Chemistry of Cells - Marengo Community High School
... – Different steroids are created by varying functional groups attached to the rings. ...
... – Different steroids are created by varying functional groups attached to the rings. ...
Macromolecules PPT
... Structure- monomers and polymers of each Function- what are they used for? Food sources- what foods will you find these in? Indicator Tests- what tests do we use to find out if a food ...
... Structure- monomers and polymers of each Function- what are they used for? Food sources- what foods will you find these in? Indicator Tests- what tests do we use to find out if a food ...
Chongqing Biospes Co., Ltd - Antibodies, Proteins, ELISA kits and
... precipitate, leave very small volume of supernatant to avoid touching.) 10. For precipitate: discard the supernatant, add 50 μl of NER (containing PMSF) to the precipitate. (Discard the supernatant thoroughly to avoid contamination of cytoplasmic proteins.) 11. Vortex at maximum speed for 15-30 seco ...
... precipitate, leave very small volume of supernatant to avoid touching.) 10. For precipitate: discard the supernatant, add 50 μl of NER (containing PMSF) to the precipitate. (Discard the supernatant thoroughly to avoid contamination of cytoplasmic proteins.) 11. Vortex at maximum speed for 15-30 seco ...
In Vitro Protein Synthesis of Perdeuterated Proteins for NMR Studies
... It is well documented that high levels of deuteration are indispensable for solution NMR studies of polypeptides in structures of sizes above 40 kDa (Fiaux et al., 2002; LeMaster 1989; Pachter et al. 1992). In addition to studies on protein structure and dynamics, obtaining a perdeuterated backgroun ...
... It is well documented that high levels of deuteration are indispensable for solution NMR studies of polypeptides in structures of sizes above 40 kDa (Fiaux et al., 2002; LeMaster 1989; Pachter et al. 1992). In addition to studies on protein structure and dynamics, obtaining a perdeuterated backgroun ...
ppt.
... intercellular communication. In this animation a hormone binds to the receptor. This causes the receptor protein to release a chemical signal to perform a specific action. ...
... intercellular communication. In this animation a hormone binds to the receptor. This causes the receptor protein to release a chemical signal to perform a specific action. ...
Hydrolyzed Soy Protein
... Soy Advantage . When tested against other hydrolyzates, Vege Tech Hydrolyzed Soy Protein demonstrates superb Hair Repair by means of Cortex Penetration and FilmForming. With a Dalton range of approx. 1,000 to 10,000, it imparts increased Moisture Retention, Hair Tensile Strength & Thickness, Flexibi ...
... Soy Advantage . When tested against other hydrolyzates, Vege Tech Hydrolyzed Soy Protein demonstrates superb Hair Repair by means of Cortex Penetration and FilmForming. With a Dalton range of approx. 1,000 to 10,000, it imparts increased Moisture Retention, Hair Tensile Strength & Thickness, Flexibi ...
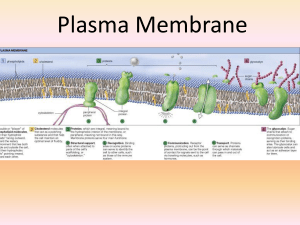
Plasma Membrane
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
Presentation Slides II - Vandiver, June 29, 2016
... beta pleated sheet. These structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. 3) Tertiary structure –the folding of the chains governed by hydrophobic or hydrophilic interactions. 4) Quaternary structure-- protein chains associating with other chains. The Star BioChem computer activity requires a working k ...
... beta pleated sheet. These structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. 3) Tertiary structure –the folding of the chains governed by hydrophobic or hydrophilic interactions. 4) Quaternary structure-- protein chains associating with other chains. The Star BioChem computer activity requires a working k ...
In silico Study of Target Proteins for Mycobacterium
... pathogenic bacteria genome provided lots of raw material for in silico analysis and drug designing1. Identification of essential gene from the genome of bacteria play significant role and are thus important for the survival of an organism and are non-homologous to human genes. Thus, Identification o ...
... pathogenic bacteria genome provided lots of raw material for in silico analysis and drug designing1. Identification of essential gene from the genome of bacteria play significant role and are thus important for the survival of an organism and are non-homologous to human genes. Thus, Identification o ...
