Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... • Lipids: A group of polymers that have one characteristic in common, they do not mix with water. They are hydrophobic. Some important groups are fats, phospholipids, and steroids. ...
... • Lipids: A group of polymers that have one characteristic in common, they do not mix with water. They are hydrophobic. Some important groups are fats, phospholipids, and steroids. ...
Protein Degradation, Volume 1 ch01_p 1..9
... ered was that proteins may be modified by some energy-dependent reaction prior to their degradation, and that such modification renders them susceptible to the action of some proteolytic enzyme [11]. To examine the existence of such (or any other) mechanism, a cell-free system was required, which fait ...
... ered was that proteins may be modified by some energy-dependent reaction prior to their degradation, and that such modification renders them susceptible to the action of some proteolytic enzyme [11]. To examine the existence of such (or any other) mechanism, a cell-free system was required, which fait ...
AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN The Gene—Protein Connection ...
... AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN The Gene—Protein Connection ...
slides on Protein Structure
... –7 Å repeat length & two rotatable bonds at Ca (f & y) –highly polar bond due to resonance –high energy bond due to resonance ...
... –7 Å repeat length & two rotatable bonds at Ca (f & y) –highly polar bond due to resonance –high energy bond due to resonance ...
Lecture 5: Major Nutrient Groups
... simple proteins: essentially pure proteins, when hydrolyzed, produce individual amino acids (e.g., egg albumin) conjugated: protein unit linked to another nonprotein unit (e.g., casein, the protein component of milk with phosphorus esterified to it via the ...
... simple proteins: essentially pure proteins, when hydrolyzed, produce individual amino acids (e.g., egg albumin) conjugated: protein unit linked to another nonprotein unit (e.g., casein, the protein component of milk with phosphorus esterified to it via the ...
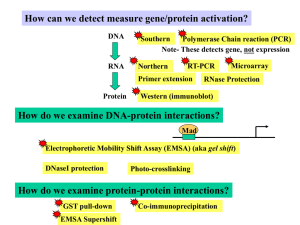
Bio4751signaltransductionTechniques
... 1. Southern- Detect DNA only 2. Northern- Detect RNA 3. Microarray- Detect RNA of 100s of expressed genes 4. RT-PCR ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. Western (Immunoblot)- Detect protein 6. Immunostaining- Detect proteins in situ 7. EMSA- protein-DNA interactions 8 ...
... 1. Southern- Detect DNA only 2. Northern- Detect RNA 3. Microarray- Detect RNA of 100s of expressed genes 4. RT-PCR ( Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction- to detect RNA) 5. Western (Immunoblot)- Detect protein 6. Immunostaining- Detect proteins in situ 7. EMSA- protein-DNA interactions 8 ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose Consist of many monomers bonded together Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) Test for complex sugars: use iodine: turns from brown to black in the presence of starch ...
... Examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose Consist of many monomers bonded together Used for energy storage and to build cell structures Broken down through cellular respiration to create energy (ATP) Test for complex sugars: use iodine: turns from brown to black in the presence of starch ...
... 8. (10 pts) Please do one of the following three questions. Please indicate your choice when answering the question. Choice A: A glutamic acid residue must be deprotonated for a protein to have biological function. The pKa of this glutamic acid residue is 5.0. Draw a graph that shows the activity of ...
AP Macromolecule Notes 09
... o Signal: detect stimuli, communicate between cells, hormones; Insulin o Transport: carry nutrients in the blood, sugar to cells; Hemoglobin o Storage: store amino acid; Ovalbumin o Enzymes:* catalyze reactions; Amylase o Milk: amino acids in babies, protein for seed; Casein Nucleic Acids* ...
... o Signal: detect stimuli, communicate between cells, hormones; Insulin o Transport: carry nutrients in the blood, sugar to cells; Hemoglobin o Storage: store amino acid; Ovalbumin o Enzymes:* catalyze reactions; Amylase o Milk: amino acids in babies, protein for seed; Casein Nucleic Acids* ...
Chapter 13: RNA and Protein Synthesis
... – Synthesis of RNA molecule from a DNA pattern – Creation of RNA – Complementary strand of DNA sequence • Same as the DNA sequence hence the same bases except for uracil ...
... – Synthesis of RNA molecule from a DNA pattern – Creation of RNA – Complementary strand of DNA sequence • Same as the DNA sequence hence the same bases except for uracil ...
Cheng BY 123 Raut – Mock Exam Unit I 09/21/14 1. Which of the
... C) plants that receive more water everyday D) plants that have more soil in their pots E) a new laboratory 7. T/F Trace elements are not essential and are relatively small in size. 8. Phosphorus-31 is an isotope of phosphorus. Given that phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, what is proper number o ...
... C) plants that receive more water everyday D) plants that have more soil in their pots E) a new laboratory 7. T/F Trace elements are not essential and are relatively small in size. 8. Phosphorus-31 is an isotope of phosphorus. Given that phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, what is proper number o ...
