Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
... Periodic Law • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
... Periodic Law • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Models of the Atom The
... An _______________________ orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. The energy levels of _____________________________ in the quantum mechanical model are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n). These are assigned the values n=1, ...
... An _______________________ orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. The energy levels of _____________________________ in the quantum mechanical model are labeled by principal quantum numbers (n). These are assigned the values n=1, ...
Atomic structure and bonding I can name group 1, 7 and 0 of the
... I can state the mass, charge and position of a proton, neutron and electron within an atom. I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of atomic number and mass number. I can use the atomic number and mass number to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons withi ...
... I can state the mass, charge and position of a proton, neutron and electron within an atom. I can state the definition of an isotope. I can state the meaning of atomic number and mass number. I can use the atomic number and mass number to determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons withi ...
HW 8
... the longest wavelength corresponds to photons with the smallest energy. From the Bohr frequency condition the energy of the emitted photon must be equal to the difference in energy between the higher and lower levels. An energy level diagram for the H-atom shows that as the energy levels get higher, ...
... the longest wavelength corresponds to photons with the smallest energy. From the Bohr frequency condition the energy of the emitted photon must be equal to the difference in energy between the higher and lower levels. An energy level diagram for the H-atom shows that as the energy levels get higher, ...
November 18
... and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use first formula, c=lambda x frequency Frequency = 3x 108 m/s / 700 x 10-9 meters = 4.29 x 1014 Hz To find Energy, plug it into the second formula: E = hf = (6.6 x 10-34) x (4.29 x 1014 Hz) = 2.82 x 10-19 Joules What is Fire? Excited electrons wh ...
... and how much energy does it have? To find frequency, use first formula, c=lambda x frequency Frequency = 3x 108 m/s / 700 x 10-9 meters = 4.29 x 1014 Hz To find Energy, plug it into the second formula: E = hf = (6.6 x 10-34) x (4.29 x 1014 Hz) = 2.82 x 10-19 Joules What is Fire? Excited electrons wh ...
script
... The kinetic energy of Auger electrons is characteristic of the emitting atom and is well suited for elemental analysis. Yet, the exact energy value of the transition depends on several relaxation mechanisms. The intraatomic relaxation is a term associated with the redistribution of charge before the ...
... The kinetic energy of Auger electrons is characteristic of the emitting atom and is well suited for elemental analysis. Yet, the exact energy value of the transition depends on several relaxation mechanisms. The intraatomic relaxation is a term associated with the redistribution of charge before the ...
Chapter 4 Test Question Topics
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
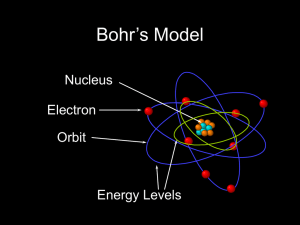
The Address of the Electrons
... Lower energy levels closer to nucleus Higher energy levels farther from nucleus Described by integers ...
... Lower energy levels closer to nucleus Higher energy levels farther from nucleus Described by integers ...
No Slide Title
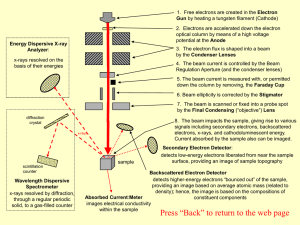
... x-rays resolved by diffraction, through a regular periodic solid, to a gas-filled counter ...
... x-rays resolved by diffraction, through a regular periodic solid, to a gas-filled counter ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum Wavelength Wavenumber Frequency
... Dative Covalent Bond Coordination number ...
... Dative Covalent Bond Coordination number ...
1. Millikan did his experiments with the balance of
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 6 Outline for Concepts to Know 6.1 Wave
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
... 6.3 Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Emission spectrum of hydrogen (see p. 225) is due to energy transitions of the single electron of hydrogen being excited to higher energy levels and then falling back down, emitting specific wavelengths of light. Line spectra for other elements are generally m ...
1-7-
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
... That electrons each contain a specific amount of energy as defined by their orbit. The further out the electron orbits, more energy the electron has. Orbits are fixed distances. ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.