Ch. 5.1 Models of the Atom
... The Quantum Mechanical Model Experimental results were inconsistent with the idea of electrons moving like large objects in orbit. Schrodinger proposed the quantum mechanical model. It does not involve the exact path an electron takes around the nucleus. ...
... The Quantum Mechanical Model Experimental results were inconsistent with the idea of electrons moving like large objects in orbit. Schrodinger proposed the quantum mechanical model. It does not involve the exact path an electron takes around the nucleus. ...
AP Chemistry
... What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with visible light of wavelength 550 nm? ...
... What is the energy in joules of a mole of photons associated with visible light of wavelength 550 nm? ...
Study Guide Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe
... have 7 valence electrons are active nonmetals usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain re ...
... have 7 valence electrons are active nonmetals usually combined w/ other elements * Know that there is a difference between fission and fusion: fusion- put atoms together with enormous amounts of energy released fission- splitting atoms- energy released- not as much as fusion- may occur in a chain re ...
HW8 not graded v3 - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... The graph shows the distribution of photon energies for a light source that emits 4 million photons per second. In the energy range 0 – 0.1 eV, there are 105 photons per second. In the energy range 0.1 – 0.2 eV, there are 105 photons per second, and ...
... The graph shows the distribution of photon energies for a light source that emits 4 million photons per second. In the energy range 0 – 0.1 eV, there are 105 photons per second. In the energy range 0.1 – 0.2 eV, there are 105 photons per second, and ...
Unit 2 Review KEY
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
... Electromagnetic Radiation – form of energy that exhibits wavelength behavior as it travels through space. Wavelength (λ) – the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves. Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emissio ...
... luppe, state has a lifetime of 1.4ps, the lower state 3.0 ps. A) What is the fractional uncertainty AEIE in tht energy of the gainma ray? B) What is the percentage spread in wavelength of the gamma ray (Ahlh)? 11. (10) The ground state wave function of Hydrogen atom is ryloo=~~ooe~r'aO . What is the ...
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
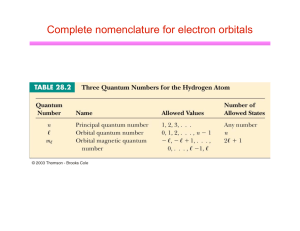
... hydrogen (or any other type of atom) can be specified by the quantum numbers: n,l,ml and ms l Wolfgang Pauli (one of founders of quantum mechanics) discovered that no two electrons in the same atom can ever have exactly the same values for the set of quantum numbers u u ...
... hydrogen (or any other type of atom) can be specified by the quantum numbers: n,l,ml and ms l Wolfgang Pauli (one of founders of quantum mechanics) discovered that no two electrons in the same atom can ever have exactly the same values for the set of quantum numbers u u ...
Problem Set 05
... rotational energies of the molecule. [Result: n 2 2 /md 2 ] b) The wavelength of the photon needed to excite the molecule from the n to the n+1 rotational state. [Result: λ=2πcmd 2/(2n+1)] c) The wavelength of the photon need to excite € a nitrogen molecule (N2) from its ground state (n=0) to the ...
... rotational energies of the molecule. [Result: n 2 2 /md 2 ] b) The wavelength of the photon needed to excite the molecule from the n to the n+1 rotational state. [Result: λ=2πcmd 2/(2n+1)] c) The wavelength of the photon need to excite € a nitrogen molecule (N2) from its ground state (n=0) to the ...
Ch1-8 Brown and LeMay Review
... M Ba(OH)2 ? Assume the volumes are additive. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Hund’s Rule Wave nature of light Pauli Exclusion Principle Shielding effect A) Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic. B) Explains electron diffraction. C) Indicates that atom ...
... M Ba(OH)2 ? Assume the volumes are additive. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Hund’s Rule Wave nature of light Pauli Exclusion Principle Shielding effect A) Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic. B) Explains electron diffraction. C) Indicates that atom ...
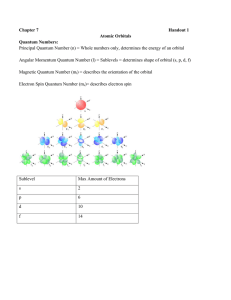
Chapter 7 Handout 1 Atomic Orbitals Quantum Numbers: Principal
... Rules for filling orbitals: 1. Aufbau Principle: a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must ha ...
... Rules for filling orbitals: 1. Aufbau Principle: a. Electrons fill up orbitals of lowest energy first b. Orbitals in the same sublevel are equal in energy c. Sometimes energy levels overlap 2. Pauli Exculsion Principle a. There is a max of 2 electrons in any one orbital b. These 2 electrons must ha ...
energy levels
... – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
... – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level ...
1st Semester Final Exam Review Guide
... How many grams are there in 2.00 mol of calcium? Calculate the atomic mass of carbon based on the following mass numbers of the isotopes of carbon found in nature. mass # 12 at 81.00% mass # 13 at 10.00% mass # 14 at 9.000% 9. Define “isotope”. Give an example of 2 isotopes of a particular element. ...
... How many grams are there in 2.00 mol of calcium? Calculate the atomic mass of carbon based on the following mass numbers of the isotopes of carbon found in nature. mass # 12 at 81.00% mass # 13 at 10.00% mass # 14 at 9.000% 9. Define “isotope”. Give an example of 2 isotopes of a particular element. ...
Auger electron spectroscopy
.jpg?width=300)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES; pronounced [oʒe] in French) is a common analytical technique used specifically in the study of surfaces and, more generally, in the area of materials science. Underlying the spectroscopic technique is the Auger effect, as it has come to be called, which is based on the analysis of energetic electrons emitted from an excited atom after a series of internal relaxation events. The Auger effect was discovered independently by both Lise Meitner and Pierre Auger in the 1920s. Though the discovery was made by Meitner and initially reported in the journal Zeitschrift für Physik in 1922, Auger is credited with the discovery in most of the scientific community. Until the early 1950s Auger transitions were considered nuisance effects by spectroscopists, not containing much relevant material information, but studied so as to explain anomalies in x-ray spectroscopy data. Since 1953 however, AES has become a practical and straightforward characterization technique for probing chemical and compositional surface environments and has found applications in metallurgy, gas-phase chemistry, and throughout the microelectronics industry.