Organic Chemistry
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
... • Each "Rung" of the DNA "staircase" is formed by the linking of 2 Nucleotides through Hydrogen Bonds. • These Hydrogen bonds form only between specific Nucleotides. This is known as Base Pairing. The rules are as follows: – Adenine (A) will ONLY bond to Thymine (T) – Cytosine (C) will ONLY bond to ...
Week 4 - Composition of Cells
... Add a couple more water molecules to your diagram and illustrate how they stick together. ...
... Add a couple more water molecules to your diagram and illustrate how they stick together. ...
02_Classification and functions of simple and complex proteins
... two major types: fibrous proteins and globular proteins. • А fibrous protein is а protein that has а long, thin, fibrous shape. Such proteins are made up of long rod-shaped or stringlike molecules that can intertwine with one another and form strong fibers. They are water-insoluble and generally hav ...
... two major types: fibrous proteins and globular proteins. • А fibrous protein is а protein that has а long, thin, fibrous shape. Such proteins are made up of long rod-shaped or stringlike molecules that can intertwine with one another and form strong fibers. They are water-insoluble and generally hav ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Amount of protein initially Example: ...
... Amount of protein initially Example: ...
word
... What are the scientific names of some of the model organisms? How are fluorescent-labeled antibodies viewed binding to a specimen? Transmission electron microscopy is used for what type of specimens? What is an advantage of using GFP? What do the initials GFP stand for? Explain different cell struct ...
... What are the scientific names of some of the model organisms? How are fluorescent-labeled antibodies viewed binding to a specimen? Transmission electron microscopy is used for what type of specimens? What is an advantage of using GFP? What do the initials GFP stand for? Explain different cell struct ...
cell drinking
... primary structure of one protein • DNA : 4 type of nucleotides (ATCG), which differ by the bases (no the sugars of pgospate groups) • Gene : has a sequences of nucleotides, which ultimately encodes a sequences of amino acids. ...
... primary structure of one protein • DNA : 4 type of nucleotides (ATCG), which differ by the bases (no the sugars of pgospate groups) • Gene : has a sequences of nucleotides, which ultimately encodes a sequences of amino acids. ...
Chapter 3
... • Complex carbohydrates are long polymer chains. • Because they contain many C-H bonds, these carbohydrates are good for storing energy. • These bond types are the ones most often broken by organisms to obtain energy. • The long chains are called polysaccharides. ...
... • Complex carbohydrates are long polymer chains. • Because they contain many C-H bonds, these carbohydrates are good for storing energy. • These bond types are the ones most often broken by organisms to obtain energy. • The long chains are called polysaccharides. ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 11: Regulation by proteolytic cleavage
... is structurally equivalent to Lys6 and Ile7 in trypsinogen. The newly exposed N-terminal Ile is similarly positioned to make an ion pair with Asp 194, and the mechanism of activation is the same as for trypsin. The immediate product is called π -chymotrypsin and is fully active as a protease. Self-e ...
... is structurally equivalent to Lys6 and Ile7 in trypsinogen. The newly exposed N-terminal Ile is similarly positioned to make an ion pair with Asp 194, and the mechanism of activation is the same as for trypsin. The immediate product is called π -chymotrypsin and is fully active as a protease. Self-e ...
Proteins - foothill.edu
... •The 15 neutral amino acids are further divided into those with nonpolar side chains and those with polar functional groups such as amide or hydroxyl groups in their side chains. •It is the sequence of amino acids in a protein and the chemical nature of their side chains that enable proteins to ...
... •The 15 neutral amino acids are further divided into those with nonpolar side chains and those with polar functional groups such as amide or hydroxyl groups in their side chains. •It is the sequence of amino acids in a protein and the chemical nature of their side chains that enable proteins to ...
document
... Zwitterion effect causes crystalline form of amino acids to have high decomposition temperatures ...
... Zwitterion effect causes crystalline form of amino acids to have high decomposition temperatures ...