Option C - Human biochemistry C.1 Diet-
... C.5.1 Role in Metabolism: • -Metabolism- all of an organism's biochemical reactions • -In order for reactions to take place in the body, catalysts are needed-these are called enzymes (see section on enzymes for more info) • -Enzymes do not work alone, and sometimes require the help of coenzymes in ...
... C.5.1 Role in Metabolism: • -Metabolism- all of an organism's biochemical reactions • -In order for reactions to take place in the body, catalysts are needed-these are called enzymes (see section on enzymes for more info) • -Enzymes do not work alone, and sometimes require the help of coenzymes in ...
Macromolecules, Chemical Reactions & Enzymes
... 3) label the water molecule with O, H, +, and – 4) Match the pH scale with the following word: Neutral, Strong Acid, Strong Base, Weak Acid, Weak Base ...
... 3) label the water molecule with O, H, +, and – 4) Match the pH scale with the following word: Neutral, Strong Acid, Strong Base, Weak Acid, Weak Base ...
Structure-function study of the C-terminal tail of Thioredoxin Reductase
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
Document
... the protein 100–200 amino acids long encoded by a specific DNA sequence (exon) Quaternary - forms when two or more polypeptide chains associate to form a functional protein ...
... the protein 100–200 amino acids long encoded by a specific DNA sequence (exon) Quaternary - forms when two or more polypeptide chains associate to form a functional protein ...
Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
... and a cofactor (usually an ion) or coenzyme • Enzymes are chemically specific • Frequently named for the type of reaction they ...
... and a cofactor (usually an ion) or coenzyme • Enzymes are chemically specific • Frequently named for the type of reaction they ...
Biochemistry (Unit 1) Exam Review
... temperature, ph and inhibitors all affect enzyme activity because each enzyme has optimum conditions. Some enzymes are limited by inorganic cofactors that bind to the substrate or active site. enzymes regulated by competitive inhibitors that adhere to the substrate or enzyme and prevent it from bind ...
... temperature, ph and inhibitors all affect enzyme activity because each enzyme has optimum conditions. Some enzymes are limited by inorganic cofactors that bind to the substrate or active site. enzymes regulated by competitive inhibitors that adhere to the substrate or enzyme and prevent it from bind ...
ppt
... DNA - double-stranded molecule, 2 chains. • Bases on inside joined by H bonds between complementary base pairs: G-C and A-T (A-U) • Complementary base pairing → 1 strand of DNA (or RNA) acts as template for synthesis of complementary strand. • Nucleic acids are capable of self-replication ...
... DNA - double-stranded molecule, 2 chains. • Bases on inside joined by H bonds between complementary base pairs: G-C and A-T (A-U) • Complementary base pairing → 1 strand of DNA (or RNA) acts as template for synthesis of complementary strand. • Nucleic acids are capable of self-replication ...
LIVING WITHOUT OXYGEN
... cryoprotectants (polyols, sugars) • Defend against intracellular desiccation ...
... cryoprotectants (polyols, sugars) • Defend against intracellular desiccation ...
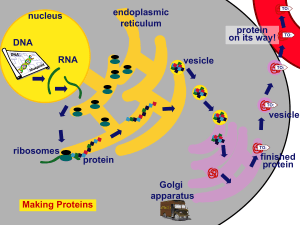
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
... making proteins that may become enzymes or hormone for use within the body. ...
Transcription and Translation
... Protein Folding Proteins are the functional part of a cell • Cellular “machinery” or tools • Cannot function as a flat chain of amino acids • Instead need to fold in very specific confirmations in order to function properly ...
... Protein Folding Proteins are the functional part of a cell • Cellular “machinery” or tools • Cannot function as a flat chain of amino acids • Instead need to fold in very specific confirmations in order to function properly ...
English Version
... (5) Shuttle Systems Indirectly Convey Cytosolic NADH into Mitochondria for Oxidation 3. MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASES ...
... (5) Shuttle Systems Indirectly Convey Cytosolic NADH into Mitochondria for Oxidation 3. MITOCHONDRIAL DISEASES ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.