BIO C211 - BITS Pilani
... 2. Lipids 3. Protein, structure & function, protein folding & conformation, Synthesis & regulations 4. Nucleic acids, Genomic structure & function, systhesis B. Enzymes 4 Ch. 1. Classification 2. Enzyme kinetics 3. Enzyme inhibitors and regulators 4. Allosteric enzymes 5. Multienzyme systems 6. Isoe ...
... 2. Lipids 3. Protein, structure & function, protein folding & conformation, Synthesis & regulations 4. Nucleic acids, Genomic structure & function, systhesis B. Enzymes 4 Ch. 1. Classification 2. Enzyme kinetics 3. Enzyme inhibitors and regulators 4. Allosteric enzymes 5. Multienzyme systems 6. Isoe ...
Research Applications Of Proteolytic Enzymes In Molecular Biology
... capable of hydrolyzing peptide bonds in proteins. They can be found in all living organisms, from viruses to animals and humans. Proteolytic enzymes have great medical and pharmaceutical importance due to their key role in biological processes and in the life-cycle of many pathogens. Proteases are e ...
... capable of hydrolyzing peptide bonds in proteins. They can be found in all living organisms, from viruses to animals and humans. Proteolytic enzymes have great medical and pharmaceutical importance due to their key role in biological processes and in the life-cycle of many pathogens. Proteases are e ...
Bio A
... Carbon has lots of properties that make it essential to building lots of different molecules Due to the number of electrons in it’s outer shell, carbon is most likely to make a covalent bond Covalent bonds are formed when an element shares electrons with another molecule. Carbon would need to ...
... Carbon has lots of properties that make it essential to building lots of different molecules Due to the number of electrons in it’s outer shell, carbon is most likely to make a covalent bond Covalent bonds are formed when an element shares electrons with another molecule. Carbon would need to ...
Discovery Research and Cell Culture
... of things, e.g. within blood (for carrying molecules and for clotting), for digestion (enzymes are proteins), for movement (actin and myosin in muscle), etc. One other major role of proteins is that of "structural proteins", i.e. those proteins that contribute to and sustain the integrity of the hum ...
... of things, e.g. within blood (for carrying molecules and for clotting), for digestion (enzymes are proteins), for movement (actin and myosin in muscle), etc. One other major role of proteins is that of "structural proteins", i.e. those proteins that contribute to and sustain the integrity of the hum ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zinc is used in over 80 enzyme reactions that are critical for life in all people! Another example is that of sodium. Unlike table salt or sodium chloride, bio-organic sodium, i.e., sodium carried n ...
... that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zinc is used in over 80 enzyme reactions that are critical for life in all people! Another example is that of sodium. Unlike table salt or sodium chloride, bio-organic sodium, i.e., sodium carried n ...
Daily Essential Electrolytes, Protein, and Probiotics
... that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zinc is used in over 80 enzyme reactions that are critical for life in all people! Another example is that of sodium. Unlike table salt or sodium chloride, bio-organic sodium, i.e., sodium carried n ...
... that build or tear down body tissue. Manganese is used by enzymes needed to utilize several vitamins. Zinc is used in over 80 enzyme reactions that are critical for life in all people! Another example is that of sodium. Unlike table salt or sodium chloride, bio-organic sodium, i.e., sodium carried n ...
Biological Molecules - Parkland Secondary School
... - hemoglobin: transports O2 in the blood. cell recognition roles - complement system proteins: aid the immune response - antibodies: used by immune system to help identify foreign material or specific antigens in the blood - MHC proteins: mark cells as belonging to ‘self’ - glycoproteins: are cell m ...
... - hemoglobin: transports O2 in the blood. cell recognition roles - complement system proteins: aid the immune response - antibodies: used by immune system to help identify foreign material or specific antigens in the blood - MHC proteins: mark cells as belonging to ‘self’ - glycoproteins: are cell m ...
General Biology Notes CH 12: TRANSLATION A.K.A. PROTEIN
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
... into a sequence of amino acids that makes up proteins. ...
practice making a protein from dna
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
... Look up each 3 letter codon on the table of amino acids and write down the three letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Do this next to the word "Protein" (Amino acids can be written as words or abbreviations like this: Arginine or Arg or R) It should look like MET - ARG - ... - ... - GLN STOP (bu ...
Organic molecules
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
... **can bond to many different elements **can bond to other C atoms **form covalent bonds **can form single, double, triple bonds **can form a chain or ring • Carbon compounds: 4 found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins ...
enzymes
... The ENZYMES are the driving force behind all biochemical reactions happening in cells. Enzymes lower the energy barrier between reactants and products, thus increasing the rate of the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. A catalyst is a species that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction ...
... The ENZYMES are the driving force behind all biochemical reactions happening in cells. Enzymes lower the energy barrier between reactants and products, thus increasing the rate of the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts. A catalyst is a species that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.