! ...
Document
... If an electron falls from the third orbit to the first, how much energy does it lose? ...
... If an electron falls from the third orbit to the first, how much energy does it lose? ...
FYS0460 / FYSZ460 Ohjelmatyö Elektronisuhkulitografia
... Working in laboratory and in cleanroom conditions ...
... Working in laboratory and in cleanroom conditions ...
Atomic Radii Answers File
... The electrons are going into the same shell so the increasing nuclear change pulls them closer to the nucleus. ...
... The electrons are going into the same shell so the increasing nuclear change pulls them closer to the nucleus. ...
Review Exam #1 - Seattle Central College
... Energy-Potential and Kinetic and Thermal Transfer of Energy-work and heat Exothermic-chemical system loses heat to the surroundings Endothermic-chemical system gains energy from the surroundings Electrons have Both Wave Characteristics (Electrons can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Character ...
... Energy-Potential and Kinetic and Thermal Transfer of Energy-work and heat Exothermic-chemical system loses heat to the surroundings Endothermic-chemical system gains energy from the surroundings Electrons have Both Wave Characteristics (Electrons can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Character ...
Chpater 5.3 PPT
... less regularity than Main Group Elements. Still electrons in d orbitals are often responsible for characteristics of elements in the d-block Atomic radius tends to decrease across the block Ionization energies generally increase across both the d and f-blocks ...
... less regularity than Main Group Elements. Still electrons in d orbitals are often responsible for characteristics of elements in the d-block Atomic radius tends to decrease across the block Ionization energies generally increase across both the d and f-blocks ...
Ch. 7 Sections 7.9 and 7.11 Powerpoint
... • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the purposes of this class, we are going to assume that ALL atoms (or ions) that end in d4 or d9 are ...
... • If we can’t fill these sublevels, then the next best thing is to be HALF full (one electron in each orbital in the sublevel) • There are many exceptions, but the most common ones are d4 and d9 For the purposes of this class, we are going to assume that ALL atoms (or ions) that end in d4 or d9 are ...
Quiz 1 Key
... Describe what the emission spectra of a hydrogen atom looks like compared to that of white light and report what this indicated about the energy of the electrons around the hydrogen atom. White light has all of the colors and therefore wavelengths present. The emission spectrum of hydrogen had only ...
... Describe what the emission spectra of a hydrogen atom looks like compared to that of white light and report what this indicated about the energy of the electrons around the hydrogen atom. White light has all of the colors and therefore wavelengths present. The emission spectrum of hydrogen had only ...
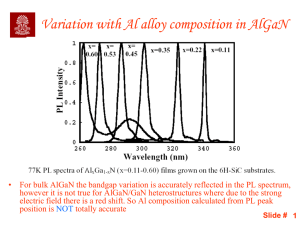
Slide 1
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 7 Review Packet
... atoms falling from 3p to 3s orbitals. The wavelength of one orange-yellow line in the spectrum of sodium is 589 nm. a. Write the electron configuration for the ground state of sodium. b. Write the electron configuration of the excited state of the sodium atom that is involved in this change in energ ...
... atoms falling from 3p to 3s orbitals. The wavelength of one orange-yellow line in the spectrum of sodium is 589 nm. a. Write the electron configuration for the ground state of sodium. b. Write the electron configuration of the excited state of the sodium atom that is involved in this change in energ ...
CH1710 HW#7 (2017)-Quanta, electron config
... 3. Cobalt-60 is a radioactive isotope used to treat cancers of the brain and other tissues. A gamma ray emitted by an atom of the isotope has an energy of 1.33 MeV (million electron volts). a. If 1 eV= 1.602 x 10-19 J, what is the frequency (in Hz) of this gamma ray ? ...
... 3. Cobalt-60 is a radioactive isotope used to treat cancers of the brain and other tissues. A gamma ray emitted by an atom of the isotope has an energy of 1.33 MeV (million electron volts). a. If 1 eV= 1.602 x 10-19 J, what is the frequency (in Hz) of this gamma ray ? ...
5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom
... • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars • Used in drug testing ...
... • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars • Used in drug testing ...
Unit 3: Electrons
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 13. The energy required to remove an electron from metal X is ΔE = 3.31 x 10-20 J. Calculate the maximum wavelength of light that can photo eject an electron from metal X. ...
... 13. The energy required to remove an electron from metal X is ΔE = 3.31 x 10-20 J. Calculate the maximum wavelength of light that can photo eject an electron from metal X. ...
Atomic Emissions LAB Questions
... EACH ELEMENT HAS A UNIQUE SET OF SPECTAL LINES (IS LIKE A FINGER PRINT). F. Why is it possible for a sample of the element hydrogen, in which each atom only has one electron, to have an emission spectrum with more than one color of light? A SAMPLE HAS MANY ATOMS; EACH ELECTRON IN EACH ATOM WILL MOVE ...
... EACH ELEMENT HAS A UNIQUE SET OF SPECTAL LINES (IS LIKE A FINGER PRINT). F. Why is it possible for a sample of the element hydrogen, in which each atom only has one electron, to have an emission spectrum with more than one color of light? A SAMPLE HAS MANY ATOMS; EACH ELECTRON IN EACH ATOM WILL MOVE ...
Atomic Structure Practice Answers
... 5. This is a possible configuration for a transition metal atom. B 6. This electron configuration is not possible. A 7. This is a possible configuration for a transition metal ion. C 8-11 refer to the following: A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 5. This is a possible configuration for a transition metal atom. B 6. This electron configuration is not possible. A 7. This is a possible configuration for a transition metal ion. C 8-11 refer to the following: A. B. C. D. E. ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.