e - Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... • Electron moves in special circular orbits – stationary states • Only certain orbits are allowed; quantization of angular momentum determines radius of orbit: r=n2ao; n=positive non-zero integer • Electron gives off no radiation when in stationary orbit • Radiation only emitted when electron makes ...
... • Electron moves in special circular orbits – stationary states • Only certain orbits are allowed; quantization of angular momentum determines radius of orbit: r=n2ao; n=positive non-zero integer • Electron gives off no radiation when in stationary orbit • Radiation only emitted when electron makes ...
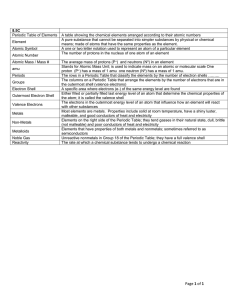
Unit 5 – Test Study Guide
... For example: Ionization energy decreases down a column because with the addition of another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner cor ...
... For example: Ionization energy decreases down a column because with the addition of another energy level and many more inner core electrons the atoms is much bigger. This means the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus and they are less attracted to the nucleus due to all the inner cor ...
Exam and Study Notes
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
Which scientist developed the quantum mechanical model of the
... electromagnetic waves have the highest frequencies? A) B) C) D) ...
... electromagnetic waves have the highest frequencies? A) B) C) D) ...
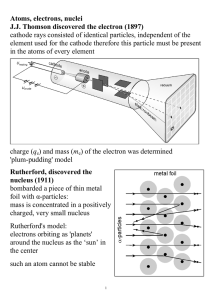
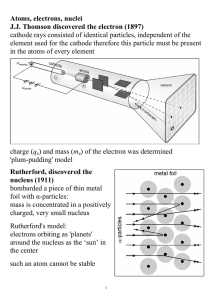
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the ...
... electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the ...
Louie de Broglie
... Numbers, and they are used to describe the properties, such as the energy level and shape (s, p, d or f), and Orientation of the atomic orbitals. ...
... Numbers, and they are used to describe the properties, such as the energy level and shape (s, p, d or f), and Orientation of the atomic orbitals. ...
Seeing Atoms and Electrons in Motion - The Munich
... However, our world is not static. Any reaction or process is essentially defined by movement paths on a (sub-)atomic level. ...
... However, our world is not static. Any reaction or process is essentially defined by movement paths on a (sub-)atomic level. ...
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... ψ(x,t) itself is a completely determined function but the position and momentum of the 'electron' – are uncertain if uncertainty of position (∆x) and uncertainty of momentum (∆p) ∆x ⋅ ∆p ≥ h the more determined the position of the electron, the less determined the momentum, and vice versa based on d ...
... ψ(x,t) itself is a completely determined function but the position and momentum of the 'electron' – are uncertain if uncertainty of position (∆x) and uncertainty of momentum (∆p) ∆x ⋅ ∆p ≥ h the more determined the position of the electron, the less determined the momentum, and vice versa based on d ...
Vocabulary Terms Defined
... quantum (93) the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom (plural: quanta) A quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. continuous spectrum (94) the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation excited state ...
... quantum (93) the minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom (plural: quanta) A quantum is the minimum amount of any physical entity involved in an interaction. continuous spectrum (94) the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation excited state ...
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but instead a probability of finding an electron in a region of space. ...
... The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but instead a probability of finding an electron in a region of space. ...
Section 13.2 - CPO Science
... nucleus in an area called an electron cloud. • The energy levels occur because electrons in the cloud are at different average distances from the nucleus. ...
... nucleus in an area called an electron cloud. • The energy levels occur because electrons in the cloud are at different average distances from the nucleus. ...
Honors Chemistry Name_________________________________
... 2. Define ionization energy? (p. 133-134) 3. List the order in which electrons are filled. (p. 97-98) (H.O. p. 297-298) 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s... 4. In an electron configuration, explain what is meant when it is written: 1s2.(p. 97-98) (H.O. p. 331) 5.Identify the s-block, p-block, d=block, and f-block on t ...
... 2. Define ionization energy? (p. 133-134) 3. List the order in which electrons are filled. (p. 97-98) (H.O. p. 297-298) 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s... 4. In an electron configuration, explain what is meant when it is written: 1s2.(p. 97-98) (H.O. p. 331) 5.Identify the s-block, p-block, d=block, and f-block on t ...
المحاضرة الثانية اساسيات الكم
... where m = mass of electron; v = velocity of electron; r = radius of the orbit; h = the Planck constant. ...
... where m = mass of electron; v = velocity of electron; r = radius of the orbit; h = the Planck constant. ...
(s) If 5.00 moles of zinc is placed into 1.50 L... 34. solution,what is the mass of the hydrogen gas produced?
... If 5.00 moles of zinc is placed into 1.50 L of a 3.00MHCI 34. solution,what is the mass of the hydrogen gas produced? (A) 0.750 g (D) 5.00 g (B) 2.25 g (E) 10.0 g (C) 4.50 g 32. How many grams of Zinc (atomic mass 65.0 g) are required to react completelywith 1.00 mol HCI? (A) 32.5 g (D) 195. g (B) 6 ...
... If 5.00 moles of zinc is placed into 1.50 L of a 3.00MHCI 34. solution,what is the mass of the hydrogen gas produced? (A) 0.750 g (D) 5.00 g (B) 2.25 g (E) 10.0 g (C) 4.50 g 32. How many grams of Zinc (atomic mass 65.0 g) are required to react completelywith 1.00 mol HCI? (A) 32.5 g (D) 195. g (B) 6 ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 15. A photon with some energy Ep strikes a metal surface. An electron is ejected with a velocity of 5.00 Mm/s. The threshold frequency of the metal is 6.30 x 1013 s-1. What is the wavelength of the photon, in nm? Significant figures count. 17 nm ...
... 15. A photon with some energy Ep strikes a metal surface. An electron is ejected with a velocity of 5.00 Mm/s. The threshold frequency of the metal is 6.30 x 1013 s-1. What is the wavelength of the photon, in nm? Significant figures count. 17 nm ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.