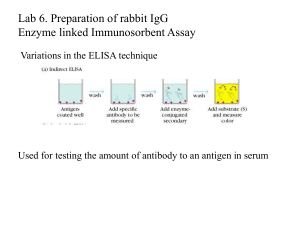
Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies
... bound to the solid phase. 2. The avidity of the first antibody for the antigen. 3. The avidity of the second antibody for the antigen. 4. The specific activity of the enzyme attached to the second ...
... bound to the solid phase. 2. The avidity of the first antibody for the antigen. 3. The avidity of the second antibody for the antigen. 4. The specific activity of the enzyme attached to the second ...
This exam has 8 pages, including this one.
... 6-residue long sequence was dropped on the floor, thus it was only possible to obtain the sequence of the 2 residue peptide: Leu-Leu. Determine as much of the sequence of this peptide as possible (Hint, you may not have enough information to completely determine the sequence). ...
... 6-residue long sequence was dropped on the floor, thus it was only possible to obtain the sequence of the 2 residue peptide: Leu-Leu. Determine as much of the sequence of this peptide as possible (Hint, you may not have enough information to completely determine the sequence). ...
Fusion, Affinity and Epitope Tags Lecture Notes Handout
... ü Sometimes found with 2 or 3 in a row for higher affinity binding ü Hydrophilic aa sequence ü First tag to be published ü May not work on both terminus ü There are different versions of the sequence ü Some antibodies (M1, M2, M5) only recognize one version! Affinity Tags Small protein, large ...
... ü Sometimes found with 2 or 3 in a row for higher affinity binding ü Hydrophilic aa sequence ü First tag to be published ü May not work on both terminus ü There are different versions of the sequence ü Some antibodies (M1, M2, M5) only recognize one version! Affinity Tags Small protein, large ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... • Total height at a position is the ‘Information Content’ measured in bits. • Height of letter is the proportional to the frequency of that letter. • A Logo plot is a visualization of a mutiple alignment. ...
... • Total height at a position is the ‘Information Content’ measured in bits. • Height of letter is the proportional to the frequency of that letter. • A Logo plot is a visualization of a mutiple alignment. ...
Ligand Binding - Stroud -Lecture 1
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
... • Thermodynamics of Protein Assembly • Structural Change on complexation • Empirical fitting of Atomic Interactions with Free Energy of Association • Estimate of free energy of H bonds and charge interactions in protein complexes and role of hydrophobic effect _______________________________________ ...
Unit 1 – Introduction to Biology STUDY GUIDE
... 12. Based on the Macromolecule Diet Lab, which two macromolecules are most important for energy in our cells? Which of these contains the greatest amount of energy? Explain how you know this. Carbohydrates and Lipids are the most important macromolecules for energy in our cells. Lipids contain more ...
... 12. Based on the Macromolecule Diet Lab, which two macromolecules are most important for energy in our cells? Which of these contains the greatest amount of energy? Explain how you know this. Carbohydrates and Lipids are the most important macromolecules for energy in our cells. Lipids contain more ...
PPT (without movies)
... (http://depts.washington.edu/bakerpg/drupal/) Foldit is a revolutionary new computer game enabling you to contribute to important scientific research. Join this free online game and help us predict the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting da ...
... (http://depts.washington.edu/bakerpg/drupal/) Foldit is a revolutionary new computer game enabling you to contribute to important scientific research. Join this free online game and help us predict the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting da ...
Slide 1
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
print last name first name
... 14. a. It is difficult to prevent cancer because cancer is caused by _________________________, which may result randomly from radiation, chemical, and viruses. b. Every time a normal cell divides, the __________________________ shorten, but this does not happen in cancer cells, which is why they a ...
... 14. a. It is difficult to prevent cancer because cancer is caused by _________________________, which may result randomly from radiation, chemical, and viruses. b. Every time a normal cell divides, the __________________________ shorten, but this does not happen in cancer cells, which is why they a ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.